The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control
- PMID: 24713629
- PMCID: PMC4393108
- DOI: 10.1038/nrm3785
The dynamic epitranscriptome: N6-methyladenosine and gene expression control
Abstract
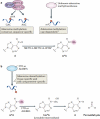
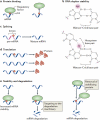
N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A) is a modified base that has long been known to be present in non-coding RNAs, ribosomal RNA, polyadenylated RNA and at least one mammalian mRNA. However, our understanding of the prevalence of this modification has been fundamentally redefined by transcriptome-wide m(6)A mapping studies, which have shown that m(6)A is present in a large subset of the transcriptome in specific regions of mRNA. This suggests that mRNA may undergo post-transcriptional methylation to regulate its fate and function, which is analogous to methyl modifications in DNA. Thus, the pattern of methylation constitutes an mRNA 'epitranscriptome'. The identification of adenosine methyltransferases ('writers'), m(6)A demethylating enzymes ('erasers') and m(6)A-binding proteins ('readers') is helping to define cellular pathways for the post-transcriptional regulation of mRNAs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Molecular biology. Internal mRNA methylation finally finds functions.Science. 2014 Mar 14;343(6176):1207-8. doi: 10.1126/science.1249340. Science. 2014. PMID: 24626918 No abstract available.
-
Dynamic RNA modifications in disease.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2014 Jun;26:47-52. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2014.05.006. Epub 2014 Jul 5. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2014. PMID: 25005745 Review.
-
FTO, m6 Am , and the hypothesis of reversible epitranscriptomic mRNA modifications.FEBS Lett. 2018 Jun;592(12):2012-2022. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13092. Epub 2018 May 24. FEBS Lett. 2018. PMID: 29754392 Review.
-
The m6A landscape of polyadenylated nuclear (PAN) RNA and its related methylome in the context of KSHV replication.RNA. 2021 Sep;27(9):1102-1125. doi: 10.1261/rna.078777.121. Epub 2021 Jun 29. RNA. 2021. Retraction in: RNA. 2022 Feb;28(2):274. doi: 10.1261/rna.079042.121 PMID: 34187903 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Gene expression regulation mediated through reversible m⁶A RNA methylation.Nat Rev Genet. 2014 May;15(5):293-306. doi: 10.1038/nrg3724. Epub 2014 Mar 25. Nat Rev Genet. 2014. PMID: 24662220 Review.
Cited by
-
A Bayesian hierarchical model for analyzing methylated RNA immunoprecipitation sequencing data.Quant Biol. 2018 Sep;6(3):275-286. doi: 10.1007/s40484-018-0149-2. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Quant Biol. 2018. PMID: 33833899 Free PMC article.
-
Biological roles of adenine methylation in RNA.Nat Rev Genet. 2023 Mar;24(3):143-160. doi: 10.1038/s41576-022-00534-0. Epub 2022 Oct 19. Nat Rev Genet. 2023. PMID: 36261710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide detection of high abundance N6-methyladenosine sites by microarray.RNA. 2015 Aug;21(8):1511-8. doi: 10.1261/rna.051474.115. Epub 2015 Jun 19. RNA. 2015. PMID: 26092943 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative analysis of methylome profiles of Campylobacter jejuni sheep abortion isolate and gastroenteric strains using PacBio data.Front Microbiol. 2015 Jan 14;5:782. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2014.00782. eCollection 2014. Front Microbiol. 2015. PMID: 25642218 Free PMC article.
-
The RNA m6A writer METTL3 in tumor microenvironment: emerging roles and therapeutic implications.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 22;15:1335774. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1335774. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38322265 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Lewis JD, et al. Purification, sequence, and cellular localization of a novel chromosomal protein that binds to methylated DNA. Cell. 1992;69:905–14. - PubMed
-
- Pawson T, Scott JD. Protein phosphorylation in signaling--50 years and counting. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005;30:286–90. - PubMed
-
- Meyer KD, et al. Comprehensive analysis of mRNA methylation reveals enrichment in 3' UTRs and near stop codons. Cell. 2012;149:1635–46. [Provides the first demonstration that m6A is a widespread modification in mammalian mRNAs and reveals that m6A is highly enriched surrounding stop codons and in UTRs. Also identifies many methylated noncoding RNAs which were not previously known to contain m6A.] - PMC - PubMed
-
- Dominissini D, et al. Topology of the human and mouse m6A RNA methylomes revealed by m6A-seq. Nature. 2012;485:201–6. [Demonstrates, together with reference 3, that m6A is a pervasive feature of the transcriptome which exhibits a unique distribution within mRNAs. Identifies YTHDF2-3 and HuR as potential m6A binding proteins.] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

