Mass primaquine treatment to eliminate vivax malaria: lessons from the past
- PMID: 24502194
- PMCID: PMC3931915
- DOI: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-51
Mass primaquine treatment to eliminate vivax malaria: lessons from the past
Abstract
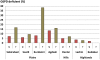
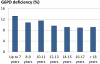
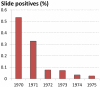
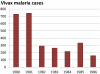
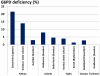
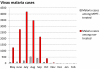
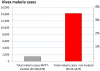
Recent successes in malaria control have put malaria eradication back on the public health agenda. A significant obstacle to malaria elimination in Asia is the large burden of Plasmodium vivax, which is more difficult to eliminate than Plasmodium falciparum. Persistent P. vivax liver stages can be eliminated only by radical treatment with a ≥ seven-day course of an 8-aminoquinoline, with the attendant risk of acute haemolytic anaemia in individuals with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency. Primaquine is the only generally available 8-aminoquinoline. Testing for G6PD deficiency is not widely available, and so whilst it is widely recommended, primaquine is often not prescribed. In the past, some countries aiming for vivax malaria eradication deployed mass treatments with primaquine on a massive scale, without G6PD testing. In Azerbaijan, Tajikistan (formerly USSR), North Afghanistan and DPR Korea 8,270,185 people received either a 14-day "standard" or a 17-day "interrupted" primaquine treatment to control post-eradication malaria epidemics. These mass primaquine preventive treatment campaigns were conducted by dedicated teams who administered the drugs under supervision and then monitored the population for adverse events. Despite estimated G6PD prevalences up to 38.7%, the reported frequency of severe adverse events related to primaquine was very low. This experience shows that with careful planning and implementation of mass treatment strategies using primaquine and adequate medical support to manage haemolytic toxicity, it is possible to achieve high population coverage, substantially reduce malaria transmission, and manage the risk of severe acute haemolytic anaemia in communities with a relatively high prevalence of G6PD deficiency safely.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Primaquine alternative dosing schedules for preventing malaria relapse in people with Plasmodium vivax.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Aug 19;8:CD012656. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD012656.pub3. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32816320
-
[Role of primaquine in malaria control and elimination in French-speaking Africa].Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 2017 Aug;110(3):198-206. doi: 10.1007/s13149-017-0556-z. Epub 2017 Apr 17. Bull Soc Pathol Exot. 2017. PMID: 28417346 Review. French.
-
Use of primaquine and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency testing: Divergent policies and practices in malaria endemic countries.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Apr 19;12(4):e0006230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006230. eCollection 2018 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29672516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tolerability and safety of weekly primaquine against relapse of Plasmodium vivax in Cambodians with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency.BMC Med. 2015 Aug 25;13:203. doi: 10.1186/s12916-015-0441-1. BMC Med. 2015. PMID: 26303162 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Sex-Stratified Plasmodium vivax Treatment Strategies Using Available G6PD Diagnostics to Accelerate Access to Radical Cure.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020 Jul;103(1):394-403. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.19-0943. Epub 2020 Apr 30. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2020. PMID: 32372747 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mathematical modelling of the impact of expanding levels of malaria control interventions on Plasmodium vivax.Nat Commun. 2018 Aug 17;9(1):3300. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-05860-8. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 30120250 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic Variation of G6PD and CYP2D6: Clinical Implications on the Use of Primaquine for Elimination of Plasmodium vivax.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Nov 26;12:784909. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.784909. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34899347 Free PMC article.
-
Primaquine: the risks and the benefits.Malar J. 2014 Nov 3;13:418. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-13-418. Malar J. 2014. PMID: 25363455 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Malaria Diagnosis Across the International Centers of Excellence for Malaria Research: Platforms, Performance, and Standardization.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015 Sep;93(3 Suppl):99-109. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.15-0004. Epub 2015 Aug 10. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2015. PMID: 26259937 Free PMC article. Review.
-
To Eradicate Malaria on the Korean Peninsula, Accurate Democratic People's Republic of Korea Malaria Statistics Are Needed.J Korean Med Sci. 2019 Sep 23;34(36):e249. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e249. J Korean Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 31538421 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Luzzatto L, Poggi V. In: Nathan and Oski’s hematology of infancy and childhood. 7. Orkin, editor. Canada: Saunders; 2009. Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Deficiency (chapter 17)
-
- Howes RE, Battle KE, Satyagraha AW, Baird JK, Hay SI. G6PD deficiency: global distribution, genetic variants and primaquine therapy. Adv Parasitol. 2013;81:133–201. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

