Weighted set enrichment of gene expression data
- PMID: 24565001
- PMCID: PMC3854649
- DOI: 10.1186/1752-0509-7-S4-S10
Weighted set enrichment of gene expression data
Abstract
Background: Sets of genes that are known to be associated with each other can be used to interpret microarray data. This gene set approach to microarray data analysis can illustrate patterns of gene expression which may be more informative than analyzing the expression of individual genes. Various statistical approaches exist for the analysis of gene sets. There are three main classes of these methods: over-representation analysis, functional class scoring, and pathway topology based methods.
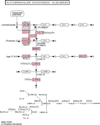
Methods: We propose weighted hypergeometric and weighted chi-squared methods in order to assign a rank to the degree to which each gene participates in the enrichment. Each gene is assigned a weight determined by the absolute value of its log fold change, which is then raised to a certain power. The power value can be adjusted as needed. Datasets from the Gene Expression Omnibus are used to test the method. The significantly enriched pathways are validated through searching the literature in order to determine their relevance to the dataset.
Results: Although these methods detect fewer significantly enriched pathways, they can potentially produce more relevant results. Furthermore, we compare the results of different enrichment methods on a set of microarray studies all containing data from various rodent neuropathic pain models.
Discussion: Our method is able to produce more consistent results than other methods when evaluated on similar datasets. It can also potentially detect relevant pathways that are not identified by the standard methods. However, the lack of biological ground truth makes validating the method difficult.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Comparative study of gene set enrichment methods.BMC Bioinformatics. 2009 Sep 2;10:275. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-275. BMC Bioinformatics. 2009. PMID: 19725948 Free PMC article.
-
Concordant integrative gene set enrichment analysis of multiple large-scale two-sample expression data sets.BMC Genomics. 2014;15 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S6. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-S1-S6. Epub 2014 Jan 24. BMC Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24564564 Free PMC article.
-
Gene expression analysis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma using gene set enrichment analysis for biostatistical management.BJU Int. 2011 Jul;108(2 Pt 2):E29-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1464-410X.2010.09794.x. Epub 2011 Mar 16. BJU Int. 2011. PMID: 21435154
-
Comparing enrichment analysis and machine learning for identifying gene properties that discriminate between gene classes.Brief Bioinform. 2020 May 21;21(3):803-814. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz028. Brief Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 30895300 Review.
-
Computational approaches to analysis of DNA microarray data.Yearb Med Inform. 2006:91-103. Yearb Med Inform. 2006. PMID: 17051302 Review.
Cited by
-
The Developmental Transcriptome of Bagworm, Metisa plana (Lepidoptera: Psychidae) and Insights into Chitin Biosynthesis Genes.Genes (Basel). 2020 Dec 23;12(1):7. doi: 10.3390/genes12010007. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33374651 Free PMC article.
-
Cooperative interactions between seed-borne bacterial and air-borne fungal pathogens on rice.Nat Commun. 2018 Jan 2;9(1):31. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-02430-2. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29295978 Free PMC article.
-
Pathway Analysis: State of the Art.Front Physiol. 2015 Dec 17;6:383. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2015.00383. eCollection 2015. Front Physiol. 2015. PMID: 26733877 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Profiling of glucose-induced transcription in Sulfolobus acidocaldarius DSM 639.Genes Genomics. 2018 Nov;40(11):1157-1167. doi: 10.1007/s13258-018-0675-3. Epub 2018 Mar 6. Genes Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30315522
-
Integrative enrichment analysis: a new computational method to detect dysregulated pathways in heterogeneous samples.BMC Genomics. 2015 Nov 10;16:918. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2188-7. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26556243 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

