Activated STING in a vascular and pulmonary syndrome
- PMID: 25029335
- PMCID: PMC4174543
- DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa1312625
Activated STING in a vascular and pulmonary syndrome
Abstract
Background: The study of autoinflammatory diseases has uncovered mechanisms underlying cytokine dysregulation and inflammation.
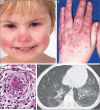
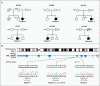
Methods: We analyzed the DNA of an index patient with early-onset systemic inflammation, cutaneous vasculopathy, and pulmonary inflammation. We sequenced a candidate gene, TMEM173, encoding the stimulator of interferon genes (STING), in this patient and in five unrelated children with similar clinical phenotypes. Four children were evaluated clinically and immunologically. With the STING ligand cyclic guanosine monophosphate-adenosine monophosphate (cGAMP), we stimulated peripheral-blood mononuclear cells and fibroblasts from patients and controls, as well as commercially obtained endothelial cells, and then assayed transcription of IFNB1, the gene encoding interferon-β, in the stimulated cells. We analyzed IFNB1 reporter levels in HEK293T cells cotransfected with mutant or nonmutant STING constructs. Mutant STING leads to increased phosphorylation of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1), so we tested the effect of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors on STAT1 phosphorylation in lymphocytes from the affected children and controls.
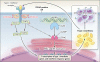
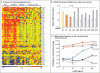
Results: We identified three mutations in exon 5 of TMEM173 in the six patients. Elevated transcription of IFNB1 and other gene targets of STING in peripheral-blood mononuclear cells from the patients indicated constitutive activation of the pathway that cannot be further up-regulated with stimulation. On stimulation with cGAMP, fibroblasts from the patients showed increased transcription of IFNB1 but not of the genes encoding interleukin-1 (IL1), interleukin-6 (IL6), or tumor necrosis factor (TNF). HEK293T cells transfected with mutant constructs show elevated IFNB1 reporter levels. STING is expressed in endothelial cells, and exposure of these cells to cGAMP resulted in endothelial activation and apoptosis. Constitutive up-regulation of phosphorylated STAT1 in patients' lymphocytes was reduced by JAK inhibitors.
Conclusions: STING-associated vasculopathy with onset in infancy (SAVI) is an autoinflammatory disease caused by gain-of-function mutations in TMEM173. (Funded by the Intramural Research Program of the National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases; ClinicalTrials.gov number, NCT00059748.).
Figures
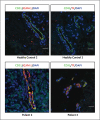
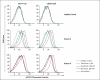
Comment in
-
STING-associated vasculopathy with onset in infancy--a new interferonopathy.N Engl J Med. 2014 Aug 7;371(6):568-71. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1407246. Epub 2014 Jul 16. N Engl J Med. 2014. PMID: 25029336 No abstract available.
-
Autoinflammation: A new STING-associated monogenic autoinflammatory disease.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014 Sep;10(9):512. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2014.126. Epub 2014 Aug 5. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 25090944 No abstract available.
-
[Early aggressive systemic inflammatory vascular diseases: mutations in adenosine desaminase 2 and interferonopathies].Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2014 Dec;141(12):808-9. doi: 10.1016/j.annder.2014.10.006. Epub 2014 Nov 1. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2014. PMID: 25433938 French. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Disease-associated mutations identify a novel region in human STING necessary for the control of type I interferon signaling.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017 Aug;140(2):543-552.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2016.10.031. Epub 2017 Jan 10. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28087229
-
A case of STING-associated vasculopathy with onset in infancy with novel STING1 variant.Pediatr Dermatol. 2024 Jul-Aug;41(4):697-700. doi: 10.1111/pde.15559. Epub 2024 Feb 18. Pediatr Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 38369300
-
Brief Report: Blockade of TANK-Binding Kinase 1/IKKɛ Inhibits Mutant Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING)-Mediated Inflammatory Responses in Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells.Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017 Jul;69(7):1495-1501. doi: 10.1002/art.40122. Epub 2017 Jun 5. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017. PMID: 28426911
-
Lung Inflammation in STING-Associated Vasculopathy with Onset in Infancy (SAVI).Cells. 2022 Jan 18;11(3):318. doi: 10.3390/cells11030318. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159128 Free PMC article. Review.
-
STING-Mediated Lung Inflammation and Beyond.J Clin Immunol. 2021 Apr;41(3):501-514. doi: 10.1007/s10875-021-00974-z. Epub 2021 Feb 2. J Clin Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33532887 Review.
Cited by
-
The common Sting1 HAQ, AQ alleles rescue CD4 T cellpenia, restore T-regs, and prevent SAVI (N153S) inflammatory disease in mice.Elife. 2024 Sep 18;13:RP96790. doi: 10.7554/eLife.96790. Elife. 2024. PMID: 39291958 Free PMC article.
-
A cell-free assay implicates a role of sphingomyelin and cholesterol in STING phosphorylation.Sci Rep. 2021 Jun 7;11(1):11996. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-91562-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34099821 Free PMC article.
-
Copa Syndrome: a Novel Autosomal Dominant Immune Dysregulatory Disease.J Clin Immunol. 2016 May;36(4):377-387. doi: 10.1007/s10875-016-0271-8. Epub 2016 Apr 5. J Clin Immunol. 2016. PMID: 27048656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
cGAS-STING Pathway Does Not Promote Autoimmunity in Murine Models of SLE.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 29;12:605930. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.605930. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33854495 Free PMC article.
-
The Third Man: DNA sensing as espionage in pulmonary vascular health and disease.Pulm Circ. 2021 Mar 2;11(1):2045894021996574. doi: 10.1177/2045894021996574. eCollection 2021 Jan-Mar. Pulm Circ. 2021. PMID: 33738095 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Crow YJ. Aicardi-Goutières syndrome. Handb Clin Neurol. 2013;113:1629–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
