Trends in biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis: results from a survey of payers and providers
- PMID: 24991313
- PMCID: PMC4046448
Trends in biologic therapies for rheumatoid arthritis: results from a survey of payers and providers
Abstract
Background: Advances in therapies for rheumatoid arthritis (RA), particularly biologics, have transformed the treatment paradigm for RA. However, the associated costs of these therapies result in a significant economic burden on the healthcare system. As a chronic disease requiring lifelong treatment, most health plans now position RA drugs as a high-priority therapeutic category.
Objective: To identify provider and payer practices and perceptions regarding coverage of RA biologics in the current marketplace, as well as emerging trends in reimbursement practices.
Method: In November 2011, Reimbursement Intelligence, a healthcare research company, collected and analyzed quantitative and qualitative data via parallel-structure online surveys of 100 rheumatologists and 50 health plan payers (medical and pharmacy directors) who represent more than 80 million covered lives. The surveys included approximately 150 questions, and the surveys were designed to force a response for each question.
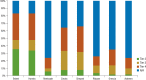
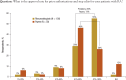
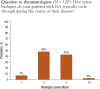
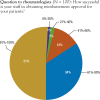
Results: Payers reported using tier placement, prior authorization, and contracting in determining coverage strategies for RA biologics. Among providers, experience with older RA agents remains the key driver for the choice of a biologic agent. A majority of payers and providers (68% and 54%, respectively) reported that they did not anticipate a change in the way their plans would manage biologics over the next 2 to 4 years. Payers' responses indicated uncertainty about how therapeutic positioning of newer, small-molecule drugs at price parity to biologics would affect the current reimbursement landscape. Survey responses show that approval of an indication for early treatment of RA is not likely to change the prescribing and reimbursement landscape for RA biologics. This survey further shows that payers and providers are generally aligned in terms of perceptions of current and future treatments for RA.
Conclusion: Advances in RA therapies allow patients increasing options for effective disease management. However, the high cost of biologic therapies and the need for lifelong treatment raise economic concerns. Payer satisfaction with current therapies and uncertainty about added value of new therapies will create challenges for new medications coming to market.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Emerging trends in cancer care: health plans' and pharmacy benefit managers' perspectives on changing care models.Am Health Drug Benefits. 2012 Jul;5(4):242-53. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2012. PMID: 24991323 Free PMC article.
-
The evolution of payer management of oncology drugs in the United States between 2017 and 2022.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2023 Oct;29(10):1138-1149. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2023.23045. Epub 2023 Sep 11. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2023. PMID: 37695273 Free PMC article.
-
Payer perceptions on the use of economic models in oncology decision making.J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021 Nov;27(11):1560-1567. doi: 10.18553/jmcp.2021.27.11.1560. J Manag Care Spec Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34714111 Free PMC article.
-
Introduction to economic modeling for clinical rheumatologists: application to biologic agents in rheumatoid arthritis.Clin Rheumatol. 2011 Mar;30 Suppl 1:S9-18. doi: 10.1007/s10067-010-1635-8. Epub 2011 Feb 26. Clin Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21359506 Review.
-
Impact of Adverse Events Associated With Medications in the Treatment and Prevention of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Clin Ther. 2019 Jul;41(7):1376-1396. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2019.04.030. Epub 2019 Jun 10. Clin Ther. 2019. PMID: 31196653 Review.
Cited by
-
Factors influencing the use of biologic therapy and adoption of treat-to-target recommendations in current European rheumatology practice.Patient Prefer Adherence. 2018 Oct 4;12:2007-2014. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S170054. eCollection 2018. Patient Prefer Adherence. 2018. PMID: 30323570 Free PMC article.
-
The Effectiveness of Intravenous Golimumab Administered Directly After Infliximab in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients.Drugs R D. 2018 Sep;18(3):211-219. doi: 10.1007/s40268-018-0240-1. Drugs R D. 2018. PMID: 30054896 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment Patterns of Newly Diagnosed Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients from a Commercially Insured Population.Rheumatol Ther. 2018 Dec;5(2):355-369. doi: 10.1007/s40744-018-0114-6. Epub 2018 May 30. Rheumatol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29846932 Free PMC article.
-
"Hidden" value: how indirect benefits of health information exchange further promote sustainability.Am Health Drug Benefits. 2012 Sep;5(6):333-41. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2012. PMID: 24991331 Free PMC article.
-
Considering patient preferences when selecting anti-tumor necrosis factor therapeutic options.Am Health Drug Benefits. 2014 Apr;7(2):71-81. Am Health Drug Benefits. 2014. PMID: 24991392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rindfleisch JA, Muller D. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis. Am Fam Physician. 2005; 72: 1037–1047 - PubMed
-
- Lee DM, Weinblatt ME. Rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 2001; 358: 903–911 - PubMed
-
- Sokka T. Work disability in early rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003; 21 (5 suppl 31): S71–S74 - PubMed
-
- Verstappen SM, Bijlsma JW, Verkleij H, et al. Utrecht Rheumatoid Arthritis Cohort Study Group. Overview of work disability in rheumatoid arthritis patients as observed in cross-sectional and longitudinal surveys. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 51: 488–497 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
