Fas-associated factor (Faf1) is a novel CD40 interactor that regulates CD40-induced NF-κB activation via a negative feedback loop
- PMID: 24810049
- PMCID: PMC4047894
- DOI: 10.1038/cddis.2014.172
Fas-associated factor (Faf1) is a novel CD40 interactor that regulates CD40-induced NF-κB activation via a negative feedback loop
Abstract
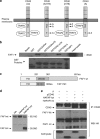
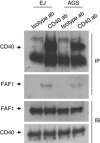
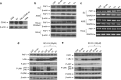
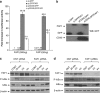
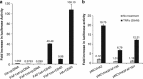
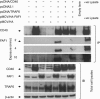
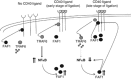
CD40-induced signalling through ligation with its natural ligand (CD40L/CD154) is dependent on recruitment of TRAF molecules to the cytoplasmic domain of the receptor. Here, we applied the yeast two-hybrid system to examine whether other proteins can interact with CD40. Fas-Associated Factor 1(FAF1) was isolated from a HeLa cDNA library using the CD40 cytoplasmic tail (216-278 aa) as a bait construct. FAF1 was able to interact with CD40 both in vitro and in vivo. The FAF1 N-terminal domain was sufficient to bind CD40 and required the TRAF6-binding domain within the cytoplasmic tail of CD40 for binding. CD40 ligation induced FAF1 expression in an NFκB-dependent manner. Knockdown of FAF1 prolonged CD40-induced NFκB, whereas overexpression of FAF1 suppressed CD40-induced NFκB activity and this required interaction of FAF1 with the CD40 receptor via its FID domain. Thus, we report a novel role for FAF1in regulating CD40-induced NFκB activation via a negative feedback loop. Loss of FAF1 function in certain human malignancies may contribute to oncogenesis through unchecked NFκB activation, and further understanding of this process may provide a biomarker of NFκB-targeted therapies for such malignancies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Fas-associated factor-1 inhibits nuclear factor-kappaB (NF-kappaB) activity by interfering with nuclear translocation of the RelA (p65) subunit of NF-kappaB.J Biol Chem. 2004 Jan 23;279(4):2544-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M304565200. Epub 2003 Nov 4. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 14600157
-
Identification of TRAF6, a novel tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor protein that mediates signaling from an amino-terminal domain of the CD40 cytoplasmic region.J Biol Chem. 1996 Nov 15;271(46):28745-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.46.28745. J Biol Chem. 1996. PMID: 8910514
-
p62 regulates CD40-mediated NFκB activation in macrophages through interaction with TRAF6.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015 Aug 14;464(1):330-5. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.06.153. Epub 2015 Jun 29. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015. PMID: 26133577
-
Roles of TRAF6 in CD40 signaling.Immunol Res. 2007;39(1-3):105-14. doi: 10.1007/s12026-007-0082-3. Immunol Res. 2007. PMID: 17917059 Review.
-
FAS-associated factor 1 (FAF1): diverse functions and implications for oncogenesis.Cell Cycle. 2009 Aug 15;8(16):2528-34. doi: 10.4161/cc.8.16.9280. Epub 2009 Aug 16. Cell Cycle. 2009. PMID: 19597341 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
ROS and ROS-Mediated Cellular Signaling.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016;2016:4350965. doi: 10.1155/2016/4350965. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2016. PMID: 26998193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel function of FAF1, which induces dopaminergic neuronal death through cell-to-cell transmission.Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Aug 24;18(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12964-020-00632-8. Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 32831099 Free PMC article.
-
C18H17NO6 and Its Combination with Scutellarin Suppress the Proliferation and Induce the Apoptosis of Human Glioma Cells via Upregulation of Fas-Associated Factor 1 Expression.Biomed Res Int. 2019 Feb 20;2019:6821219. doi: 10.1155/2019/6821219. eCollection 2019. Biomed Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30915356 Free PMC article.
-
The Human Papillomavirus (HPV) E6 Oncoprotein Regulates CD40 Expression via the AT-Hook Transcription Factor AKNA.Cancers (Basel). 2018 Dec 17;10(12):521. doi: 10.3390/cancers10120521. Cancers (Basel). 2018. PMID: 30562965 Free PMC article.
-
Reactive oxygen species in biological systems: Pathways, associated diseases, and potential inhibitors-A review.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Dec 1;12(2):675-693. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3784. eCollection 2024 Feb. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38370049 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- van Kooten C, Banchereau J. CD40-CD40 ligand. J Leukoc Biol. 2000;67:2–17. - PubMed
-
- Eliopoulos AG, Young LS. The role of the CD40 pathway in the pathogenesis and treatment of cancer. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2004;4:360–367. - PubMed
-
- Planken EV, Dijkstra NH, Willemze R, Kluin-Nelemans JC. Proliferation of B cell malignancies in all stages of differentiation upon stimulation in the CD40 system. Leukemia. 1996;10:488–493. - PubMed
-
- Funakoshi S, Longo DL, Beckwith M, Conley DK, Tsarfaty G, Tsarfaty I, et al. Inhibition of human B-cell lymphoma growth by CD40 stimulation. Blood. 1994;83:2787–2794. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

