Antibody-modified T cells: CARs take the front seat for hematologic malignancies
- PMID: 24578504
- PMCID: PMC3999751
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2013-11-492231
Antibody-modified T cells: CARs take the front seat for hematologic malignancies
Abstract
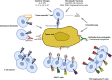
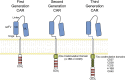
T cells redirected to specific antigen targets with engineered chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) are emerging as powerful therapies in hematologic malignancies. Various CAR designs, manufacturing processes, and study populations, among other variables, have been tested and reported in over 10 clinical trials. Here, we review and compare the results of the reported clinical trials and discuss the progress and key emerging factors that may play a role in effecting tumor responses. We also discuss the outlook for CAR T-cell therapies, including managing toxicities and expanding the availability of personalized cell therapy as a promising approach to all hematologic malignancies. Many questions remain in the field of CAR T cells directed to hematologic malignancies, but the encouraging response rates pave a wide road for future investigation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
4-1BB costimulation ameliorates T cell exhaustion induced by tonic signaling of chimeric antigen receptors.Nat Med. 2015 Jun;21(6):581-90. doi: 10.1038/nm.3838. Epub 2015 May 4. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 25939063 Free PMC article.
-
Chimeric antigen receptor-modified T cells: CD19 and the road beyond.Blood. 2018 Jun 14;131(24):2621-2629. doi: 10.1182/blood-2018-01-785840. Epub 2018 May 4. Blood. 2018. PMID: 29728402 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chimeric antigen receptors for the adoptive T cell therapy of hematologic malignancies.Int J Hematol. 2014 Apr;99(4):361-71. doi: 10.1007/s12185-013-1479-5. Epub 2013 Dec 6. Int J Hematol. 2014. PMID: 24311149 Free PMC article. Review.
-
State of the art in CAR T cell therapy for CD19+ B cell malignancies.J Clin Invest. 2020 Apr 1;130(4):1586-1594. doi: 10.1172/JCI129208. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 32235098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD19-targeted CAR T-cell therapeutics for hematologic malignancies: interpreting clinical outcomes to date.Blood. 2016 Jun 30;127(26):3312-20. doi: 10.1182/blood-2016-02-629063. Epub 2016 May 20. Blood. 2016. PMID: 27207800 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
RD-MolPack technology for the constitutive production of self-inactivating lentiviral vectors pseudotyped with the nontoxic RD114-TR envelope.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2016 May 11;3:16033. doi: 10.1038/mtm.2016.33. eCollection 2016. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2016. PMID: 27222840 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Therapies for Epstein-Barr Virus-Associated Lymphomas.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Sep 9;12(9):2565. doi: 10.3390/cancers12092565. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32916819 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Severe delayed pulmonary toxicity following PD-L1-specific CAR-T cell therapy for non-small cell lung cancer.Clin Transl Immunology. 2020 Oct 9;9(10):e1154. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1154. eCollection 2020. Clin Transl Immunology. 2020. PMID: 33072320 Free PMC article.
-
Eradication Strategies for Chronic Hepatitis B Infection.Clin Infect Dis. 2016 Jun 1;62 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S318-25. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciw044. Clin Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27190322 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Combination strategies to enhance the potency of monocyte-derived dendritic cell-based cancer vaccines.Immunotherapy. 2016 Oct;8(10):1205-18. doi: 10.2217/imt-2016-0071. Immunotherapy. 2016. PMID: 27605069 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Eshhar Z, Waks T, Bendavid A, Schindler DG. Functional expression of chimeric receptor genes in human T cells. J Immunol Methods. 2001;248(1-2):67–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

