Role of Na,K-ATPase α1 and α2 isoforms in the support of astrocyte glutamate uptake
- PMID: 24901986
- PMCID: PMC4046997
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098469
Role of Na,K-ATPase α1 and α2 isoforms in the support of astrocyte glutamate uptake
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(9): doi/10.1371/journal.pone.0110095. Illarionava, Nina B [corrected to Illarionova, Nina B]
Abstract
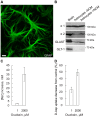
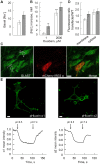
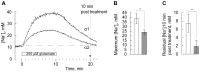
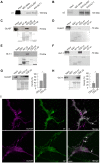
Glutamate released during neuronal activity is cleared from the synaptic space via the astrocytic glutamate/Na(+) co-transporters. This transport is driven by the transmembrane Na(+) gradient mediated by Na,K-ATPase. Astrocytes express two isoforms of the catalytic Na,K-ATPase α subunits; the ubiquitously expressed α1 subunit and the α2 subunit that has a more specific expression profile. In the brain α2 is predominantly expressed in astrocytes. The isoforms differ with regard to Na+ affinity, which is lower for α2. The relative roles of the α1 and α2 isoforms in astrocytes are not well understood. Here we present evidence that the presence of the α2 isoform may contribute to a more efficient restoration of glutamate triggered increases in intracellular sodium concentration [Na(+)]i. Studies were performed on primary astrocytes derived from E17 rat striatum expressing Na,K-ATPase α1 and α2 and the glutamate/Na(+) co-transporter GLAST. Selective inhibition of α2 resulted in a modest increase of [Na(+)]i accompanied by a disproportionately large decrease in uptake of aspartate, an indicator of glutamate uptake. To compare the capacity of α1 and α2 to handle increases in [Na(+)]i triggered by glutamate, primary astrocytes overexpressing either α1 or α2 were used. Exposure to glutamate 200 µM caused a significantly larger increase in [Na(+)]i in α1 than in α2 overexpressing cells, and as a consequence restoration of [Na(+)]i, after glutamate exposure was discontinued, took longer time in α1 than in α2 overexpressing cells. Both α1 and α2 interacted with astrocyte glutamate/Na(+) co-transporters via the 1st intracellular loop.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glutamate transporter coupling to Na,K-ATPase.J Neurosci. 2009 Jun 24;29(25):8143-55. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1081-09.2009. J Neurosci. 2009. PMID: 19553454 Free PMC article.
-
Glutamate transporter activity promotes enhanced Na+ /K+ -ATPase-mediated extracellular K+ management during neuronal activity.J Physiol. 2016 Nov 15;594(22):6627-6641. doi: 10.1113/JP272531. Epub 2016 Jun 29. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27231201 Free PMC article.
-
Links between L-glutamate transporters, Na+/K+-ATPase and cytoskeleton in astrocytes: evidence following inhibition with rottlerin.Neuroscience. 2013 Dec 19;254:335-46. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.09.043. Epub 2013 Oct 1. Neuroscience. 2013. PMID: 24095695
-
The cardiac sodium pump: structure and function.Basic Res Cardiol. 2002;97 Suppl 1:I19-24. doi: 10.1007/s003950200024. Basic Res Cardiol. 2002. PMID: 12479229 Review.
-
Glutamate Transporters/Na(+), K(+)-ATPase Involving in the Neuroprotective Effect as a Potential Regulatory Target of Glutamate Uptake.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Mar;53(2):1124-1131. doi: 10.1007/s12035-014-9071-4. Epub 2015 Jan 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 25586061 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel ATP1A2 mutation in a patient with hypokalaemic periodic paralysis and CNS symptoms.Brain. 2018 Dec 1;141(12):3308-3318. doi: 10.1093/brain/awy283. Brain. 2018. PMID: 30423015 Free PMC article.
-
Glial Cells-The Strategic Targets in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Treatment.J Clin Med. 2020 Jan 18;9(1):261. doi: 10.3390/jcm9010261. J Clin Med. 2020. PMID: 31963681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Displacing hexokinase from mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel impairs GLT-1-mediated glutamate uptake but does not disrupt interactions between GLT-1 and mitochondrial proteins.J Neurosci Res. 2015 Jul;93(7):999-1008. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23533. Epub 2014 Dec 26. J Neurosci Res. 2015. PMID: 25546576 Free PMC article.
-
A subset of synaptic transmission events is coupled to acetyl coenzyme A production.J Neurophysiol. 2022 Mar 1;127(3):623-636. doi: 10.1152/jn.00200.2021. Epub 2022 Jan 26. J Neurophysiol. 2022. PMID: 35080429 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporin 4 Forms a Macromolecular Complex with Glutamate Transporter 1 and Mu Opioid Receptor in Astrocytes and Participates in Morphine Dependence.J Mol Neurosci. 2017 May;62(1):17-27. doi: 10.1007/s12031-017-0905-1. Epub 2017 Mar 24. J Mol Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28341892
References
-
- Kirischuk S, Parpura V, Verkhratsky A (2012) Sodium dynamics: another key to astroglial excitability? Trends Neurosci 35: 497–506. - PubMed
-
- Tanaka K (2000) Functions of glutamate transporters in the brain. Neurosci Res 37: 15–19. - PubMed
-
- Rothstein JD, Dykes-Hoberg M, Pardo CA, Bristol LA, Jin L, et al. (1996) Knockout of glutamate transporters reveals a major role for astroglial transport in excitotoxicity and clearance of glutamate. Neuron 16: 675–686. - PubMed
-
- Turner RJ, Moran A (1982) Further studies of proximal tubular brush border membrane D-glucose transport heterogeneity. J Membr Biol 70: 37–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

