The SIRT1 activator SRT1720 extends lifespan and improves health of mice fed a standard diet
- PMID: 24582957
- PMCID: PMC4010117
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2014.01.031
The SIRT1 activator SRT1720 extends lifespan and improves health of mice fed a standard diet
Abstract
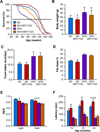
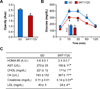
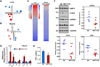
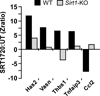
The prevention or delay of the onset of age-related diseases prolongs survival and improves quality of life while reducing the burden on the health care system. Activation of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1), an NAD(+)-dependent deacetylase, improves metabolism and confers protection against physiological and cognitive disturbances in old age. SRT1720 is a specific SIRT1 activator that has health and lifespan benefits in adult mice fed a high-fat diet. We found extension in lifespan, delayed onset of age-related metabolic diseases, and improved general health in mice fed a standard diet after SRT1720 supplementation. Inhibition of proinflammatory gene expression in both liver and muscle of SRT1720-treated animals was noted. SRT1720 lowered the phosphorylation of NF-κB pathway regulators in vitro only when SIRT1 was functionally present. Combined with our previous work, the current study further supports the beneficial effects of SRT1720 on health across the lifespan in mice.
Copyright © 2014 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
SIRT1 activator (SRT1720) improves the follicle reserve and prolongs the ovarian lifespan of diet-induced obesity in female mice via activating SIRT1 and suppressing mTOR signaling.J Ovarian Res. 2014 Oct 21;7:97. doi: 10.1186/s13048-014-0097-z. J Ovarian Res. 2014. PMID: 25330910 Free PMC article.
-
SRT1720 improves survival and healthspan of obese mice.Sci Rep. 2011;1:70. doi: 10.1038/srep00070. Epub 2011 Aug 18. Sci Rep. 2011. PMID: 22355589 Free PMC article.
-
SIRT1 upregulation protects against liver injury induced by a HFD through inhibiting CD36 and the NF‑κB pathway in mouse kupffer cells.Mol Med Rep. 2018 Aug;18(2):1609-1615. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2018.9088. Epub 2018 May 29. Mol Med Rep. 2018. PMID: 29845302 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical effects of SIRT1 activators.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Aug;1804(8):1626-34. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2009.10.025. Epub 2009 Nov 6. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 19897059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activators of Sirtuin-1 and their Involvement in Cardioprotection.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(34):4432-4456. doi: 10.2174/0929867325666180214115438. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 29446717 Review.
Cited by
-
Sirtuins in kidney health and disease.Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024 May;20(5):313-329. doi: 10.1038/s41581-024-00806-4. Epub 2024 Feb 6. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 38321168 Review.
-
Adverse Geriatric Outcomes Secondary to Polypharmacy in a Mouse Model: The Influence of Aging.J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2016 May;71(5):571-7. doi: 10.1093/gerona/glv046. Epub 2015 May 4. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 25940962 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Strategies to Retard Cardiovascular Aging.Circ Res. 2016 May 13;118(10):1626-42. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.307475. Circ Res. 2016. PMID: 27174954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Resveratrol Improves Survival and Prolongs Life Following Hemorrhagic Shock.Mol Med. 2015 Apr 13;21(1):305-12. doi: 10.2119/molmed.2015.00013. Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25879628 Free PMC article.
-
The Beneficial Roles of SIRT1 in Neuroinflammation-Related Diseases.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020 Sep 14;2020:6782872. doi: 10.1155/2020/6782872. eCollection 2020. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020. PMID: 33014276 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

