Inhibition of infection-mediated preterm birth by administration of broad spectrum chemokine inhibitor in mice
- PMID: 24894878
- PMCID: PMC4196657
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.12307
Inhibition of infection-mediated preterm birth by administration of broad spectrum chemokine inhibitor in mice
Abstract
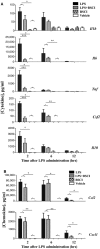
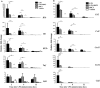
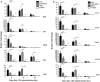
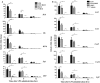
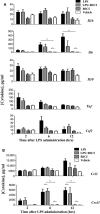
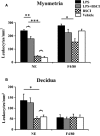
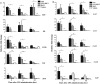
Preterm birth (PTB) is the single most important cause of perinatal and infant mortality worldwide. Maternal infection can result in PTB. We investigated the ability of a Broad Spectrum Chemokine Inhibitor (BSCI) to prevent infection-induced PTB in mice. PTB was initiated in pregnant mice by intraperitoneal injection of lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 50 μg). Half the mice received BSCI (10 mg/kg) 24 hrs prior to and immediately before LPS administration. The impact of LPS alone or LPS plus BSCI was assessed on (i) injection-to-delivery interval, foetal survival rate, placental and neonates' weight; (ii) amniotic fluid and maternal plasma cytokine levels (by Luminex assay); foetal and maternal tissue cytokine gene expression levels (by Real-Time RT-PCR); (iii) immune cells infiltration into the uterine tissue (by stereological immunohistochemistry). Pre-treatment with BSCI (i) decreased LPS-induced PTB (64% versus 100%, P < 0.05); (ii) significantly attenuated cytokine/chemokine expression in maternal tissues (plasma, liver, myometrium, decidua); (iii) significantly decreased neutrophil infiltration in the mouse myometrium. BSCI-treated mice in which PTB was delayed till term had live foetuses with normal placental and foetal weight. BSCI represents a promising new class of therapeutics for PTB. In a mouse model of preterm labour, BCSI suppresses systemic inflammation in maternal tissues which resulted in the reduced incidence of LPS-mediated PTB. These data provide support for efforts to target inflammatory responses as a means of preventing PTB.
Keywords: chemokine inhibitor; infection; leucocyte infiltration; preterm labour; uterus.
© 2014 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd and Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Broad-Spectrum Chemokine Inhibitor Blocks Inflammation-Induced Myometrial Myocyte-Macrophage Crosstalk and Myometrial Contraction.Cells. 2021 Dec 31;11(1):128. doi: 10.3390/cells11010128. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011690 Free PMC article.
-
The Local and Systemic Immune Response to Intrauterine LPS in the Prepartum Mouse.Biol Reprod. 2016 Dec;95(6):125. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.116.143289. Epub 2016 Oct 19. Biol Reprod. 2016. PMID: 27760748 Free PMC article.
-
Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GR-1 supernatant prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced preterm birth and reduces inflammation in pregnant CD-1 mice.Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014 Jul;211(1):44.e1-44.e12. doi: 10.1016/j.ajog.2014.01.029. Epub 2014 Jan 31. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2014. PMID: 24486224
-
Investigating the Et-1/SphK/S1P Pathway as a Novel Approach for the Prevention of Inflammation-Induced Preterm Birth.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(9):983-988. doi: 10.2174/1381612824666180130122739. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 29384055 Review.
-
Preterm birth: Inflammation, fetal injury and treatment strategies.J Reprod Immunol. 2017 Feb;119:62-66. doi: 10.1016/j.jri.2016.11.008. Epub 2016 Dec 2. J Reprod Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28122664 Review.
Cited by
-
Prevention of lipopolysaccharide-induced preterm labor by the lack of CX3CL1-CX3CR1 interaction in mice.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 6;13(11):e0207085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207085. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30399192 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes Cause Preterm Birth in Mice: Evidence for Paracrine Signaling in Pregnancy.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 24;9(1):608. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37002-x. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30679631 Free PMC article.
-
A Broad Spectrum Chemokine Inhibitor Prevents Preterm Labor but Not Microbial Invasion of the Amniotic Cavity or Neonatal Morbidity in a Non-human Primate Model.Front Immunol. 2020 Apr 30;11:770. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00770. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32425945 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-Free Fetal DNA Increases Prior to Labor at Term and in a Subset of Preterm Births.Reprod Sci. 2020 Jan;27(1):218-232. doi: 10.1007/s43032-019-00023-6. Epub 2020 Jan 1. Reprod Sci. 2020. PMID: 32046392 Free PMC article.
-
Preterm Birth Therapies to Target Inflammation.J Clin Pharmacol. 2022 Sep;62 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S79-S93. doi: 10.1002/jcph.2107. J Clin Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36106783 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lawn JE, Cousens S, Zupan J. 4 million neonatal deaths: when? Where? Why? Lancet. 2005;365:891–900. - PubMed
-
- Howson CP. Born too soon: global action report on preterm birth. Geneva: WHO; 2012.
-
- Too early, too small: a profile of small babies across Canada. Ottawa: Canadian Institute for Health Information; 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

