Erk1/2 activity promotes chromatin features and RNAPII phosphorylation at developmental promoters in mouse ESCs
- PMID: 24529373
- PMCID: PMC4006806
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2014.01.009
Erk1/2 activity promotes chromatin features and RNAPII phosphorylation at developmental promoters in mouse ESCs
Abstract
Erk1/2 activation contributes to mouse ES cell pluripotency. We found a direct role of Erk1/2 in modulating chromatin features required for regulated developmental gene expression. Erk2 binds to specific DNA sequence motifs typically accessed by Jarid2 and PRC2. Negating Erk1/2 activation leads to increased nucleosome occupancy and decreased occupancy of PRC2 and poised RNAPII at Erk2-PRC2-targeted developmental genes. Surprisingly, Erk2-PRC2-targeted genes are specifically devoid of TFIIH, known to phosphorylate RNA polymerase II (RNAPII) at serine-5, giving rise to its initiated form. Erk2 interacts with and phosphorylates RNAPII at its serine 5 residue, which is consistent with the presence of poised RNAPII as a function of Erk1/2 activation. These findings underscore a key role for Erk1/2 activation in promoting the primed status of developmental genes in mouse ES cells and suggest that the transcription complex at developmental genes is different than the complexes formed at other genes, offering alternative pathways of regulation.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

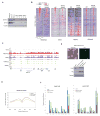

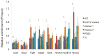
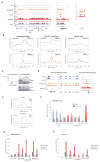
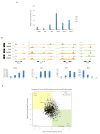

Comment in
-
Chromatin: ERK keeps promoters 'poised' for action.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Apr;15(4):219. doi: 10.1038/nrm3773. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24622618 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Pluripotency factors and Polycomb Group proteins repress aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression in murine embryonic stem cells.Stem Cell Res. 2014 Jan;12(1):296-308. doi: 10.1016/j.scr.2013.11.007. Epub 2013 Nov 16. Stem Cell Res. 2014. PMID: 24316986 Free PMC article.
-
Hira-dependent histone H3.3 deposition facilitates PRC2 recruitment at developmental loci in ES cells.Cell. 2013 Sep 26;155(1):107-20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.061. Cell. 2013. PMID: 24074864 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin: ERK keeps promoters 'poised' for action.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014 Apr;15(4):219. doi: 10.1038/nrm3773. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014. PMID: 24622618 No abstract available.
-
Working without kinase activity: phosphotransfer-independent functions of extracellular signal-regulated kinases.Sci Signal. 2011 Oct 25;4(196):re3. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.2002324. Sci Signal. 2011. PMID: 22028468 Review.
-
Modifications of RNA polymerase II are pivotal in regulating gene expression states.EMBO Rep. 2009 Nov;10(11):1213-9. doi: 10.1038/embor.2009.221. Epub 2009 Oct 16. EMBO Rep. 2009. PMID: 19834511 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinases: One Pathway, Multiple Fates.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Dec 24;16(1):95. doi: 10.3390/cancers16010095. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38201521 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nono, a Bivalent Domain Factor, Regulates Erk Signaling and Mouse Embryonic Stem Cell Pluripotency.Cell Rep. 2016 Oct 18;17(4):997-1007. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2016.09.078. Cell Rep. 2016. PMID: 27760330 Free PMC article.
-
Recruiting polycomb to chromatin.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;67:177-87. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.05.006. Epub 2015 May 14. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25982201 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel selective ERK1/2 inhibitor, Laxiflorin B, targets EGFR mutation subtypes in non-small-cell lung cancer.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Feb;45(2):422-435. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01164-w. Epub 2023 Oct 10. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 37816856 Free PMC article.
-
Conformation Selection by ATP-competitive Inhibitors and Allosteric Communication in ERK2.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 6:2023.09.12.557258. doi: 10.1101/2023.09.12.557258. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Elife. 2024 Mar 27;12:RP91507. doi: 10.7554/eLife.91507. PMID: 37745518 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

