A small physiological electric field mediated responses of extravillous trophoblasts derived from HTR8/SVneo cells: involvement of activation of focal adhesion kinase signaling
- PMID: 24643246
- PMCID: PMC3958492
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092252
A small physiological electric field mediated responses of extravillous trophoblasts derived from HTR8/SVneo cells: involvement of activation of focal adhesion kinase signaling
Abstract
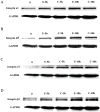
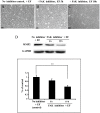
Moderate invasion of trophoblast cells into endometrium is essential for the placental development and normal pregnancy. Electric field (EF)-induced effects on cellular behaviors have been observed in many cell types. This study was to investigate the effect of physiological direct current EF (dc EF) on cellular responses such as elongation, orientation and motility of trophoblast cells. Immortalized first trimester extravillous trophoblast cells (HTR-8/SVneo) were exposed to the dc EF at physiological magnitude. Cell images were recorded and analyzed by image analyzer. Cell lysates were used to detect protein expression by Western blot. Cultured in the dc EFs the cells showed elongation, orientation and enhanced migration rate compared with non-EF stimulated cells at field strengths of 100 mV/mm to 200 mV/mm. EF exposure increased focal adhesion kinase (FAK) phosphorylation in a time-dependent manner and increased expression levels of MMP-2. Pharmacological inhibition of FAK impaired the EF-induced responses including motility and abrogated the elevation of MMP-2 expression. However, the expression levels of integrins like integrin α1, α5, αV and β1 were not affected by EF stimulation. Our results demonstrate the importance of FAK activation in migration/motility of trophobalst cells driven by EFs. In addition, it raises the feasibility of using applied EFs to promote placentation through effects on trophoblast cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
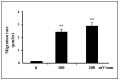
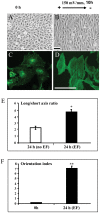
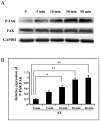
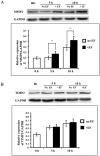
Similar articles
-
Knockdown of activated Cdc42-associated kinase inhibits human extravillous trophoblast migration and invasion and decreases protein expression of pho-Akt and matrix metalloproteinase.J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020 Apr;33(7):1125-1133. doi: 10.1080/14767058.2018.1515196. Epub 2018 Oct 3. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2020. PMID: 30282494
-
β-1,4-Galactosyltransferase III suppresses extravillous trophoblast invasion through modifying β1-integrin glycosylation.Placenta. 2015 Apr;36(4):357-64. doi: 10.1016/j.placenta.2015.01.008. Epub 2015 Jan 24. Placenta. 2015. PMID: 25659296
-
The chemokine CXCL6 restricts human trophoblast cell migration and invasion by suppressing MMP-2 activity in the first trimester.Hum Reprod. 2013 Sep;28(9):2350-62. doi: 10.1093/humrep/det258. Epub 2013 Jun 28. Hum Reprod. 2013. PMID: 23814098
-
Activin A Increases Human Trophoblast Invasion by Inducing SNAIL-Mediated MMP2 Up-Regulation Through ALK4.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Nov;100(11):E1415-27. doi: 10.1210/jc.2015-2134. Epub 2015 Aug 25. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26305619
-
Regulation of human trophoblast migration and invasiveness.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2002 Feb;80(2):116-24. doi: 10.1139/y02-016. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2002. PMID: 11934254 Review.
Cited by
-
Modulation of cell function by electric field: a high-resolution analysis.J R Soc Interface. 2015 Jun 6;12(107):20150153. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2015.0153. J R Soc Interface. 2015. PMID: 25994294 Free PMC article.
-
Electric Pulses Can Influence Galvanotaxis of Dictyostelium discoideum.Biomed Res Int. 2018 Aug 8;2018:2534625. doi: 10.1155/2018/2534625. eCollection 2018. Biomed Res Int. 2018. PMID: 30186854 Free PMC article.
-
In-vitro analysis of Quantum Molecular Resonance effects on human mesenchymal stromal cells.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 2;13(1):e0190082. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190082. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29293552 Free PMC article.
-
Src activation decouples cell division orientation from cell geometry in mammalian cells.Biomaterials. 2018 Jul;170:82-94. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.03.052. Epub 2018 Apr 3. Biomaterials. 2018. PMID: 29653289 Free PMC article.
-
Monophasic Pulsed Current Stimulation of Duty Cycle 10% Promotes Differentiation of Human Dermal Fibroblasts into Myofibroblasts.Phys Ther Res. 2021 Mar 18;24(2):145-152. doi: 10.1298/ptr.E10064. eCollection 2021. Phys Ther Res. 2021. PMID: 34532210 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Robinson KR, Messerli MA (1996) Electric embryos: the embryonic epithelium as a generator of developmental information. In: McCaig CD, editor.Nerve Growth and Nerve Guidance.\London, UK: Portland Press. pp.131–150.
-
- Chiang M, Robinson KR, Vanable JW (1992) Electrical fields in the vicinity of epithelial wounds in the isolated bovine eye. Exp Eye Res 54: 999–1003. - PubMed
-
- Sta Iglesia DD, Vanable JW (1998) Endogenous lateral electric fields around bovine corneal lesions are necessary for and can enhance normal rates of wound healing. Wound Repair Reg 6: 531–542. - PubMed
-
- Zhao M, Agius-Fernandez A, Forrester JV, McCraig CD (1996) Orientation and directed migration of cultured corneal epithelial cells in small electric fields are serum dependent. J Cell Sci 109: 1405–1414. - PubMed
-
- Chao P-HG, Roy R, Mauck RL, Liu W, Valhmu WB, et al. (2000) Chondrocyte Translocation Response to Direct Current Electric Fields. Journal of Biomechanical Engineering 122: 261–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

