Chemokines profiling of patients with preterm birth
- PMID: 24876667
- PMCID: PMC4020160
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/185758
Chemokines profiling of patients with preterm birth
Abstract
Introduction: Nowadays it is thought that the main cause of premature birth is subclinical infection. However, none of the currently used methods provide effective prevention to preterm labor. The aim of the study was to determine the concentration of selected chemokines in sera of patients with premature birth without clinical signs of infection (n = 62), threatened preterm labor (n = 47), and term births (n = 28).
Method: To assess the concentration of chemokines in the blood serum, we used a multiplex method, which allows the simultaneous determination of 40 chemokines per sample. The sets consist of the following chemokines: 6Ckine/CCL21, Axl, BTC, CCL28, CTACK/CCL27, CXCL16, ENA-78/CXCL5, Eotaxin-3/CCL26, GCP-2/CXC, GRO (GRO α /CXCL1, GRO β /CXCL2 and GRO γ /CXCL3), HCC-1/CCL14, HCC-4/CCL16, IL-9, IL-17F, IL18-BPa, IL-28A, IL-29, IL-31, IP-10/CXCL10, I-TAC/CXCL11, LIF, LIGHT/TNFSF14, Lymphotactin/XCL1, MCP-2/CCL8, MCP-3/CCL7, MCP-4/CCL13, MDC/CCL22, MIF, MIP-3 α /CCL20, MIP-3- β /CCL19, MPIF-1/CCL23, NAP-2/CXCL7, MSP α , OPN, PARC/CCL18, PF4, SDF-1/CXCL12, TARC/CCL17, TECK/CCL25, and TSLP.
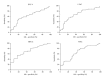
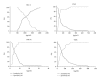
Results: We showed possible implication of 4 chemokines, that is, HCC-4, I-TAC, MIP-3 α , and TARC in women with symptoms of preterm delivery.
Conclusion: On the basis of our findings, it seems that the chemokines may play role in the pathogenesis of preterm labor. Defining their potential as biochemical markers of preterm birth requires further investigation on larger group of patients.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decreased serum level of macrophage inflammatory chemokine-3beta/CCL19 in preterm labor and delivery.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2006 Jan 1;124(1):23-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2005.05.006. Epub 2005 Jul 14. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2006. PMID: 16023779
-
Characteristics of serum chemokine profile in primary biliary cholangitis.Cytokine. 2020 Dec;136:155291. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2020.155291. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 32956949 Clinical Trial.
-
Altered profile of chemokines in fibromyalgia patients.Ann Clin Biochem. 2014 Sep;51(Pt 5):576-81. doi: 10.1177/0004563213506413. Epub 2013 Oct 8. Ann Clin Biochem. 2014. PMID: 24106344
-
CC Chemokines in a Tumor: A Review of Pro-Cancer and Anti-Cancer Properties of the Ligands of Receptors CCR1, CCR2, CCR3, and CCR4.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 9;21(21):8412. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218412. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33182504 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effects of CC, CXC, C, and CX3C chemokines on proliferation of myeloid progenitor cells, and insights into SDF-1-induced chemotaxis of progenitors.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999 Apr 30;872:142-62; discussion 163. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1999.tb08460.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1999. PMID: 10372118 Review.
Cited by
-
Human Placental Syncytiotrophoblasts Restrict Toxoplasma gondii Attachment and Replication and Respond to Infection by Producing Immunomodulatory Chemokines.mBio. 2018 Jan 9;9(1):e01678-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01678-17. mBio. 2018. PMID: 29317509 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine quantification and association with cervical length in a prospective cohort of pregnant women.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Jun 20;23(1):458. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-05776-2. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023. PMID: 37340384 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and Function of Chemokines at the Maternal-Fetal Interface.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jul 22;10:826053. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.826053. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35938162 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prediction of spontaneous preterm birth using CCL2 and CXCL10 in maternal serum of symptomatic high-risk pregnant women: a prospective cohort study.BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023 Sep 28;23(1):697. doi: 10.1186/s12884-023-06016-3. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2023. PMID: 37770883 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokines in Preterm Delivery: Proposal of a New Diagnostic Algorithm.J Immunol Res. 2018 Apr 8;2018:8073476. doi: 10.1155/2018/8073476. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 29850638 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Slattery MM, Morrison JJ. Preterm delivery. The Lancet. 2002;360(9344):1489–1497. - PubMed
-
- Lucovnik M, Chambliss LR, Garfield RE. Costs of unnecessary admissions and treatments for ‘threatened preterm labor’. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 2013;209(3):217.e1–217.e3. - PubMed
-
- Menon R, Williams SM, Fortunato SJ. Amniotic fluid interleukin-1β and interleukin-8 concentrations: racial disparity in preterm birth. Reproductive Sciences. 2007;14(3):253–259. - PubMed
-
- Laudanski P, Raba G, Kuc P, Lemancewicz A, Kisielewski R, Laudanski T. Assessment of the selected biochemical markers in predicting preterm labour. Journal of Maternal-Fetal and Neonatal Medicine. 2012;25(12):2696–2699. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous