pY RNA1-s2: a highly retina-enriched small RNA that selectively binds to Matrin 3 (Matr3)
- PMID: 24558381
- PMCID: PMC3928194
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088217
pY RNA1-s2: a highly retina-enriched small RNA that selectively binds to Matrin 3 (Matr3)
Abstract
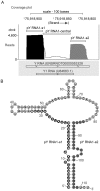
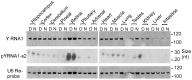
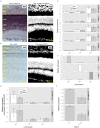
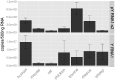
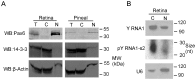
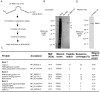
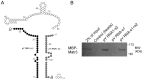
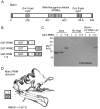
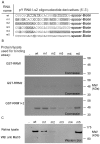
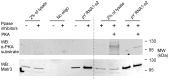
The purpose of this study was to expand our knowledge of small RNAs, which are known to function within protein complexes to modulate the transcriptional output of the cell. Here we describe two previously unrecognized, small RNAs, termed pY RNA1-s1 and pY RNA1-s2 (processed Y RNA1-stem -1 and -2), thereby expanding the list of known small RNAs. pY RNA1-s1 and pY RNA1-s2 were discovered by RNA sequencing and found to be 20-fold more abundant in the retina than in 14 other rat tissues. Retinal expression of pY RNAs is highly conserved, including expression in the human retina, and occurs in all retinal cell layers. Mass spectrometric analysis of pY RNA1-S2 binding proteins in retina indicates that pY RNA1-s2 selectively binds the nuclear matrix protein Matrin 3 (Matr3) and to a lesser degree to hnrpul1 (heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U-like protein). In contrast, pY RNA1-s1 does not bind these proteins. Accordingly, the molecular mechanism of action of pY RNA1-s2 is likely be through an action involving Matr3; this 95 kDa protein has two RNA recognition motifs (RRMs) and is implicated in transcription and RNA-editing. The high affinity binding of pY RNA1-s2 to Matr3 is strongly dependent on the sequence of the RNA and both RRMs of Matr3. Related studies also indicate that elements outside of the RRM region contribute to binding specificity and that phosphorylation enhances pY RNA-s2/Matr3 binding. These observations are of significance because they reveal that a previously unrecognized small RNA, pY RNA1-s2, binds selectively to Matr3. Hypothetically, pY RNA1-S2 might act to modulate cellular function through this molecular mechanism. The retinal enrichment of pY RNA1-s2 provides reason to suspect that the pY RNA1-s2/Matr3 interaction could play a role in vision.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Matrin 3 in neuromuscular disease: physiology and pathophysiology.JCI Insight. 2021 Jan 11;6(1):e143948. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.143948. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 33427209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Matrin 3 binds and stabilizes mRNA.PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23882. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0023882. Epub 2011 Aug 17. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21858232 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-recognition motif in Matrin-3 mediates neurodegeneration through interaction with hnRNPM.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020 Aug 18;8(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s40478-020-01021-5. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020. PMID: 32811564 Free PMC article.
-
Matrin 3-dependent neurotoxicity is modified by nucleic acid binding and nucleocytoplasmic localization.Elife. 2018 Jul 17;7:e35977. doi: 10.7554/eLife.35977. Elife. 2018. PMID: 30015619 Free PMC article.
-
A family of small nucleoplasmic RNAs with common structural features.Biol Cell. 1984;51(1):1-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1768-322x.1984.tb00278.x. Biol Cell. 1984. PMID: 6207876 Review.
Cited by
-
An augmentation in histone dimethylation at lysine nine residues elicits vision impairment following traumatic brain injury.Free Radic Biol Med. 2019 Apr;134:630-643. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.02.015. Epub 2019 Feb 18. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 30790655 Free PMC article.
-
Resource: A multi-species multi-timepoint transcriptome database and webpage for the pineal gland and retina.J Pineal Res. 2020 Oct;69(3):e12673. doi: 10.1111/jpi.12673. Epub 2020 Jul 8. J Pineal Res. 2020. PMID: 32533862 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear matrix protein Matrin3 regulates alternative splicing and forms overlapping regulatory networks with PTB.EMBO J. 2015 Mar 4;34(5):653-68. doi: 10.15252/embj.201489852. Epub 2015 Jan 19. EMBO J. 2015. PMID: 25599992 Free PMC article.
-
Matrin 3 in neuromuscular disease: physiology and pathophysiology.JCI Insight. 2021 Jan 11;6(1):e143948. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.143948. JCI Insight. 2021. PMID: 33427209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional roles of non-coding Y RNAs.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Sep;66:20-9. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.07.003. Epub 2015 Jul 6. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26159929 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Meister G, Landthaler M, Peters L, Chen PY, Urlaub H, et al. (2005) Identification of novel argonaute-associated proteins. Curr Biol 15: 2149–2155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

