An RNF168 fragment defective for focal accumulation at DNA damage is proficient for inhibition of homologous recombination in BRCA1 deficient cells
- PMID: 24829461
- PMCID: PMC4081061
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku421
An RNF168 fragment defective for focal accumulation at DNA damage is proficient for inhibition of homologous recombination in BRCA1 deficient cells
Abstract
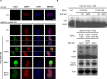
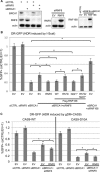
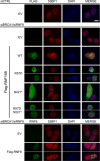
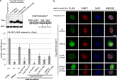
The E3 ubiquitin ligase RNF168 is a DNA damage response (DDR) factor that promotes monoubiquitination of H2A/H2AX at K13/15, facilitates recruitment of other DDR factors (e.g. 53BP1) to DNA damage, and inhibits homologous recombination (HR) in cells deficient in the tumor suppressor BRCA1. We have examined the domains of RNF168 important for these DDR events, including chromosomal HR that is induced by several nucleases (I-SceI, CAS9-WT and CAS9-D10A), since the inducing nuclease affects the relative frequency of distinct repair outcomes. We found that an N-terminal fragment of RNF168 (1-220/N221*) efficiently inhibits HR induced by each of these nucleases in BRCA1 depleted cells, and promotes recruitment of 53BP1 to DNA damage and H2AX monoubiquitination at K13/15. Each of these DDR events requires a charged residue in RNF168 (R57). Notably, RNF168-N221* fails to self-accumulate into ionizing radiation induced foci (IRIF). Furthermore, expression of RNF168 WT and N221* can significantly bypass the role of another E3 ubiquitin ligase, RNF8, for inhibition of HR in BRCA1 depleted cells, and for promotion of 53BP1 IRIF. We suggest that the ability for RNF168 to promote H2A/H2AX monoubiquitination and 53BP1 IRIF, but not RNF168 self-accumulation into IRIF, is important for inhibition of HR in BRCA1 deficient cells.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures


Similar articles
-
USP7 deubiquitinase promotes ubiquitin-dependent DNA damage signaling by stabilizing RNF168.Cell Cycle. 2015;14(9):1413-25. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1007785. Cell Cycle. 2015. PMID: 25894431 Free PMC article.
-
USP14 regulates DNA damage repair by targeting RNF168-dependent ubiquitination.Autophagy. 2018;14(11):1976-1990. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1496877. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Autophagy. 2018. PMID: 29995557 Free PMC article.
-
RNF168 ubiquitinates K13-15 on H2A/H2AX to drive DNA damage signaling.Cell. 2012 Sep 14;150(6):1182-95. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2012.08.005. Cell. 2012. PMID: 22980979
-
RNF8-dependent histone ubiquitination during DNA damage response and spermatogenesis.Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011 May;43(5):339-45. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmr016. Epub 2011 Mar 28. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 2011. PMID: 21444325 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Opposing roles of RNF8/RNF168 and deubiquitinating enzymes in ubiquitination-dependent DNA double-strand break response signaling and DNA-repair pathway choice.J Radiat Res. 2016 Aug;57 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):i33-i40. doi: 10.1093/jrr/rrw027. Epub 2016 Mar 16. J Radiat Res. 2016. PMID: 26983989 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Salient Features of Endonuclease Platforms for Therapeutic Genome Editing.Mol Ther. 2016 Mar;24(3):422-9. doi: 10.1038/mt.2016.21. Epub 2016 Jan 22. Mol Ther. 2016. PMID: 26796671 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ectopic expression of RNF168 and 53BP1 increases mutagenic but not physiological non-homologous end joining.Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 May 26;43(10):4950-61. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv336. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015. PMID: 25916843 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H2A variants alpha1-extension helix directs RNF168-mediated ubiquitination.Nat Commun. 2020 May 18;11(1):2462. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-16307-4. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32424115 Free PMC article.
-
Writers, Readers, and Erasers of Histone Ubiquitylation in DNA Double-Strand Break Repair.Front Genet. 2016 Jun 28;7:122. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2016.00122. eCollection 2016. Front Genet. 2016. PMID: 27446204 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To indel or not to indel: Factors influencing mutagenesis during chromosomal break end joining.DNA Repair (Amst). 2022 Oct;118:103380. doi: 10.1016/j.dnarep.2022.103380. Epub 2022 Jul 30. DNA Repair (Amst). 2022. PMID: 35926296 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Doil C., Mailand N., Bekker-Jensen S., Menard P., Larsen D.H., Pepperkok R., Ellenberg J., Panier S., Durocher D., Bartek J., et al. RNF168 binds and amplifies ubiquitin conjugates on damaged chromosomes to allow accumulation of repair proteins. Cell. 2009;136:435–446. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

