Identification of a novel Parkinson's disease locus via stratified genome-wide association study
- PMID: 24511991
- PMCID: PMC3925254
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-118
Identification of a novel Parkinson's disease locus via stratified genome-wide association study
Abstract
Background: Parkinson's disease (PD) is complex and heterogeneous. The numerous susceptibility loci that have been identified reaffirm the complexity of PD but do not fully explain it; e.g., it is not known if any given PD susceptibility gene is associated with all PD or a disease subtype. We also suspect that important disease genes may have escaped detection because of this heterogeneity. We used presence/absence of family history to subdivide the cases and performed genome-wide association studies (GWAS) in Sporadic-PD and Familial-PD separately. The aim was to uncover new genes and gain insight into the genetic architecture of PD.
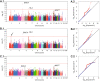
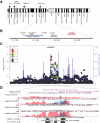
Results: Employing GWAS on the NeuroGenetics Research Consortium (NGRC) dataset stratified by family history (1565 Sporadic-PD, 435 Familial-PD, 1986 controls), we identified a novel locus on chromosome 1p21 in Sporadic-PD (PNGRC = 4 × 10(-8)) and replicated the finding (P(Replication) = 6 × 10(-3); P(Pooled) = 4 × 10(-10)) in 1528 Sporadic-PD and 796 controls from the National Institutes of Neurologic Disease and Stroke (NINDS) Repository. This is the fifth PD locus to be mapped to the short arm of chromosome 1. It is flanked by S1PR1 and OLFM3 genes, and is 200 kb from a multiple sclerosis susceptibility gene. The second aim of the study was to extend the stratified GWAS to the well-established PD genes. SNCA_ rs356220 was associated with both Sporadic-PD (OR = 1.37, P = 1 × 10(-9)) and Familial-PD (OR = 1.40, P = 2 × 10(-5)). HLA_rs3129882 was more strongly associated with Sporadic-PD (OR = 1.38, P = 5 × 10(-10)) than Familial-PD (OR = 1.12, P = 0.15). In the MAPT region, virtually every single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) had a stronger effect-size and lower P-value in Familial-PD (peak P = 8 × 10(-7)) than in Sporadic-PD (peak P = 2 × 10(-5)).
Conclusions: We discovered and replicated a new locus for Sporadic-PD which had escaped detection in un-stratified GWAS. This demonstrates that by stratifying on a key variable the power gained due to diminished heterogeneity can sometimes outweigh the power lost to reduced sample size. We also detected distinct patterns of disease associations for previously established PD susceptibility genes, which gives an insight to the genetic architecture of the disease and could aid in the selection of appropriate study population for future studies.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Meta-analysis of Parkinson's disease: identification of a novel locus, RIT2.Ann Neurol. 2012 Mar;71(3):370-84. doi: 10.1002/ana.22687. Ann Neurol. 2012. PMID: 22451204 Free PMC article.
-
Common genetic variation in the HLA region is associated with late-onset sporadic Parkinson's disease.Nat Genet. 2010 Sep;42(9):781-5. doi: 10.1038/ng.642. Epub 2010 Aug 15. Nat Genet. 2010. PMID: 20711177 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of genetic modifiers of age-at-onset for familial Parkinson's disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2016 Sep 1;25(17):3849-3862. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddw206. Epub 2016 Jul 11. Hum Mol Genet. 2016. PMID: 27402877 Free PMC article.
-
Association between alpha-synuclein (SNCA) rs11931074 variability and susceptibility to Parkinson's disease: an updated meta-analysis of 41,811 patients.Neurol Sci. 2020 Feb;41(2):271-280. doi: 10.1007/s10072-019-04107-8. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Neurol Sci. 2020. PMID: 31758346 Review.
-
Importance of familial Parkinson's disease and parkinsonism to the understanding of nigral degeneration in sporadic Parkinson's disease.J Neural Transm Suppl. 2000;(60):101-16. doi: 10.1007/978-3-7091-6301-6_6. J Neural Transm Suppl. 2000. PMID: 11205133 Review.
Cited by
-
Common Genetic Variant Association with Altered HLA Expression, Synergy with Pyrethroid Exposure, and Risk for Parkinson's Disease: An Observational and Case-Control Study.NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2015;1:15002-. doi: 10.1038/npjparkd.2015.2. Epub 2015 Apr 22. NPJ Parkinsons Dis. 2015. PMID: 27148593 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Alzheimer's Disease-Related Genes Based on Data Integration Method.Front Genet. 2019 Jan 25;9:703. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00703. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2019. PMID: 30740125 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of dimension reduction-based logistic regression models for case-control genome-wide association study: principal components analysis vs. partial least squares.J Biomed Res. 2015 Jul;29(4):298-307. doi: 10.7555/JBR.29.20140043. Epub 2015 Apr 20. J Biomed Res. 2015. PMID: 26243516 Free PMC article.
-
Sphingosine 1-Phosphate Receptors and Metabolic Enzymes as Druggable Targets for Brain Diseases.Front Pharmacol. 2019 Jul 23;10:807. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2019.00807. eCollection 2019. Front Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31427962 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neural ablation of the PARK10 candidate Plpp3 leads to dopaminergic transmission deficits without neurodegeneration.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 11;6:24028. doi: 10.1038/srep24028. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27063549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Do CB, Tung JY, Dorfman E, Kiefer AK, Drabant EM, Francke U, Mountain JL, Goldman SM, Tanner CM, Langston JW. et al.Web-based genome-wide association study identifies two novel loci and a substantial genetic component for Parkinson's disease. PLoS Genet. 2011;7:e1002141. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002141. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

