Concerted action of Nrf2-ARE pathway, MRN complex, HMGB1 and inflammatory cytokines - implication in modification of radiation damage
- PMID: 25009785
- PMCID: PMC4085347
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2014.02.008
Concerted action of Nrf2-ARE pathway, MRN complex, HMGB1 and inflammatory cytokines - implication in modification of radiation damage
Abstract
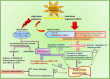
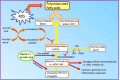
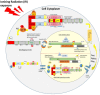
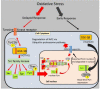
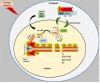
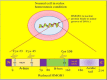
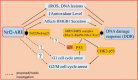
Whole body exposure to low linear energy transfer (LET) ionizing radiations (IRs) damages vital intracellular bio-molecules leading to multiple cellular and tissue injuries as well as pathophysiologies such as inflammation, immunosuppression etc. Nearly 70% of damage is caused indirectly by radiolysis of intracellular water leading to formation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals and producing a state of oxidative stress. The damage is also caused by direct ionization of biomolecules. The type of radiation injuries is dependent on the absorbed radiation dose. Sub-lethal IR dose produces more of DNA base damages, whereas higher doses produce more DNA single strand break (SSBs), and double strand breaks (DSBs). The Nrf2-ARE pathway is an important oxidative stress regulating pathway. The DNA DSBs repair regulated by MRN complex, immunomodulation and inflammation regulated by HMGB1 and various types of cytokines are some of the key pathways which interact with each other in a complex manner and modify the radiation response. Because the majority of radiation damage is via oxidative stress, it is essential to gain in depth understanding of the mechanisms of Nrf2-ARE pathway and understand its interactions with MRN complex, HMGB1 and cytokines to increase our understanding on the radiation responses. Such information is of tremendous help in development of medical radiation countermeasures, radioprotective drugs and therapeutics. Till date no approved and safe countermeasure is available for human use. This study reviews the Nrf2-ARE pathway and its crosstalk with MRN-complex, HMGB1 and cytokines (TNF-a, IL-6, IFN-? etc.). An attempt is also made to review the modification of some of these pathways in presence of selected antioxidant radioprotective compounds or herbal extracts.
Keywords: .OH, hydroxyl radical; AP1, activator protein-1; ARE, antioxidant response element; ATM, ataxia telangiectasia mutagenesis; Bcl-2, B cell lymphoma-2 protein; CBP, CREB-binding protein; Chk-2, checkpoint kinase-2 protein; DAMP, death associated molecular pattern; DDR, DNA damage response; DGR, double glycine repeats; DSB, double strands break; FGF, fibroblast growth factor; FGF2, fibroblast growth factor-2; GM-CSF, granulocytes macrophages colony stimulating factor; GPx, glutathione peroxidase; GSH, glutathione (reduced); GSK-3ß, glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta; HMGB1; HMGB1, high mobility group Box 1; HR, homologous recombination; IR, ionizing radiation; Keap1, Kelch like ECH associated protein 1; LET, linear energy transfer; MDA, malondialdehyde; MIP, macrophages inflammatory proteins; MRN complex; MRN, Mre11, Rad50 and Nbs1 subunits; MRP, multidrug resistance protein; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NES, nuclear export sequence; NHEJ, non-homologous end joining; NLS, nuclear localization sequence; Nrf2-ARE pathway; PKC, protein kinase C; RAGE, receptor for advance glycation end products; RIF, radiation induced foci; RNS, reactive nitrogen species; ROS, reactive oxygen species; Radio-modification; SOD, superoxide dismutase; SSBs, single strand DNA breaks; TRAIL, TNF related apoptosis inducing ligand; TWEAK; TWEAK, tumour necrosis factor weak inducer of apoptosis; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cells; bFGF, basal fibroblast growth factor; t-BHQ, tert butyl hydroquinone.
Figures

Similar articles
-
NBS1 is regulated by two kind of mechanisms: ATM-dependent complex formation with MRE11 and RAD50, and cell cycle-dependent degradation of protein.J Radiat Res. 2017 Jul 1;58(4):487-494. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrx014. J Radiat Res. 2017. PMID: 28369484 Free PMC article.
-
An insight into understanding the coupling between homologous recombination mediated DNA repair and chromatin remodeling mechanisms in plant genome: an update.Cell Cycle. 2021 Sep;20(18):1760-1784. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2021.1966584. Epub 2021 Aug 26. Cell Cycle. 2021. PMID: 34437813 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation.J Hepatol. 2013 Sep;59(3):583-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.033. Epub 2013 Apr 6. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23567086 Review.
-
Regulation of ATM in DNA double strand break repair accounts for the radiosensitivity in human cells exposed to high linear energy transfer ionizing radiation.Mutat Res. 2009 Nov 2;670(1-2):15-23. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2009.06.016. Epub 2009 Jul 5. Mutat Res. 2009. PMID: 19583974
-
Mre11-Rad50-Nbs1 is a keystone complex connecting DNA repair machinery, double-strand break signaling, and the chromatin template.Biochem Cell Biol. 2007 Aug;85(4):509-20. doi: 10.1139/O07-069. Biochem Cell Biol. 2007. PMID: 17713585 Review.
Cited by
-
Puerarin ameliorates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by inhibiting lipid metabolism through FMO5.Front Pharmacol. 2024 Jul 11;15:1423634. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1423634. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 39055493 Free PMC article.
-
Brain Damage and Patterns of Neurovascular Disorder after Ionizing Irradiation. Complications in Radiotherapy and Radiation Combined Injury.Radiat Res. 2021 Jul 1;196(1):1-16. doi: 10.1667/RADE-20-00147.1. Radiat Res. 2021. PMID: 33979447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53-Dependent Cytoprotective Mechanisms behind Resistance to Chemo-Radiotherapeutic Agents Used in Cancer Treatment.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jun 28;15(13):3399. doi: 10.3390/cancers15133399. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37444509 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Oligomeric Sulfated Hyaluronan and Silk-Elastinlike Polymer Combination Protects against Murine Radiation Induced Proctitis.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Jan 12;14(1):175. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14010175. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 35057068 Free PMC article.
-
Fyn Kinase: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Acute Kidney Injury.Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2020 May 1;28(3):213-221. doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2019.214. Biomol Ther (Seoul). 2020. PMID: 32336052 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hall E.J., Amato G.J., Radiobiology for the Radiologist. Seventh edition, ISBN 978-1-60831-193-4.
-
- Douki T., Cadet J. Radiation - induced damage to DNA: from model compounds to cell. In: Spothem-Maurizot M., Mostafavi M., Douki T., Belloni J., editors. Radiation Chemistry: From Basics to Applications in Material and Life Sciences. EDP Sciences; Paris: 2008.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

