RIG-I-like helicases induce immunogenic cell death of pancreatic cancer cells and sensitize tumors toward killing by CD8(+) T cells
- PMID: 25012502
- PMCID: PMC4227156
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2014.96
RIG-I-like helicases induce immunogenic cell death of pancreatic cancer cells and sensitize tumors toward killing by CD8(+) T cells
Erratum in
- Cell Death Differ. 2014 Dec;21(12):161
Abstract
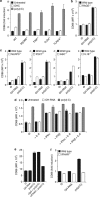
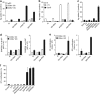
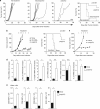
Pancreatic cancer is characterized by a microenvironment suppressing immune responses. RIG-I-like helicases (RLH) are immunoreceptors for viral RNA that induce an antiviral response program via the production of type I interferons (IFN) and apoptosis in susceptible cells. We recently identified RLH as therapeutic targets of pancreatic cancer for counteracting immunosuppressive mechanisms and apoptosis induction. Here, we investigated immunogenic consequences of RLH-induced tumor cell death. Treatment of murine pancreatic cancer cell lines with RLH ligands induced production of type I IFN and proinflammatory cytokines. In addition, tumor cells died via intrinsic apoptosis and displayed features of immunogenic cell death, such as release of HMGB1 and translocation of calreticulin to the outer cell membrane. RLH-activated tumor cells led to activation of dendritic cells (DCs), which was mediated by tumor-derived type I IFN, whereas TLR, RAGE or inflammasome signaling was dispensable. Importantly, CD8α(+) DCs effectively engulfed apoptotic tumor material and cross-presented tumor-associated antigen to naive CD8(+) T cells. In comparison, tumor cell death mediated by oxaliplatin, staurosporine or mechanical disruption failed to induce DC activation and antigen presentation. Tumor cells treated with sublethal doses of RLH ligands upregulated Fas and MHC-I expression and were effectively sensitized towards Fas-mediated apoptosis and cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL)-mediated lysis. Vaccination of mice with RLH-activated tumor cells induced protective antitumor immunity in vivo. In addition, MDA5-based immunotherapy led to effective tumor control of established pancreatic tumors. In summary, RLH ligands induce a highly immunogenic form of tumor cell death linking innate and adaptive immunity.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Induction of immunogenic cell death by targeting RIG-I-like helicases in pancreatic cancer.Oncoimmunology. 2014 Dec 13;3(9):e955687. doi: 10.4161/21624011.2014.955687. eCollection 2014 Oct. Oncoimmunology. 2014. PMID: 25941620 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptotic pancreatic tumor cells are superior to cell lysates in promoting cross-priming of cytotoxic T cells and activate NK and gammadelta T cells.Cancer Res. 2002 Apr 15;62(8):2347-52. Cancer Res. 2002. PMID: 11956095
-
Immunostimulatory RNA leads to functional reprogramming of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in pancreatic cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2019 Nov 6;7(1):288. doi: 10.1186/s40425-019-0778-7. J Immunother Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31694706 Free PMC article.
-
CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes in cancer immunotherapy: A review.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Jun;234(6):8509-8521. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27782. Epub 2018 Nov 22. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30520029 Review.
-
Cytotoxicity as a form of immunogenic cell death leading to efficient tumor antigen cross-priming.Immunol Rev. 2024 Jan;321(1):143-151. doi: 10.1111/imr.13281. Epub 2023 Oct 11. Immunol Rev. 2024. PMID: 37822051 Review.
Cited by
-
RIG-1-Like Receptor Activation Synergizes With Intratumoral Alpha Radiation to Induce Pancreatic Tumor Rejection, Triple-Negative Breast Metastases Clearance, and Antitumor Immune Memory in Mice.Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 17;10:990. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00990. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32766128 Free PMC article.
-
RIG-I immunotherapy overcomes radioresistance in p53-positive malignant melanoma.J Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Jun 1;15(1):mjad001. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjad001. J Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36626927 Free PMC article.
-
Dissecting the role of toll-like receptor 7 in pancreatic cancer.Cancer Med. 2023 Apr;12(7):8542-8556. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5606. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36602302 Free PMC article.
-
RIG-I activating immunostimulatory RNA boosts the efficacy of anticancer vaccines and synergizes with immune checkpoint blockade.EBioMedicine. 2019 Mar;41:146-155. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.02.056. Epub 2019 Mar 6. EBioMedicine. 2019. PMID: 30852164 Free PMC article.
-
A minimal RNA ligand for potent RIG-I activation in living mice.Sci Adv. 2018 Feb 21;4(2):e1701854. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1701854. eCollection 2018 Feb. Sci Adv. 2018. PMID: 29492454 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Siegel R, Naishadham D, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 2013;63:11–30. - PubMed
-
- Fatima J, Schnelldorfer T, Barton J, Wood CM, Wiste HJ, Smyrk TC, et al. Pancreatoduodenectomy for ductal adenocarcinoma: implications of positive margin on survival. Arch Surg. 2010;145:167–172. - PubMed
-
- Gabitass RF, Annels NE, Stocken DD, Pandha HA, Middleton GW. Elevated myeloid-derived suppressor cells in pancreatic, esophageal and gastric cancer are an independent prognostic factor and are associated with significant elevation of the Th2 cytokine interleukin-13. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2011;60:1419–1430. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

