Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycle of HP1α governs accurate mitotic progression
- PMID: 24786771
- PMCID: PMC4111712
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.29065
Phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycle of HP1α governs accurate mitotic progression
Abstract
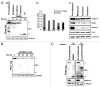
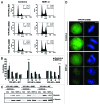
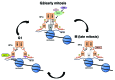
Heterochromatin protein 1α (HP1α), a bona fide factor of silent chromatin, is required for establishing as well as maintaining the higher-order chromatin structure in eukaryotes. HP1α is decorated with several post-translational modifications, and many of these are critical for its cellular functions. HP1α is heavily phosphorylated; however, its physiological relevance had remained to be completely understood. We have recently demonstrated that human HP1α is a mitotic target for NDR kinase, and the phosphorylation at the hinge region of HP1α at the G 2/M phase of the cell cycle is crucial for mitotic progression and Sgo1 loading at mitotic centromeres (Chakraborty et al., 2014). We now demonstrate that the dephosphorylation of HP1α within its hinge domain occurs during mitosis, specifically soon after prometaphase. In the absence of the hinge-specific HP1α phosphorylation, either as a consequence of depleting NDR1 or in cells expressing a non-phosphorylatable HP1α mutant, the cells arrest in prometaphase with several mitotic defects. In this study we show that NDR1-depleted cells expressing hinge-specific phosphomimetic HP1α mutant rescues the prometaphase arrest but displays defects in mitotic exit, suggesting that the dephosphorylation of HP1α is required for the completion of cytokinesis. Taken together, our results reveal that the phosphorylation-dephosphorylation cycle of HP1α orchestrates accurate progression of cells through mitosis.
Keywords: HP1α; NDR kinases; cell cycle; dephosphorylation; mitosis; phosphorylation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dynamic phosphorylation of HP1α regulates mitotic progression in human cells.Nat Commun. 2014 Mar 12;5:3445. doi: 10.1038/ncomms4445. Nat Commun. 2014. PMID: 24619172 Free PMC article.
-
Mitotic phosphorylation of HP1α regulates its cell cycle-dependent chromatin binding.J Biochem. 2019 May 1;165(5):433-446. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvy117. J Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30590679
-
HP1α targets the chromosomal passenger complex for activation at heterochromatin before mitotic entry.EMBO J. 2018 Mar 15;37(6):e97677. doi: 10.15252/embj.201797677. Epub 2018 Feb 21. EMBO J. 2018. PMID: 29467217 Free PMC article.
-
The chromosomal passenger complex: guiding Aurora-B through mitosis.J Cell Biol. 2006 Jun 19;173(6):833-7. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200604032. Epub 2006 Jun 12. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 16769825 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphorylation of histone and histone-like proteins by aurora kinases during mitosis.Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003;5:369-74. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 2003. PMID: 14593731 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNA 675 cooperates PKM2 to aggravate progression of human liver cancer stem cells induced from embryonic stem cells.J Mol Med (Berl). 2018 Oct;96(10):1119-1130. doi: 10.1007/s00109-018-1687-9. Epub 2018 Aug 23. J Mol Med (Berl). 2018. PMID: 30140938
-
NLRP12 downregulates the Wnt/β-catenin pathway via interaction with STK38 to suppress colorectal cancer.J Clin Invest. 2023 Oct 2;133(19):e166295. doi: 10.1172/JCI166295. J Clin Invest. 2023. PMID: 37581937 Free PMC article.
-
Modeling post-translational modifications and cancer-associated mutations that impact the heterochromatin protein 1α-importin α heterodimers.Proteins. 2019 Nov;87(11):904-916. doi: 10.1002/prot.25752. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Proteins. 2019. PMID: 31152607 Free PMC article.
-
Heterochromatin protein 1 (HP1): interactions with itself and chromatin components.Biophys Rev. 2020 Apr;12(2):387-400. doi: 10.1007/s12551-020-00663-y. Epub 2020 Mar 6. Biophys Rev. 2020. PMID: 32144738 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Beyond the histone tale: HP1α deregulation in breast cancer epigenetics.Cancer Biol Ther. 2015;16(2):189-200. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2014.1001277. Cancer Biol Ther. 2015. PMID: 25588111 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
