DNA damage and its links to neurodegeneration
- PMID: 25033177
- PMCID: PMC5564444
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2014.06.034
DNA damage and its links to neurodegeneration
Abstract
The integrity of our genetic material is under constant attack from numerous endogenous and exogenous agents. The consequences of a defective DNA damage response are well studied in proliferating cells, especially with regards to the development of cancer, yet its precise roles in the nervous system are relatively poorly understood. Here we attempt to provide a comprehensive overview of the consequences of genomic instability in the nervous system. We highlight the neuropathology of congenital syndromes that result from mutations in DNA repair factors and underscore the importance of the DNA damage response in neural development. In addition, we describe the findings of recent studies, which reveal that a robust DNA damage response is also intimately connected to aging and the manifestation of age-related neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer's disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
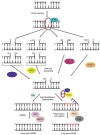
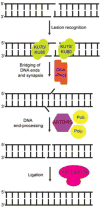
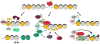
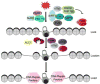
Similar articles
-
Base excision repair in physiology and pathology of the central nervous system.Int J Mol Sci. 2012 Nov 30;13(12):16172-222. doi: 10.3390/ijms131216172. Int J Mol Sci. 2012. PMID: 23203191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Somatic mutations in neurons during aging and neurodegeneration.Acta Neuropathol. 2018 Jun;135(6):811-826. doi: 10.1007/s00401-018-1850-y. Epub 2018 Apr 28. Acta Neuropathol. 2018. PMID: 29705908 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Base excision repair in the mammalian brain: implication for age related neurodegeneration.Mech Ageing Dev. 2013 Oct;134(10):440-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2013.04.005. Epub 2013 May 2. Mech Ageing Dev. 2013. PMID: 23643943 Free PMC article.
-
The role of DNA repair in brain related disease pathology.DNA Repair (Amst). 2013 Aug;12(8):578-87. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2013.04.010. Epub 2013 May 27. DNA Repair (Amst). 2013. PMID: 23721970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA damage and repair: relevance to mechanisms of neurodegeneration.J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008 May;67(5):377-87. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0b013e31816ff780. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 2008. PMID: 18431258 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
C9orf72 functions in the nucleus to regulate DNA damage repair.Cell Death Differ. 2023 Mar;30(3):716-730. doi: 10.1038/s41418-022-01074-0. Epub 2022 Oct 11. Cell Death Differ. 2023. PMID: 36220889 Free PMC article.
-
Tau beyond Tangles: DNA Damage Response and Cytoskeletal Protein Crosstalk on Neurodegeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 19;25(14):7906. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147906. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063148 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connecting the Dots: From DNA Damage and Repair to Aging.Int J Mol Sci. 2016 May 6;17(5):685. doi: 10.3390/ijms17050685. Int J Mol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27164092 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Redox regulation of genome stability by effects on gene expression, epigenetic pathways and DNA damage/repair.Redox Biol. 2015 Aug;5:275-289. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2015.05.008. Epub 2015 Jun 3. Redox Biol. 2015. PMID: 26079210 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome instability in Alzheimer disease.Mech Ageing Dev. 2017 Jan;161(Pt A):83-94. doi: 10.1016/j.mad.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 Apr 20. Mech Ageing Dev. 2017. PMID: 27105872 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adamec E, Vonsattel JP, Nixon RA. DNA strand breaks in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res. 1999;849:67–77. - PubMed
-
- Ahel I, Rass U, El-Khamisy SF, Katyal S, Clements PM, McKinnon PJ, Caldecott KW, West SC. The neurodegenerative disease protein aprataxin resolves abortive DNA ligation intermediates. Nature. 2006;443:713–716. - PubMed
-
- Anttinen A, Koulu L, Nikoskelainen E, Portin R, Kurki T, Erkinjuntti M, Jaspers NG, Raams A, Green MH, Lehmann AR, et al. Neurological symptoms and natural course of xeroderma pigmentosum. Brain. 2008;131:1979–1989. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

