SOX9: a stem cell transcriptional regulator of secreted niche signaling factors
- PMID: 24532713
- PMCID: PMC3937512
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.233247.113
SOX9: a stem cell transcriptional regulator of secreted niche signaling factors
Abstract
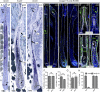
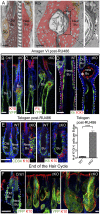
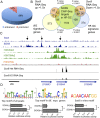
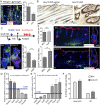
Hair follicles (HFs) undergo cyclical periods of growth, which are fueled by stem cells (SCs) at the base of the resting follicle. HF-SC formation occurs during HF development and requires transcription factor SOX9. Whether and how SOX9 functions in HF-SC maintenance remain unknown. By conditionally targeting Sox9 in adult HF-SCs, we show that SOX9 is essential for maintaining them. SOX9-deficient HF-SCs still transition from quiescence to proliferation and launch the subsequent hair cycle. However, once activated, bulge HF-SCs begin to differentiate into epidermal cells, which naturally lack SOX9. In addition, as HF-SC numbers dwindle, outer root sheath production is not sustained, and HF downgrowth arrests prematurely. Probing the mechanism, we used RNA sequencing (RNA-seq) to identify SOX9-dependent transcriptional changes and chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) and deep sequencing (ChIP-seq) to identify SOX9-bound genes in HF-SCs. Intriguingly, a large cohort of SOX9-sensitive targets encode extracellular factors, most notably enhancers of Activin/pSMAD2 signaling. Moreover, compromising Activin signaling recapitulates SOX9-dependent defects, and Activin partially rescues them. Overall, our findings reveal roles for SOX9 in regulating adult HF-SC maintenance and suppressing epidermal differentiation in the niche. In addition, our studies expose a role for SCs in coordinating their own behavior in part through non-cell-autonomous signaling within the niche.
Keywords: Activin; SOX9; hair follicle; skin; stem cells.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mapping the expression of epithelial hair follicle stem cell-related transcription factors LHX2 and SOX9 in the human hair follicle.Exp Dermatol. 2015 Jun;24(6):462-7. doi: 10.1111/exd.12700. Exp Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 25808706
-
Lhx2 differentially regulates Sox9, Tcf4 and Lgr5 in hair follicle stem cells to promote epidermal regeneration after injury.Development. 2011 Nov;138(22):4843-52. doi: 10.1242/dev.070284. Development. 2011. PMID: 22028024 Free PMC article.
-
Sox9 is essential for outer root sheath differentiation and the formation of the hair stem cell compartment.Curr Biol. 2005 Aug 9;15(15):1340-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.06.064. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16085486
-
Unveiling hair follicle stem cells.Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2010 Dec;6(4):658-64. doi: 10.1007/s12015-010-9172-z. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2010. PMID: 20676942 Review.
-
Notch signaling and the developing hair follicle.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;727:142-60. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4614-0899-4_11. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012. PMID: 22399345 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Non-coding RNAs in the Response of Glioblastoma to Temozolomide.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Feb;62(2):1726-1755. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04316-z. Epub 2024 Jul 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 39023794 Review.
-
Chemotherapy-Induced Distal Enhancers Drive Transcriptional Programs to Maintain the Chemoresistant State in Ovarian Cancer.Cancer Res. 2019 Sep 15;79(18):4599-4611. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0215. Epub 2019 Jul 29. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31358529 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of SOX9 Is Related to Prognosis in Patients with Oesophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma.In Vivo. 2018 Jul-Aug;32(4):835-838. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11316. In Vivo. 2018. PMID: 29936467 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring differentially expressed genes between anagen and telogen secondary hair follicle stem cells from the Cashmere goat (Capra hircus) by RNA-Seq.PLoS One. 2020 Apr 16;15(4):e0231376. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231376. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32298297 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-5195-3p mediated malignant biological behaviour of insulin-resistant liver cancer cells via SOX9 and TPM4.BMC Cancer. 2023 Jun 16;23(1):557. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-11068-x. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37328795 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blanpain C, Lowry WE, Geoghegan A, Polak L, Fuchs E 2004. Self-renewal, multipotency, and the existence of two cell populations within an epithelial stem cell niche. Cell 118: 635–648 - PubMed
-
- Botchkarev VA, Botchkareva NV, Roth W, Nakamura M, Chen LH, Herzog W, Lindner G, McMahon JA, Peters C, Lauster R, et al. 1999. Noggin is a mesenchymally derived stimulator of hair-follicle induction. Nat Cell Biol 1: 158–164 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
