Morphine inhibits migration of tumor-infiltrating leukocytes and suppresses angiogenesis associated with tumor growth in mice
- PMID: 24495739
- PMCID: PMC3969995
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.12.019
Morphine inhibits migration of tumor-infiltrating leukocytes and suppresses angiogenesis associated with tumor growth in mice
Abstract
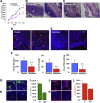
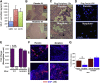
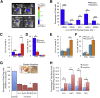
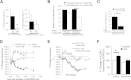
Tumor cells secrete factors that stimulate the migration of peripheral blood leukocytes and enhance tumor progression by affecting angiogenesis. In these studies, we investigated the effect of morphine, a known immunosuppressant, on leukocyte migration and recruitment to conditioned media derived from long-term cultures of mouse Lewis lung carcinoma cells. Our results indicate that morphine treatment reduced the migration and recruitment of tumor-infiltrating leukocytes into Matrigel plugs and polyvinyl alcohol sponges containing conditioned media derived from long-term cultures of mouse Lewis lung carcinoma cells when compared with placebo. A reciprocal increase in peripheral blood leukocytes was observed at the time of plug or sponge removal in morphine-treated mice. Decreased angiogenesis was observed in conditioned media derived from long-term cultures of mouse Lewis lung carcinoma cells Matrigel plugs taken from morphine-treated wild-type mice when compared with placebo but was abolished in morphine-treated μ-opioid receptor knockout mice. In addition, in vitro studies using trans-well and electric cell substrate impedance sensing system studies reveal for the first time morphine's inhibitory effects on leukocyte migration and their ability to transmigrate across an activated endothelial monolayer. Taken together, these studies indicate that morphine treatment can potentially decrease leukocyte transendothelial migration and reduce angiogenesis associated with tumor growth. The use of morphine for cancer pain management may be beneficial through its effects on angiogenesis.
Copyright © 2014 American Society for Investigative Pathology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Morphine suppresses tumor angiogenesis through a HIF-1alpha/p38MAPK pathway.Am J Pathol. 2010 Aug;177(2):984-97. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2010.090621. Epub 2010 Jul 8. Am J Pathol. 2010. PMID: 20616349 Free PMC article.
-
The immunosuppressive effects of chronic morphine treatment are partially dependent on corticosterone and mediated by the mu-opioid receptor.J Leukoc Biol. 2002 May;71(5):782-90. J Leukoc Biol. 2002. PMID: 11994502
-
The novel role of the mu opioid receptor in lung cancer progression: a laboratory investigation.Anesth Analg. 2011 Mar;112(3):558-67. doi: 10.1213/ANE.0b013e31820568af. Epub 2010 Dec 14. Anesth Analg. 2011. PMID: 21156980 Free PMC article.
-
Natriuretic peptide receptor A signaling regulates stem cell recruitment and angiogenesis: a model to study linkage between inflammation and tumorigenesis.Stem Cells. 2013 Jul;31(7):1321-9. doi: 10.1002/stem.1376. Stem Cells. 2013. PMID: 23533187 Free PMC article.
-
The role of morphine in regulation of cancer cell growth.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011 Sep;384(3):221-30. doi: 10.1007/s00210-011-0672-4. Epub 2011 Jul 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21800094 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Morphine as a treatment of cancer-induced pain-is it safe? A review of in vivo studies and mechanisms.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018 Nov;391(11):1169-1178. doi: 10.1007/s00210-018-1565-6. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30232510 Review.
-
Opioids and matrix metalloproteinases: the influence of morphine on MMP-9 production and cancer progression.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2019 Feb;392(2):123-133. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01613-6. Epub 2019 Jan 17. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 30656360 Review.
-
Influence of Perioperative Anesthesia on Cancer Recurrence: from Basic Science to Clinical Practice.Curr Oncol Rep. 2023 Feb;25(2):63-81. doi: 10.1007/s11912-022-01342-9. Epub 2022 Dec 13. Curr Oncol Rep. 2023. PMID: 36512273 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic immune effects of anesthetics and their intracellular targets in tumors.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 28;9:810189. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.810189. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35966857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Could Perioperative Opioid Use Increase the Risk of Cancer Progression and Metastases?Int Anesthesiol Clin. 2016 Fall;54(4):e1-e16. doi: 10.1097/AIA.0000000000000112. Int Anesthesiol Clin. 2016. PMID: 27602710 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
References
-
- Eyelade O.R., Ajayi I.O., Elumelu T.N., Soyannwo O.A., Akinyemi O.A. Oral morphine effectiveness in Nigerian patients with advanced cancer. J Pain Palliat Care Pharmacother. 2012;26:24–29. - PubMed
-
- Ohshima H., Bartsch H. Chronic infections and inflammatory processes as cancer risk factors: possible role of nitric oxide in carcinogenesis. Mutat Res. 1994;305:253–264. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y.C., Chen J.H., Richard K., Chen P.Y., Christiani D.C. Lung adenocarcinoma and human papillomavirus infection. Cancer. 2004;101:1428–1436. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DA012104/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DE007288/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- F31 DA021005/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- CA114340/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA015349/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- F31-DA021005-01/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA 022935/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K02 DA 015349/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- K05 DA033881/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA037843/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA034582/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA022935/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA031202/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA011806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- T32DE007288/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA114340/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DA 12104/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 DA 011806/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

