Stem cell imaging: from bench to bedside
- PMID: 24702995
- PMCID: PMC4024441
- DOI: 10.1016/j.stem.2014.03.009
Stem cell imaging: from bench to bedside
Abstract
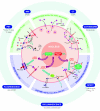
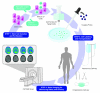
Although cellular therapies hold great promise for the treatment of human disease, results from several initial clinical trials have not shown a level of efficacy required for their use as a first line therapy. Here we discuss how in vivo molecular imaging has helped identify barriers to clinical translation and potential strategies that may contribute to successful transplantation and improved outcomes, with a focus on cardiovascular and neurological diseases. We conclude with a perspective on the future role of molecular imaging in defining safety and efficacy for clinical implementation of stem cell therapies.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Seeing stem cells at work in vivo.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2014 Feb;10(1):127-44. doi: 10.1007/s12015-013-9468-x. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2014. PMID: 23975604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noninvasive stem cell tracking.J Nucl Cardiol. 2011 Oct;18(5):966-73. doi: 10.1007/s12350-011-9436-2. J Nucl Cardiol. 2011. PMID: 21800230 Review. No abstract available.
-
Molecular imaging and tracking stem cells in neurosciences.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1052:195-201. doi: 10.1007/7651_2013_27. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 23640257 Review.
-
In vivo Cell Tracking Using Non-invasive Imaging of Iron Oxide-Based Particles with Particular Relevance for Stem Cell-Based Treatments of Neurological and Cardiac Disease.Mol Imaging Biol. 2020 Dec;22(6):1469-1488. doi: 10.1007/s11307-019-01440-4. Mol Imaging Biol. 2020. PMID: 31802361 Review.
-
Non-invasive in-vivo imaging of stem cells after transplantation in cardiovascular tissue.Theranostics. 2013 Jul 20;3(8):561-72. doi: 10.7150/thno.5787. eCollection 2013. Theranostics. 2013. PMID: 23946822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
[18F]FDG-labelled stem cell PET imaging in different route of administrations and multiple animal species.Sci Rep. 2021 May 25;11(1):10896. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-90383-4. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34035416 Free PMC article.
-
Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-based therapy: mechanism, systemic safety and biodistribution for precision clinical applications.J Biomed Sci. 2021 Apr 14;28(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12929-021-00725-7. J Biomed Sci. 2021. PMID: 33849537 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Photoacoustic Imaging of Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes in Living Hearts with Ultrasensitive Semiconducting Polymer Nanoparticles.Adv Funct Mater. 2018 Jan 4;28(1):1704939. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201704939. Epub 2017 Nov 8. Adv Funct Mater. 2018. PMID: 30473658 Free PMC article.
-
Prospect of cell penetrating peptides in stem cell tracking.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021 Aug 14;12(1):457. doi: 10.1186/s13287-021-02522-3. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2021. PMID: 34391472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Concise Review: Quantitative Detection and Modeling the In Vivo Kinetics of Therapeutic Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells.Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018 Jan;7(1):78-86. doi: 10.1002/sctm.17-0209. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018. PMID: 29210198 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abdullah Z, Saric T, Kashkar H, Baschuk N, Yazdanpanah B, Fleischmann BK, Hescheler J, Kronke M, Utermohlen O. Serpin-6 expression protects embryonic stem cells from lysis by antigen-specific CTL. Journal of Immunology. 2007;178:3390–3399. - PubMed
-
- Alper J. Geron gets green light for human trial of ES cell-derived product. Nat Biotechnol. 2009;27:213–214. - PubMed
-
- Araki R, Uda M, Hoki Y, Sunayama M, Nakamura M, Ando S, Sugiura M, Ideno H, Shimada A, Nifuji A, et al. Negligible immunogenicity of terminally differentiated cells derived from induced pluripotent or embryonic stem cells. Nature. 2013;494:100–104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

