Hippo signaling regulates microprocessor and links cell-density-dependent miRNA biogenesis to cancer
- PMID: 24581491
- PMCID: PMC3982296
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.043
Hippo signaling regulates microprocessor and links cell-density-dependent miRNA biogenesis to cancer
Abstract
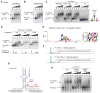
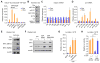
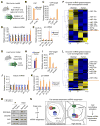
Global downregulation of microRNAs (miRNAs) is commonly observed in human cancers and can have a causative role in tumorigenesis. The mechanisms responsible for this phenomenon remain poorly understood. Here, we show that YAP, the downstream target of the tumor-suppressive Hippo-signaling pathway regulates miRNA biogenesis in a cell-density-dependent manner. At low cell density, nuclear YAP binds and sequesters p72 (DDX17), a regulatory component of the miRNA-processing machinery. At high cell density, Hippo-mediated cytoplasmic retention of YAP facilitates p72 association with Microprocessor and binding to a specific sequence motif in pri-miRNAs. Inactivation of the Hippo pathway or expression of constitutively active YAP causes widespread miRNA suppression in cells and tumors and a corresponding posttranscriptional induction of MYC expression. Thus, the Hippo pathway links contact-inhibition regulation to miRNA biogenesis and may be responsible for the widespread miRNA repression observed in cancer.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
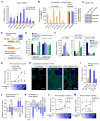
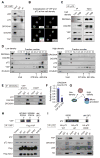
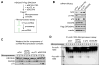
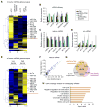
Comment in
-
Tumour suppressors: Hippo promotes microRNA processing.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 Apr;14(4):216-7. doi: 10.1038/nrc3715. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24658271 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
The Hippo pathway effectors TAZ/YAP regulate dicer expression and microRNA biogenesis through Let-7.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 24;289(4):1886-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.C113.529362. Epub 2013 Dec 9. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24324261 Free PMC article.
-
Mutant p53 inhibits miRNA biogenesis by interfering with the microprocessor complex.Oncogene. 2016 Jul 21;35(29):3760-70. doi: 10.1038/onc.2016.51. Epub 2016 Mar 21. Oncogene. 2016. PMID: 26996669
-
Transcription and processing: multilayer controls of RNA biogenesis by the Hippo pathway.EMBO J. 2014 May 2;33(9):942-4. doi: 10.1002/embj.201488329. Epub 2014 Mar 17. EMBO J. 2014. PMID: 24639555 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between Hippo signalling and miRNAs in tumour progression.FEBS J. 2017 Apr;284(7):1045-1055. doi: 10.1111/febs.13985. Epub 2017 Jan 21. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 27973704 Review.
-
miRNAs and the Hippo pathway in cancer: Exploring the therapeutic potential (Review).Oncol Rep. 2022 Jul;48(1):135. doi: 10.3892/or.2022.8346. Epub 2022 Jun 14. Oncol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35699111 Review.
Cited by
-
A Driver Never Works Alone-Interplay Networks of Mutant p53, MYC, RAS, and Other Universal Oncogenic Drivers in Human Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jun 11;12(6):1532. doi: 10.3390/cancers12061532. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32545208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YAP and TAZ Mediators at the Crossroad between Metabolic and Cellular Reprogramming.Metabolites. 2021 Mar 8;11(3):154. doi: 10.3390/metabo11030154. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 33800464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
YAP Mediates Tumorigenesis in Neurofibromatosis Type 2 by Promoting Cell Survival and Proliferation through a COX-2-EGFR Signaling Axis.Cancer Res. 2016 Jun 15;76(12):3507-19. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-15-1144. Epub 2016 May 23. Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 27216189 Free PMC article.
-
The role of miRNAs in cholangiocarcinoma.Hepat Oncol. 2016 Apr;3(2):167-180. doi: 10.2217/hep-2015-0003. Epub 2016 Mar 29. Hepat Oncol. 2016. PMID: 30191036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay between noncoding RNA and YAP/TAZ signaling in cancers: molecular functions and mechanisms.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Jun 14;41(1):202. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02403-4. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35701841 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Camargo FD, Gokhale S, Johnnidis JB, Fu D, Bell GW, Jaenisch R, Brummelkamp TR. YAP1 increases organ size and expands undifferentiated progenitor cells. Curr Biol. 2007;17:2054–2060. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

