3D trajectories adopted by coding and regulatory DNA elements: first-passage times for genomic interactions
- PMID: 24998931
- PMCID: PMC4113018
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.05.036
3D trajectories adopted by coding and regulatory DNA elements: first-passage times for genomic interactions
Abstract
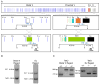
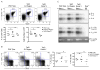
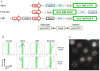
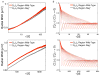
During B lymphocyte development, immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable (VH), diversity (DH), and joining (JH) segments assemble to generate a diverse antigen receptor repertoire. Here, we have marked the distal VH and DH-JH-Eμ regions with Tet-operator binding sites and traced their 3D trajectories in pro-B cells transduced with a retrovirus encoding Tet-repressor-EGFP. We found that these elements displayed fractional Langevin motion (fLm) due to the viscoelastic hindrance from the surrounding network of proteins and chromatin fibers. Using fractional Langevin dynamics modeling, we found that, with high probability, DHJH elements reach a VH element within minutes. Spatial confinement emerged as the dominant parameter that determined the frequency of such encounters. We propose that the viscoelastic nature of the nuclear environment causes coding elements and regulatory elements to bounce back and forth in a spring-like fashion until specific genomic interactions are established and that spatial confinement of topological domains largely controls first-passage times for genomic interactions.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

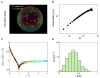
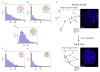
Comment in
-
The contraction of time and space in remote chromosomal interactions.Cell. 2014 Jul 17;158(2):243-244. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.06.039. Cell. 2014. PMID: 25036625 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
An immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region gene is generated from three segments of DNA: VH, D and JH.Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):981-92. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90089-6. Cell. 1980. PMID: 6769593
-
Chromosome dynamics near the sol-gel phase transition dictate the timing of remote genomic interactions.Nat Commun. 2019 Jun 24;10(1):2771. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-10628-9. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31235807 Free PMC article.
-
CCCTC-binding factor (CTCF) and cohesin influence the genomic architecture of the Igh locus and antisense transcription in pro-B cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jun 7;108(23):9566-71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1019391108. Epub 2011 May 23. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21606361 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene rearrangements.Immunol Rev. 2004 Aug;200:182-96. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2004.00177.x. Immunol Rev. 2004. PMID: 15242405 Review.
-
Chromatin Interactions in the Control of Immunoglobulin Heavy Chain Gene Assembly.Adv Immunol. 2015;128:41-92. doi: 10.1016/bs.ai.2015.08.001. Epub 2015 Sep 11. Adv Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26477365 Review.
Cited by
-
AID targeting: old mysteries and new challenges.Trends Immunol. 2015 Sep;36(9):527-35. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2015.07.003. Epub 2015 Aug 4. Trends Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26254147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physics and Biology (of Chromosomes).J Mol Biol. 2020 Jan 17;432(2):621-631. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2019.11.022. Epub 2019 Dec 20. J Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 31866291 Free PMC article.
-
Stochastic motion and transcriptional dynamics of pairs of distal DNA loci on a compacted chromosome.Science. 2023 Jun 30;380(6652):1357-1362. doi: 10.1126/science.adf5568. Epub 2023 Jun 29. Science. 2023. PMID: 37384691 Free PMC article.
-
The 3D Genome as Moderator of Chromosomal Communication.Cell. 2016 Mar 10;164(6):1110-1121. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.007. Cell. 2016. PMID: 26967279 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The nuclear matrix protein HNRNPU maintains 3D genome architecture globally in mouse hepatocytes.Genome Res. 2018 Feb;28(2):192-202. doi: 10.1101/gr.224576.117. Epub 2017 Dec 22. Genome Res. 2018. PMID: 29273625 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boveri T. Die Blastomerenkerne von Ascaris meglocephala und die Theorie der Chromosomenindividualitaet. Archiv für Zellforschung. 1909;3:181–268.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

