Targeting the PI3K/mTOR Pathway in Pediatric Hematologic Malignancies
- PMID: 24904824
- PMCID: PMC4032892
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00108
Targeting the PI3K/mTOR Pathway in Pediatric Hematologic Malignancies
Abstract
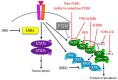
A complex interplay of intracellular signaling networks orchestrates normal cell growth and survival, including translation, transcription, proliferation, and cell cycle progression. Dysregulation of such signals occurs commonly in many malignancies, thereby giving the cancer cell a survival advantage, but also providing possible targets for therapeutic intervention. Activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt)/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway contributes to the proliferative advantage of malignant cells and may confer resistance to chemotherapy in various hematologic malignancies. The initial mTOR inhibitor, sirolimus (also known as rapamycin), was first discovered in 1975 in the soil of Easter Island. Sirolimus was originally developed as an anti-fungal agent given its macrolide properties, but was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1999 as an immunosuppressive agent for renal transplantation patients once its T cell suppression characteristics were recognized. Shortly thereafter, recognition of sirolimus's ability to inhibit cellular proliferation and cell cycle progression brought sirolimus to the forefront as a possible inhibitor of mTOR. In the subsequent decade, the functional roles of the mTOR protein have been more fully elucidated, and this protein is now known to be a key regulator in a highly complex signaling pathway that controls cell growth, proliferation, metabolism, and apoptosis. This article discusses the dysregulation of PI3K/mTOR signaling in hematologic malignancies, including acute and chronic leukemias, lymphomas, and lymphoproliferative disorders. The current repertoire of PI3K/mTOR pathway inhibitors in development and clinical trials to date are described with emphasis upon pediatric hematologic malignancies (Figure 1). Investigation of small molecule inhibitors of this complex signaling network is an active area of oncology drug development.
Keywords: Hodgkin lymphoma; PI3K/mTOR; acute lymphoblastic leukemia; acute myeloid leukemia; clinical trial; non-Hodgkin lymphoma; pediatric; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Figures
Similar articles
-
PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling Pathway in Blood Malignancies-New Therapeutic Possibilities.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Nov 5;15(21):5297. doi: 10.3390/cancers15215297. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37958470 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential effects of selective inhibitors targeting the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in acute lymphoblastic leukemia.PLoS One. 2013 Nov 14;8(11):e80070. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0080070. eCollection 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 24244612 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin module for acute myelogenous leukemia therapy: from bench to bedside.Curr Med Chem. 2007;14(19):2009-23. doi: 10.2174/092986707781368423. Curr Med Chem. 2007. PMID: 17691943 Review.
-
New insights into Notch1 regulation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR1 signaling axis: targeted therapy of γ-secretase inhibitor resistant T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia.Cell Signal. 2014 Jan;26(1):149-61. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.09.021. Epub 2013 Oct 16. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24140475 Review.
-
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling network as a therapeutic target in acute myelogenous leukemia patients.Oncotarget. 2010 Jun;1(2):89-103. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.114. Oncotarget. 2010. PMID: 20671809 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Impact of mTOR expression on clinical outcome in paediatric patients with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukaemia - preliminary report.Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2016;20(4):291-6. doi: 10.5114/wo.2016.61848. Epub 2016 Sep 5. Contemp Oncol (Pozn). 2016. PMID: 27688725 Free PMC article.
-
Everolimus in combination with Imatinib overcomes resistance in Chronic myeloid leukaemia.Med Oncol. 2019 Feb 22;36(3):30. doi: 10.1007/s12032-019-1253-5. Med Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30796703
-
Current Views on the Interplay between Tyrosine Kinases and Phosphatases in Chronic Myeloid Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 12;13(10):2311. doi: 10.3390/cancers13102311. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34065882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Verteporfin Inhibits Cell Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Human Leukemia NB4 Cells without Light Activation.Int J Med Sci. 2017 Sep 3;14(10):1031-1039. doi: 10.7150/ijms.19682. eCollection 2017. Int J Med Sci. 2017. PMID: 28924376 Free PMC article.
-
Combined Application of Pan-AKT Inhibitor MK-2206 and BCL-2 Antagonist Venetoclax in B-Cell Precursor Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 9;22(5):2771. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052771. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33803402 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

