The microRNA-23b/27b/24 cluster promotes breast cancer lung metastasis by targeting metastasis-suppressive gene prosaposin
- PMID: 24966325
- PMCID: PMC4139207
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M114.582866
The microRNA-23b/27b/24 cluster promotes breast cancer lung metastasis by targeting metastasis-suppressive gene prosaposin
Abstract
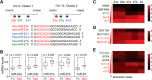
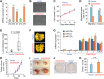
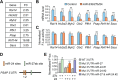
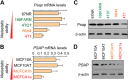
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been shown to function as key regulators of tumor progression and metastasis. Recent studies have indicated that the miRNAs comprising the miR-23b/27b/24 cluster might influence tumor metastasis, although the precise nature of this regulation remains unclear. Here, expression of the miR-23b/27b/24 cluster is found to correlate with metastatic potential in mouse and human breast cancer cell lines and is elevated in metastatic lung lesions in human breast cancer patients. Ectopic expression of the miRNAs in the weakly metastatic mouse 4TO7 mammary tumor cell line had no effect on proliferation or morphology of tumor cells in vitro but was found to increase lung metastasis in a mouse model of breast cancer metastasis. Furthermore, gene expression profiling analysis of miRNA overexpressing 4TO7 cells revealed the direct targeting of prosaposin (PSAP), which encodes a secreted protein found to be inversely correlated with metastatic progression in human breast cancer patients. Importantly, ectopic expression of PSAP was able to suppress the metastatic phenotype in highly metastatic 4T1 and MDA-MB-231 SCP28 cells, as well as in cells ectopically expressing miR-23b/27b/24. These findings support a metastasis-promoting function of the miR-23b/27b/24 cluster of miRNAs, which functions in part through the direct inhibition of PSAP.
Keywords: Breast Cancer; Invasion; Metastasis; MicroRNA (miRNA); Tumor Metastases.
© 2014 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The microRNA-23b/-27b cluster suppresses prostate cancer metastasis via Huntingtin-interacting protein 1-related.Oncogene. 2016 Sep 8;35(36):4752-61. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.6. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26898757 Free PMC article.
-
miR-23b and miR-27b are oncogenic microRNAs in breast cancer: evidence from a CRISPR/Cas9 deletion study.BMC Cancer. 2019 Jun 28;19(1):642. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5839-2. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31253120 Free PMC article.
-
Dual regulation of receptor tyrosine kinase genes EGFR and c-Met by the tumor-suppressive microRNA-23b/27b cluster in bladder cancer.Int J Oncol. 2015 Feb;46(2):487-96. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2752. Epub 2014 Nov 14. Int J Oncol. 2015. PMID: 25405368 Free PMC article.
-
[microRNA expression in breast development and breast cancer].Pathologe. 2013 Nov;34 Suppl 2:195-200. doi: 10.1007/s00292-013-1878-7. Pathologe. 2013. PMID: 24196612 Review. German.
-
Promising therapeutic role of miR-27b in tumor.Tumour Biol. 2017 Mar;39(3):1010428317691657. doi: 10.1177/1010428317691657. Tumour Biol. 2017. PMID: 28351320 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA analysis of breast ductal fluid in breast cancer patients.Int J Oncol. 2016 May;48(5):2071-8. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2016.3435. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Int J Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26984519 Free PMC article.
-
Experimental procedures to identify and validate specific mRNA targets of miRNAs.EXCLI J. 2015 Jul 2;14:758-90. doi: 10.17179/excli2015-319. eCollection 2015. EXCLI J. 2015. PMID: 27047316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The reciprocal regulation loop of Notch2 pathway and miR-23b in controlling gastric carcinogenesis.Oncotarget. 2015 Jul 20;6(20):18012-26. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.4000. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26041881 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating MicroRNAs and Blood-Brain-Barrier Function in Breast Cancer Metastasis.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(13):1417-1427. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200316151720. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32175838 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNAs and Other Epigenetic Changes as Biomarkers in Triple Negative Breast Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2015 Nov 30;16(12):28347-76. doi: 10.3390/ijms161226090. Int J Mol Sci. 2015. PMID: 26633365 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Harquail J., Benzina S., Robichaud G. A. (2012) MicroRNAs and breast cancer malignancy: an overview of miRNA-regulated cancer processes leading to metastasis. Cancer Biomark 11, 269–280 - PubMed
-
- Lu J., Getz G., Miska E. A., Alvarez-Saavedra E., Lamb J., Peck D., Sweet-Cordero A., Ebert B. L., Mak R. H., Ferrando A. A., Downing J. R., Jacks T., Horvitz H. R., Golub T. R. (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435, 834–838 - PubMed
-
- Volinia S., Calin G. A., Liu C. G., Ambs S., Cimmino A., Petrocca F., Visone R., Iorio M., Roldo C., Ferracin M., Prueitt R. L., Yanaihara N., Lanza G., Scarpa A., Vecchione A., Negrini M., Harris C. C., Croce C. M. (2006) A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 103, 2257–2261 - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

