Elastin-like polypeptides as a promising family of genetically-engineered protein based polymers
- PMID: 24699809
- PMCID: PMC4072924
- DOI: 10.1007/s11274-014-1649-5
Elastin-like polypeptides as a promising family of genetically-engineered protein based polymers
Abstract
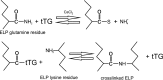
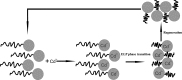
Elastin-like polypeptides (ELP) are artificial, genetically encodable biopolymers, belonging to elastomeric proteins, which are widespread in a wide range of living organisms. They are composed of a repeating pentapeptide sequence Val-Pro-Gly-Xaa-Gly, where the guest residue (Xaa) can be any naturally occurring amino acid except proline. These polymers undergo reversible phase transition that can be triggered by various environmental stimuli, such as temperature, pH or ionic strength. This behavior depends greatly on the molecular weight, concentration of ELP in the solution and composition of the amino acids constituting ELPs. At a temperature below the inverse transition temperature (Tt), ELPs are soluble, but insoluble when the temperature exceeds Tt. Furthermore, this feature is retained even when ELP is fused to the protein of interest. These unique properties make ELP very useful for a wide variety of biomedical applications (e.g. protein purification, drug delivery etc.) and it can be expected that smart biopolymers will play a significant role in the development of most new materials and technologies. Here we present the structure and properties of thermally responsive elastin-like polypeptides with a particular emphasis on biomedical and biotechnological application.
Figures
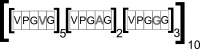
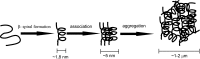

Similar articles
-
Cadmium detection by a thermally responsive elastin copolymer with metal-binding functionality.Enzyme Microb Technol. 2013 Aug 15;53(3):189-93. doi: 10.1016/j.enzmictec.2013.03.023. Epub 2013 Apr 8. Enzyme Microb Technol. 2013. PMID: 23830461
-
Chemical synthesis and characterization of elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs) with variable guest residues.J Pept Sci. 2016 May;22(5):334-42. doi: 10.1002/psc.2871. Epub 2016 Mar 22. J Pept Sci. 2016. PMID: 27005861
-
Stimulus responsive elastin biopolymers: Applications in medicine and biotechnology.Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2006 Dec;10(6):652-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpa.2006.10.010. Epub 2006 Oct 19. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2006. PMID: 17055770 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting a genetically engineered elastin-like polypeptide to solid tumors by local hyperthermia.Cancer Res. 2001 Feb 15;61(4):1548-54. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11245464
-
Elastin-Like Polypeptides for Biomedical Applications.Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2020 Jun 4;22:343-369. doi: 10.1146/annurev-bioeng-092419-061127. Epub 2020 Apr 28. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2020. PMID: 32343908 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic Functionalization of Protein-Based Biomaterials via Protein Fusions.Biomacromolecules. 2024 Aug 12;25(8):4639-4662. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.4c00188. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Biomacromolecules. 2024. PMID: 39074364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation of a Monoclonal Antibody to Detect Elastin-like Polypeptides.Biomacromolecules. 2019 Aug 12;20(8):2942-2952. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.9b00503. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Biomacromolecules. 2019. PMID: 31276401 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and simple purification of elastin-like polypeptides directly from whole cells and cell lysates by organic solvent extraction.Biomater Sci. 2018 Mar 26;6(4):863-876. doi: 10.1039/c8bm00124c. Biomater Sci. 2018. PMID: 29488993 Free PMC article.
-
Degradable Polymeric Bio(nano)materials and Their Biomedical Applications: A Comprehensive Overview and Recent Updates.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jan 10;16(2):206. doi: 10.3390/polym16020206. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38257005 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elastin-like polypeptides: Therapeutic applications for an emerging class of nanomedicines.J Control Release. 2016 Oct 28;240:93-108. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.11.010. Epub 2015 Nov 11. J Control Release. 2016. PMID: 26578439 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ayala JC, Pimienta E, Rodríguez C, Anné J, Vallín C, Milanés MT, King-Batsios E, Huygen K, Van Mellaert L. Use of strep-tag II for rapid detection and purification of Mycobacterium tuberculosis recombinant antigens secreted by Streptomyces lividans. J Microbiol Methods. 2013;94:192–198. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2013.06.004. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

