Interleukin-18 as a therapeutic target in acute myocardial infarction and heart failure
- PMID: 24804827
- PMCID: PMC4069269
- DOI: 10.2119/molmed.2014.00034
Interleukin-18 as a therapeutic target in acute myocardial infarction and heart failure
Abstract
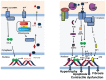
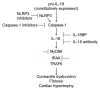
Interleukin 18 (IL-18) is a proinflammatory cytokine in the IL-1 family that has been implicated in a number of disease states. In animal models of acute myocardial infarction (AMI), pressure overload, and LPS-induced dysfunction, IL-18 regulates cardiomyocyte hypertrophy and induces cardiac contractile dysfunction and extracellular matrix remodeling. In patients, high IL-18 levels correlate with increased risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD) and with a worse prognosis in patients with established CVD. Two strategies have been used to counter the effects of IL-18:IL-18 binding protein (IL-18BP), a naturally occurring protein, and a neutralizing IL-18 antibody. Recombinant human IL-18BP (r-hIL-18BP) has been investigated in animal studies and in phase I/II clinical trials for psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis. A phase II clinical trial using a humanized monoclonal IL-18 antibody for type 2 diabetes is ongoing. Here we review the literature regarding the role of IL-18 in AMI and heart failure and the evidence and challenges of using IL-18BP and blocking IL-18 antibodies as a therapeutic strategy in patients with heart disease.
Figures

Similar articles
-
β2 adrenergic activation induces the expression of IL-18 binding protein, a potent inhibitor of isoproterenol induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy in vitro and myocardial hypertrophy in vivo.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012 Jan;52(1):206-18. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2011.09.022. Epub 2011 Oct 8. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2012. PMID: 22004899 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis for antagonism of human interleukin 18 by poxvirus interleukin 18-binding protein.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008 Dec 30;105(52):20711-5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809086106. Epub 2008 Dec 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008. PMID: 19104048 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-18, more than a Th1 cytokine.Semin Immunol. 2013 Dec 15;25(6):439-48. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2013.10.014. Epub 2013 Nov 22. Semin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 24275602 Review.
-
IL-18-binding protein protects against lipopolysaccharide- induced lethality and prevents the development of Fas/Fas ligand-mediated models of liver disease in mice.J Immunol. 2001 Nov 15;167(10):5913-20. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.167.10.5913. J Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11698468
-
Interleukin-1 blockade in cardiovascular diseases: a clinical update.Eur Heart J. 2018 Jun 7;39(22):2063-2069. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy128. Eur Heart J. 2018. PMID: 29584915 Review.
Cited by
-
Acute exposure to LPS induces cardiac dysfunction via the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome.Sci Rep. 2024 Oct 17;14(1):24378. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-76066-w. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39420211 Free PMC article.
-
The inflammasome in heart failure.Curr Opin Physiol. 2021 Feb;19:105-112. doi: 10.1016/j.cophys.2020.09.013. Epub 2020 Oct 7. Curr Opin Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34917871 Free PMC article.
-
No association between interleukin-18 levels and risk of cardiovascular disease: A Mendelian randomization study.Hereditas. 2020 Apr 7;157(1):12. doi: 10.1186/s41065-020-00121-5. Hereditas. 2020. PMID: 32264954 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin‑18 binding protein: Biological properties and roles in human and animal immune regulation (Review).Biomed Rep. 2024 Apr 9;20(6):87. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1775. eCollection 2024 Jun. Biomed Rep. 2024. PMID: 38665423 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory Cytokines as Risk Factors for Mortality After Acute Cardiac Events.Med Arch. 2016 Jul 27;70(4):252-255. doi: 10.5455/medarh.2016.70.252-255. Med Arch. 2016. PMID: 27703283 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seropian IM, Toldo S, Van Tassell BW, Abbate A. Anti-inflammatory strategies for ventricular remodeling following ST-segment elevation acute myocardial infarction. J Amer Coll Cardiol. 2014;63:1593–603. - PubMed
-
- Gullestad L, et al. Inflammatory cytokines in heart failure: mediators and markers. Cardiology. 2012;122:23–35. - PubMed
-
- Kalogeropoulos AP, Georgiopoulou VV, Butler J. From risk factors to structural heart disease: the role of inflammation. Heart Fail Clin. 2012;8:113–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

