Integrated analysis of differential miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in human radioresistant and radiosensitive nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
- PMID: 24498188
- PMCID: PMC3909230
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0087767
Integrated analysis of differential miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in human radioresistant and radiosensitive nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells
Abstract
Background: The purpose of this study was to identify miRNAs and genes involved in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) radioresistance, and explore the underlying mechanisms in the development of radioresistance.
Methods: We used microarrays to compare the differences of both miRNA and mRNA expression profiles in the radioresistant NPC CNE2-IR and radiosensitive NPC CNE2 cells, applied qRT-PCR to confirm the reliability of microarray data, adopted databases prediction and anticorrelated analysis of miRNA and mRNA expression to identify the miRNA target genes, and employed bioinformatics tools to examine the functions and pathways in which miRNA target genes are involved, and construct a miRNA-target gene regulatory network. We further investigated the roles of miRNA-23a and its target gene IL-8 in the NPC radioresistance.
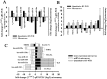
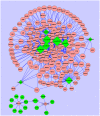
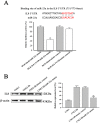
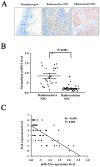
Results: THE MAIN FINDINGS WERE FOURFOLD: (1) fifteen differential miRNAs and 372 differential mRNAs were identified, and the reliability of microarray data was validated for randomly selected eight miRNAs and nine genes; (2) 174 miRNA target were identified, and most of their functions and regulating pathways were related to tumor therapeutic resistance; (3) a posttranscriptional regulatory network including 375 miRNA-target gene pairs was constructed, in which the ten genes were coregulated by the six miRNAs; (4) IL-8 was a direct target of miRNA-23a, the expression levels of IL-8 were elevated in the radioresistant NPC tissues and showed inverse correlation with miRNA-23a expression, and genetic upregulation of miRNA-23a and antibody neutralization of secretory IL-8 could reduce NPC cells radioresistance.
Conclusions: We identified fifteen differential miRNAs and 372 differential mRNAs in the radioresistant NPC cells, constructed a posttranscriptional regulatory network including 375 miRNA-target gene pairs, discovered the ten target genes coregulated by the six miRNAs, and validated that downregulated miRNA-23a was involved in NPC radioresistance through directly targeting IL-8. Our data form a basis for further investigating the mechanisms of NPC radioresistance.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
MiR-23a sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma to irradiation by targeting IL-8/Stat3 pathway.Oncotarget. 2015 Sep 29;6(29):28341-56. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5117. Oncotarget. 2015. PMID: 26314966 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-wide analyses of long noncoding RNA expression profiles correlated with radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via next-generation deep sequencing.BMC Cancer. 2016 Sep 6;16(1):719. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2755-6. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27599611 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of miRNA/mRNA-Negative Regulation Pairs in Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma.Med Sci Monit. 2016 Jun 28;22:2215-34. doi: 10.12659/msm.896047. Med Sci Monit. 2016. PMID: 27350400 Free PMC article.
-
Radio-Susceptibility of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma: Focus on Epstein- Barr Virus, MicroRNAs, Long Non-Coding RNAs and Circular RNAs.Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2020;13(3):192-205. doi: 10.2174/1874467213666191227104646. Curr Mol Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31880267 Review.
-
MicroRNAs in nasopharyngeal carcinoma.Chin Clin Oncol. 2016 Apr;5(2):17. doi: 10.21037/cco.2016.03.09. Chin Clin Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27121877 Review.
Cited by
-
m6A Reader YTHDC2 Promotes Radiotherapy Resistance of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma via Activating IGF1R/AKT/S6 Signaling Axis.Front Oncol. 2020 Jul 31;10:1166. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.01166. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32850334 Free PMC article.
-
Improved Radiotherapy Sensitivity of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Cells by miR-29-3p Targeting COL1A1 3'-UTR.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Apr 29;25:3161-3169. doi: 10.12659/MSM.915624. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31034464 Free PMC article.
-
miRNA-17 promotes nasopharyngeal carcinoma radioresistance by targeting PTEN/AKT.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019 Jan 1;12(1):229-240. eCollection 2019. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2019. PMID: 31933738 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated analyses to reconstruct microRNA-mediated regulatory networks in mouse liver using high-throughput profiling.BMC Genomics. 2015;16 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-16-S2-S12. Epub 2015 Jan 21. BMC Genomics. 2015. PMID: 25707768 Free PMC article.
-
RNA-Seq analysis of peripheral blood mononuclear cells reveals unique transcriptional signatures associated with radiotherapy response of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and prognosis of head and neck cancer.Cancer Biol Ther. 2020;21(2):139-146. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2019.1670521. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Cancer Biol Ther. 2020. PMID: 31698994 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kristensen CA, Kjaer-Kristoffersen F, Sapru W, Berthelsen AK, Loft A, et al. (2007) Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Treatment planning with IMRT and 3D conformal radiotherapy. Acta Oncol 46: 214–20. - PubMed
-
- Lee AW, Poon YF, Foo W, Law SC, Cheung FK, et al. (1992) Retrospective analysis of 5037 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated during 1976–1985: overall survival and patterns of failure. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 23: 261–70. - PubMed
-
- Zhang Z, Zhu W, Zhang J, Guo L (2011) Tyrosine kinase Etk/BMX protects nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells from apoptosis induced by radiation. Cancer Biol Ther 11: 690–8. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

