Unambiguous identification of miRNA:target site interactions by different types of ligation reactions
- PMID: 24857550
- PMCID: PMC4181535
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2014.03.049
Unambiguous identification of miRNA:target site interactions by different types of ligation reactions
Abstract
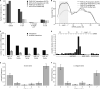
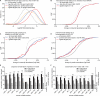
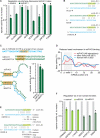
To exert regulatory function, miRNAs guide Argonaute (AGO) proteins to partially complementary sites on target RNAs. Crosslinking and immunoprecipitation (CLIP) assays are state-of-the-art to map AGO binding sites, but assigning the targeting miRNA to these sites relies on bioinformatics predictions and is therefore indirect. To directly and unambiguously identify miRNA:target site interactions, we modified our CLIP methodology in C. elegans to experimentally ligate miRNAs to their target sites. Unexpectedly, ligation reactions also occurred in the absence of the exogenous ligase. Our in vivo data set and reanalysis of published mammalian AGO-CLIP data for miRNA-chimeras yielded ∼17,000 miRNA:target site interactions. Analysis of interactions and extensive experimental validation of chimera-discovered targets of viral miRNAs suggest that our strategy identifies canonical, noncanonical, and nonconserved miRNA:targets. About 80% of miRNA interactions have perfect or partial seed complementarity. In summary, analysis of miRNA:target chimeras enables the systematic, context-specific, in vivo discovery of miRNA binding.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

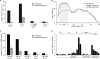
Similar articles
-
miRNA-target chimeras reveal miRNA 3'-end pairing as a major determinant of Argonaute target specificity.Nat Commun. 2015 Nov 25;6:8864. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9864. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26602609 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miRNA-Target RNA Interactions Using CLASH.Methods Mol Biol. 2016;1358:229-51. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-3067-8_14. Methods Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26463387
-
Pairing beyond the Seed Supports MicroRNA Targeting Specificity.Mol Cell. 2016 Oct 20;64(2):320-333. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Oct 6. Mol Cell. 2016. PMID: 27720646 Free PMC article.
-
A tale of two sequences: microRNA-target chimeric reads.Genet Sel Evol. 2016 Apr 4;48:31. doi: 10.1186/s12711-016-0209-x. Genet Sel Evol. 2016. PMID: 27044644 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Seq and CLIP through the miRNA world.Genome Biol. 2014 Jan 25;15(1):202. doi: 10.1186/gb4151. Genome Biol. 2014. PMID: 24460822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Expression, not sequence, distinguishes miR-238 from its miR-239ab sister miRNAs in promoting longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans.PLoS Genet. 2023 Nov 27;19(11):e1011055. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1011055. eCollection 2023 Nov. PLoS Genet. 2023. PMID: 38011256 Free PMC article.
-
Computational Analysis Tutorial for Chimeric Small Noncoding RNA: Target RNA Sequencing Libraries.J Vis Exp. 2023 Dec 1;(202):10.3791/65779. doi: 10.3791/65779. J Vis Exp. 2023. PMID: 38108375 Free PMC article.
-
The biochemical basis of microRNA targeting efficacy.Science. 2019 Dec 20;366(6472):eaav1741. doi: 10.1126/science.aav1741. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Science. 2019. PMID: 31806698 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of proteins and miRNAs that specifically bind an mRNA in vivo.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 16;10(1):4205. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-12050-7. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31527589 Free PMC article.
-
Integration of Bioinformatic Predictions and Experimental Data to Identify circRNA-miRNA Associations.Genes (Basel). 2019 Aug 24;10(9):642. doi: 10.3390/genes10090642. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31450634 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bagga S, Bracht J, Hunter S, Massirer K, Holtz J, Eachus R, Pasquinelli AE. Regulation by let-7 and lin-4 miRNAs results in target mRNA degradation. Cell. 2005;122:553–563. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
