Effects of lowering LDL cholesterol on progression of kidney disease
- PMID: 24790178
- PMCID: PMC4116066
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013090965
Effects of lowering LDL cholesterol on progression of kidney disease
Abstract
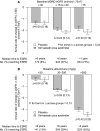
Lowering LDL cholesterol reduces the risk of developing atherosclerotic events in CKD, but the effects of such treatment on progression of kidney disease remain uncertain. Here, 6245 participants with CKD (not on dialysis) were randomly assigned to simvastatin (20 mg) plus ezetimibe (10 mg) daily or matching placebo. The main prespecified renal outcome was ESRD (defined as the initiation of maintenance dialysis or kidney transplantation). During 4.8 years of follow-up, allocation to simvastatin plus ezetimibe resulted in an average LDL cholesterol difference (SEM) of 0.96 (0.02) mmol/L compared with placebo. There was a nonsignificant 3% reduction in the incidence of ESRD (1057 [33.9%] cases with simvastatin plus ezetimibe versus 1084 [34.6%] cases with placebo; rate ratio, 0.97; 95% confidence interval [95% CI], 0.89 to 1.05; P=0.41). Similarly, allocation to simvastatin plus ezetimibe had no significant effect on the prespecified tertiary outcomes of ESRD or death (1477 [47.4%] events with treatment versus 1513 [48.3%] events with placebo; rate ratio, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.90 to 1.04; P=0.34) or ESRD or doubling of baseline creatinine (1189 [38.2%] events with treatment versus 1257 [40.2%] events with placebo; rate ratio, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.86 to 1.01; P=0.09). Exploratory analyses also showed no significant effect on the rate of change in eGFR. Lowering LDL cholesterol by 1 mmol/L did not slow kidney disease progression within 5 years in a wide range of patients with CKD.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Study of Heart and Renal Protection (SHARP): randomized trial to assess the effects of lowering low-density lipoprotein cholesterol among 9,438 patients with chronic kidney disease.Am Heart J. 2010 Nov;160(5):785-794.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.ahj.2010.08.012. Epub 2010 Sep 18. Am Heart J. 2010. PMID: 21095263 Clinical Trial.
-
The effects of lowering LDL cholesterol with simvastatin plus ezetimibe in patients with chronic kidney disease (Study of Heart and Renal Protection): a randomised placebo-controlled trial.Lancet. 2011 Jun 25;377(9784):2181-92. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60739-3. Epub 2011 Jun 12. Lancet. 2011. PMID: 21663949 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The effect of lowering LDL cholesterol on vascular access patency: post hoc analysis of the Study of Heart and Renal Protection.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 May;9(5):914-9. doi: 10.2215/CJN.10371013. Epub 2014 Mar 13. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24626433 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Reaching goal in hypercholesterolaemia: dual inhibition of cholesterol synthesis and absorption with simvastatin plus ezetimibe.Curr Med Res Opin. 2006 Mar;22(3):511-28. doi: 10.1185/030079906X89856. Curr Med Res Opin. 2006. PMID: 16574035 Review.
-
Ezetimibe as a potential treatment for dyslipidemia associated with chronic renal failure and renal transplant.Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2010 Nov;21(6):1021-9. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2010. PMID: 21060168 Review.
Cited by
-
HMG CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) for people with chronic kidney disease not requiring dialysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Nov 29;11(11):CD007784. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD007784.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 38018702 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic kidney disease: Statins in chronic kidney disease: time to move on?Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015 May;11(5):262-3. doi: 10.1038/nrneph.2015.36. Epub 2015 Mar 24. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2015. PMID: 25802077
-
Impact of outcome adjudication in kidney disease trials: observations from the Study of Heart and Renal Protection (SHARP).Kidney Int Rep. 2023 Aug;8(8):1489-1495. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2023.05.008. Kidney Int Rep. 2023. PMID: 37538810 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of dyslipidemia on estimated glomerular filtration rate in apparently healthy children and adolescents: the CASPIAN-V study.World J Pediatr. 2019 Oct;15(5):471-475. doi: 10.1007/s12519-019-00270-2. Epub 2019 Jun 25. World J Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 31240635
-
Effect on non-vascular outcomes of lowering LDL cholesterol in patients with chronic kidney disease: results from the Study of Heart and Renal Protection.BMC Nephrol. 2017 May 1;18(1):147. doi: 10.1186/s12882-017-0545-2. BMC Nephrol. 2017. PMID: 28460629 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Levey AS, Coresh J: Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 379: 165–180, 2012 - PubMed
-
- Foley RN, Parfrey PS, Sarnak MJ: Clinical epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in chronic renal disease. Am J Kidney Dis 32[Suppl 3]: S112–S119, 1998 - PubMed
-
- Evans RW, Manninen DL, Garrison LP, Jr., Hart LG, Blagg CR, Gutman RA, Hull AR, Lowrie EG: The quality of life of patients with end-stage renal disease. N Engl J Med 312: 553–559, 1985 - PubMed
-
- US Renal Data System: 2010 Annual Data Report: Atlas of Chronic Kidney Disease. Costs of End-Stage Renal Disease, 2010. Available at: http://www.usrds.org/2010/pdf/v2_11.pdf Accessed June 18, 2013
-
- Jafar TH, Schmid CH, Landa M, Giatras I, Toto R, Remuzzi G, Maschio G, Brenner BM, Kamper A, Zucchelli P, Becker G, Himmelmann A, Bannister K, Landais P, Shahinfar S, de Jong PE, de Zeeuw D, Lau J, Levey AS: Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and progression of nondiabetic renal disease. A meta-analysis of patient-level data. Ann Intern Med 135: 73–87, 2001 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

