Mixed oligomers and monomeric amyloid-β disrupts endothelial cells integrity and reduces monomeric amyloid-β transport across hCMEC/D3 cell line as an in vitro blood-brain barrier model
- PMID: 24997450
- PMCID: PMC4133170
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.06.029
Mixed oligomers and monomeric amyloid-β disrupts endothelial cells integrity and reduces monomeric amyloid-β transport across hCMEC/D3 cell line as an in vitro blood-brain barrier model
Abstract
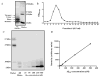
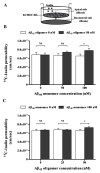
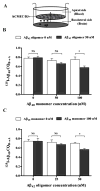
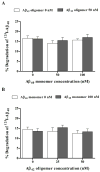
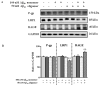
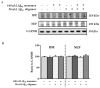
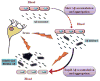
Senile amyloid plaques are one of the diagnostic hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, the severity of clinical symptoms of AD is weakly correlated with the plaque load. AD symptoms severity is reported to be more strongly correlated with the level of soluble amyloid-β (Aβ) assemblies. Formation of soluble Aβ assemblies is stimulated by monomeric Aβ accumulation in the brain, which has been related to its faulty cerebral clearance. Studies tend to focus on the neurotoxicity of specific Aβ species. There are relatively few studies investigating toxic effects of Aβ on the endothelial cells of the blood-brain barrier (BBB). We hypothesized that a soluble Aβ pool more closely resembling the in vivo situation composed of a mixture of Aβ40 monomer and Aβ42 oligomer would exert higher toxicity against hCMEC/D3 cells as an in vitro BBB model than either component alone. We observed that, in addition to a disruptive effect on the endothelial cells integrity due to enhancement of the paracellular permeability of the hCMEC/D3 monolayer, the Aβ mixture significantly decreased monomeric Aβ transport across the cell culture model. Consistent with its effect on Aβ transport, Aβ mixture treatment for 24h resulted in LRP1 down-regulation and RAGE up-regulation in hCMEC/D3 cells. The individual Aβ species separately failed to alter Aβ clearance or the cell-based BBB model integrity. Our study offers, for the first time, evidence that a mixture of soluble Aβ species, at nanomolar concentrations, disrupts endothelial cells integrity and its own transport across an in vitro model of the BBB.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Amyloid-β; Blood–brain barrier; Clearance.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differences in amyloid-β clearance across mouse and human blood-brain barrier models: kinetic analysis and mechanistic modeling.Neuropharmacology. 2014 Apr;79:668-78. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2014.01.023. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Neuropharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24467845 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of High Cholesterol Regulation of LRP1 and RAGE on Aβ Transport Across the Blood-Brain Barrier in Alzheimer's Disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2021;18(5):428-442. doi: 10.2174/1567205018666210906092940. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2021. PMID: 34488598
-
Aβ₁₋₄₂-RAGE interaction disrupts tight junctions of the blood-brain barrier via Ca²⁺-calcineurin signaling.J Neurosci. 2012 Jun 27;32(26):8845-54. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6102-11.2012. J Neurosci. 2012. PMID: 22745485 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the blood-brain barrier in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer's disease.Curr Alzheimer Res. 2007 Apr;4(2):191-7. doi: 10.2174/156720507780362245. Curr Alzheimer Res. 2007. PMID: 17430246 Review.
-
Clearance of amyloid-beta peptide across the blood-brain barrier: implication for therapies in Alzheimer's disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2009 Mar;8(1):16-30. doi: 10.2174/187152709787601867. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2009. PMID: 19275634 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endothelial leakiness elicited by amyloid protein aggregation.Nat Commun. 2024 Jan 19;15(1):613. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-44814-1. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38242873 Free PMC article.
-
Blood-Brain Barrier Dysfunction in a 3D In Vitro Model of Alzheimer's Disease.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019 Aug 12;6(20):1900962. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900962. eCollection 2019 Oct 16. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019. PMID: 31637161 Free PMC article.
-
Somatostatin Maintains Permeability and Integrity of Blood-Brain Barrier in β-Amyloid Induced Toxicity.Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Jan;56(1):292-306. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1045-5. Epub 2018 Apr 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 29700775
-
Extra-virgin olive oil attenuates amyloid-β and tau pathologies in the brains of TgSwDI mice.J Nutr Biochem. 2015 Dec;26(12):1479-90. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2015.07.022. Epub 2015 Aug 13. J Nutr Biochem. 2015. PMID: 26344778 Free PMC article.
-
Amyloid Beta Oligomers Activate Death Receptors and Mitochondria-Mediated Apoptotic Pathways in Cerebral Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells; Protective Effects of Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors.Cells. 2023 Dec 14;12(24):2840. doi: 10.3390/cells12242840. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132159 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Citron M. Alzheimer’s disease: strategies for disease modification. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010;9:387–398. - PubMed
-
- Ubhi K, Masliah E. Alzheimer’s disease: recent advances and future perspectives. J Alzheimers Dis. 2013;33(Suppl 1):S185–194. - PubMed
-
- Selkoe DJ. Physiological production of the beta-amyloid protein and the mechanism of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci. 1993;16:403–409. - PubMed
-
- Benilova I, Karran E, De Strooper B. The toxic Abeta oligomer and Alzheimer’s disease: an emperor in need of clothes. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15:349–357. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

