The histone lysine demethylase JMJD3/KDM6B is recruited to p53 bound promoters and enhancer elements in a p53 dependent manner
- PMID: 24797517
- PMCID: PMC4010471
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0096545
The histone lysine demethylase JMJD3/KDM6B is recruited to p53 bound promoters and enhancer elements in a p53 dependent manner
Abstract
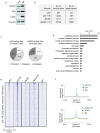
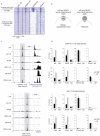
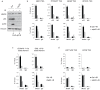
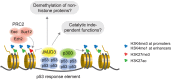
The JmjC domain-containing protein JMJD3/KDM6B catalyses the demethylation of H3K27me3 and H3K27me2. JMJD3 appears to be highly regulated at the transcriptional level and is upregulated in response to diverse stimuli such as differentiation inducers and stress signals. Accordingly, JMJD3 has been linked to the regulation of different biological processes such as differentiation of embryonic stem cells, inflammatory responses in macrophages, and induction of cellular senescence via regulation of the INK4A-ARF locus. Here we show here that JMJD3 interacts with the tumour suppressor protein p53. We find that the interaction is dependent on the p53 tetramerization domain. Following DNA damage, JMJD3 is transcriptionally upregulated and by performing genome-wide mapping of JMJD3, we demonstrate that it binds genes involved in basic cellular processes, as well as genes regulating cell cycle, response to stress and apoptosis. Moreover, we find that JMJD3 binding sites show significant overlap with p53 bound promoters and enhancer elements. The binding of JMJD3 to p53 target sites is increased in response to DNA damage, and we demonstrate that the recruitment of JMJD3 to these sites is dependent on p53 expression. Therefore, we propose a model in which JMJD3 is recruited to p53 responsive elements via its interaction with p53 and speculate that JMJD3 could act as a fail-safe mechanism to remove low levels of H3K27me3 and H3K27me2 to allow for efficient acetylation of H3K27.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


Similar articles
-
p53 interaction with JMJD3 results in its nuclear distribution during mouse neural stem cell differentiation.PLoS One. 2011 Mar 31;6(3):e18421. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0018421. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21483786 Free PMC article.
-
Histone demethylase Jumonji D3 (JMJD3/KDM6B) at the nexus of epigenetic regulation of inflammation and the aging process.J Mol Med (Berl). 2014 Oct;92(10):1035-43. doi: 10.1007/s00109-014-1182-x. Epub 2014 Jun 14. J Mol Med (Berl). 2014. PMID: 24925089 Review.
-
The histone H3 Lys 27 demethylase JMJD3 regulates gene expression by impacting transcriptional elongation.Genes Dev. 2012 Jun 15;26(12):1364-75. doi: 10.1101/gad.186056.111. Genes Dev. 2012. PMID: 22713873 Free PMC article.
-
The localization of histone H3K27me3 demethylase Jmjd3 is dynamically regulated.Epigenetics. 2014 Jun;9(6):834-41. doi: 10.4161/epi.28524. Epub 2014 Mar 19. Epigenetics. 2014. PMID: 24646476 Free PMC article.
-
JMJD3 as an epigenetic regulator in development and disease.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;67:148-57. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26193001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dopamine Transporter Knockout Rats Display Epigenetic Alterations in Response to Cocaine Exposure.Biomolecules. 2023 Jul 12;13(7):1107. doi: 10.3390/biom13071107. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509143 Free PMC article.
-
Context-Dependent Functions of KDM6 Lysine Demethylases in Physiology and Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1433:139-165. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-38176-8_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 37751139
-
JMJD3 suppresses stem cell-like characteristics in breast cancer cells by downregulation of Oct4 independently of its demethylase activity.Oncotarget. 2017 Mar 28;8(13):21918-21929. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15747. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28423536 Free PMC article.
-
Adaptive Chromatin Remodeling Drives Glioblastoma Stem Cell Plasticity and Drug Tolerance.Cell Stem Cell. 2017 Feb 2;20(2):233-246.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2016.11.003. Epub 2016 Dec 15. Cell Stem Cell. 2017. PMID: 27989769 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer Stem Cell-Inducing Media Activates Senescence Reprogramming in Fibroblasts.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 30;12(7):1745. doi: 10.3390/cancers12071745. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32629974 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boyer LA, Plath K, Zeitlinger J, Brambrink T, Medeiros LA, et al. (2006) Polycomb complexes repress developmental regulators in murine embryonic stem cells. Nature 441: 349–353. - PubMed
-
- Schwartz YB, Kahn TG, Nix DA, Li XY, Bourgon R, et al. (2006) Genome-wide analysis of Polycomb targets in Drosophila melanogaster. Nat Genet 38: 700–705. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

