Dysregulation of Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (Wif1) expression resulted in aberrant Wnt-β-catenin signaling and cell death of the cloaca endoderm, and anorectal malformations
- PMID: 24632949
- PMCID: PMC4013516
- DOI: 10.1038/cdd.2014.20
Dysregulation of Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (Wif1) expression resulted in aberrant Wnt-β-catenin signaling and cell death of the cloaca endoderm, and anorectal malformations
Abstract
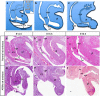
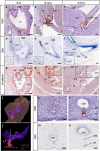
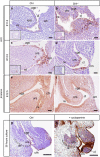
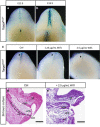
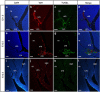
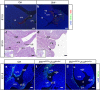
In mammalian urorectal development, the urorectal septum (urs) descends from the ventral body wall to the cloaca membrane (cm) to partition the cloaca into urogenital sinus and rectum. Defective urs growth results in human congenital anorectal malformations (ARMs), and their pathogenic mechanisms are unclear. Recent studies only focused on the importance of urs mesenchyme proliferation, which is induced by endoderm-derived Sonic Hedgehog (Shh). Here, we showed that the programmed cell death of the apical urs and proximal cm endoderm is particularly crucial for the growth of urs during septation. The apoptotic endoderm was closely associated with the tempo-spatial expression of Wnt inhibitory factor 1 (Wif1), which is an inhibitor of Wnt-β-catenin signaling. In Wif1(lacZ/lacZ) mutant mice and cultured urorectum with exogenous Wif1, cloaca septation was defective with undescended urs and hypospadias-like phenotypes, and such septation defects were also observed in Shh(-/-) mutants and in endodermal β-catenin gain-of-function (GOF) mutants. In addition, Wif1 and Shh were expressed in a complementary manner in the cloaca endoderm, and Wif1 was ectopically expressed in the urs and cm associated with excessive endodermal apoptosis and septation defects in Shh(-/-) mutants. Furthermore, apoptotic cells were markedly reduced in the endodermal β-catenin GOF mutant embryos, which counteracted the inhibitory effects of Wif1. Taken altogether, these data suggest that regulated expression of Wif1 is critical for the growth of the urs during cloaca septation. Hence, Wif1 governs cell apoptosis of urs endoderm by repressing β-catenin signal, which may facilitate the protrusion of the underlying proliferating mesenchymal cells towards the cm for cloaca septation. Dysregulation of this endodermal Shh-Wif1-β-catenin signaling axis contributes to ARM pathogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Disruption of the temporally regulated cloaca endodermal β-catenin signaling causes anorectal malformations.Cell Death Differ. 2014 Jun;21(6):990-7. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.21. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Cell Death Differ. 2014. PMID: 24632946 Free PMC article.
-
Dkk1 in the peri-cloaca mesenchyme regulates formation of anorectal and genitourinary tracts.Dev Biol. 2014 Jan 1;385(1):41-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.10.016. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24479159 Free PMC article.
-
Multiphasic and tissue-specific roles of sonic hedgehog in cloacal septation and external genitalia development.Development. 2009 Dec;136(23):3949-57. doi: 10.1242/dev.042291. Development. 2009. PMID: 19906862 Free PMC article.
-
Wnt inhibitory factor 1 induces apoptosis and inhibits cervical cancer growth, invasion and angiogenesis in vivo.Oncogene. 2012 May 31;31(22):2725-37. doi: 10.1038/onc.2011.455. Epub 2011 Oct 17. Oncogene. 2012. PMID: 22002305
-
[Research progress of Wif1 in development of nervous system].Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010 Jan;39(1):93-6. doi: 10.3785/j.issn.1008-9292.2010.01.016. Zhejiang Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2010. PMID: 20175243 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Systematic stereoscopic analyses for cloacal development: The origin of anorectal malformations.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 10;5:13943. doi: 10.1038/srep13943. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26354024 Free PMC article.
-
Histology Atlas of the Developing Mouse Urinary System With Emphasis on Prenatal Days E10.5-E18.5.Toxicol Pathol. 2019 Oct;47(7):865-886. doi: 10.1177/0192623319873871. Epub 2019 Oct 10. Toxicol Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31599209 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional deletion of platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha (Pdgfra) in urorectal mesenchyme causes mesenchyme apoptosis and urorectal developmental anomalies in mice.Cell Death Differ. 2019 Aug;26(8):1396-1410. doi: 10.1038/s41418-018-0216-2. Epub 2018 Oct 15. Cell Death Differ. 2019. PMID: 30323271 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of the temporally regulated cloaca endodermal β-catenin signaling causes anorectal malformations.Cell Death Differ. 2014 Jun;21(6):990-7. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2014.21. Epub 2014 Mar 14. Cell Death Differ. 2014. PMID: 24632946 Free PMC article.
-
Hormonal and Molecular Regulation of Phallus Differentiation in a Marsupial Tammar Wallaby.Genes (Basel). 2020 Jan 16;11(1):106. doi: 10.3390/genes11010106. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31963388 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mundt E, Bates MD. Genetics of Hirschsprung disease and anorectal malformations. Semin Pediatr Surg. 2010;19:107–117. - PubMed
-
- Kohlhase J, Wischermann A, Reichenbach H, Froster U, Engel W. Mutations in the SALL1 putative transcription factor gene cause Townes-Brocks syndrome. Nat Genet. 1998;18:81–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

