DLK1 promotes lung cancer cell invasion through upregulation of MMP9 expression depending on Notch signaling
- PMID: 24621612
- PMCID: PMC3951400
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091509
DLK1 promotes lung cancer cell invasion through upregulation of MMP9 expression depending on Notch signaling
Abstract
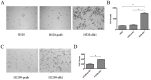
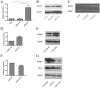
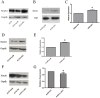
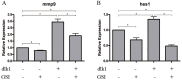
The transmembrane and secreted protein delta-like 1 homolog (DLK1) belongs to the EGF-like family. It is widely accepted that DLK1 plays important roles in regulating cell differentiation, such as adipogenesis and osteogenesis. Aberrant expression of DLK1 has been found in various types of human cancers, including lung cancer. A previous study in this lab has revealed that DLK1 is associated with tumor invasion, although the mechanism is still unknown. To explore the potential effects that DLK1 might have on invasion, DLK1 was overexpressed or knocked down in the human lung cancer cell lines. The protein's influences on cell invasion were subsequently evaluated. A transwell assay showed that DLK1 overexpression significantly promoted cancer cell invasion. Western blotting and gelatin zymography analysis indicated that DLK1 could affect both matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9) expression and its extracellular activity. An analysis of NOTCH1 and HES1 gene expression and Notch intracellular domain (NICD) nuclear translocation during DLK1 stimulation or depletion demonstrated that DLK1 could activate Notch signaling in lung cancer cells. Additionally, the elevated expression of MMP9 induced by DLK1 stimulation could be significantly decreased by inhibiting Notch signaling using γ-secretase inhibitor (GSI). The data presented in this study suggest that DLK1 can promote the invasion of lung cancer cells by upregulating MMP9 expression, which depends on Notch signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Different expression levels of DLK1 inversely modulate the oncogenic potential of human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells through inhibition of NOTCH1 signaling.FASEB J. 2017 Aug;31(8):3484-3496. doi: 10.1096/fj.201601341RRR. Epub 2017 May 1. FASEB J. 2017. PMID: 28461338
-
The EGF-like proteins DLK1 and DLK2 function as inhibitory non-canonical ligands of NOTCH1 receptor that modulate each other's activities.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011 Jun;1813(6):1153-64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2011.03.004. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2011. PMID: 21419176
-
DLK1 promotes neurogenesis of human and mouse pluripotent stem cell-derived neural progenitors via modulating Notch and BMP signalling.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2012 Jun;8(2):459-71. doi: 10.1007/s12015-011-9298-7. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2012. PMID: 21761283
-
The imprinted gene Delta like non-canonical Notch ligand 1 (Dlk1) is conserved in mammals, and serves a growth modulatory role during tissue development and regeneration through Notch dependent and independent mechanisms.Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019 Apr;46:17-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019.03.006. Epub 2019 Mar 23. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019. PMID: 30930082 Review.
-
Possible roles of DLK1 in the Notch pathway during development and disease.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012 Jun;1822(6):988-95. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2012.02.003. Epub 2012 Feb 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012. PMID: 22353464 Review.
Cited by
-
Cd248a and Cd248b in zebrafish participate in innate immune responses.Front Immunol. 2022 Aug 31;13:970626. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.970626. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36119065 Free PMC article.
-
Regulated genes in mesenchymal stem cells and gastric cancer.World J Stem Cells. 2015 Jan 26;7(1):208-22. doi: 10.4252/wjsc.v7.i1.208. World J Stem Cells. 2015. PMID: 25621121 Free PMC article.
-
Testicular cancer in mice: interplay between stem cells and endocrine insults.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022 Jun 8;13(1):243. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-02784-5. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35676718 Free PMC article.
-
Notch signaling in lung diseases: focus on Notch1 and Notch3.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2016 Oct;10(5):468-84. doi: 10.1177/1753465816654873. Epub 2016 Jul 4. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2016. PMID: 27378579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Crosstalk between TLR4 and Notch1 signaling in the IgA nephropathy during inflammatory response.Int Urol Nephrol. 2018 Apr;50(4):779-785. doi: 10.1007/s11255-017-1760-2. Epub 2017 Dec 11. Int Urol Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 29230705
References
-
- Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, et al. (2008) Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin 58: 71–96. - PubMed
-
- Herbst RS, Lippman SM (2007) Molecular signatures of lung cancer—toward personalized therapy. N Engl J Med 356: 76–78. - PubMed
-
- Nueda ML, Baladron V, Sanchez-Solana B, Ballesteros MA, Laborda J (2007) The EGF-like protein dlk1 inhibits notch signaling and potentiates adipogenesis of mesenchymal cells. J Mol Biol 367: 1281–1293. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

