Genomic imprinting in mammals
- PMID: 24492710
- PMCID: PMC3941233
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a018382
Genomic imprinting in mammals
Abstract
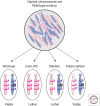
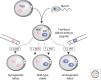
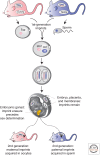
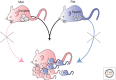
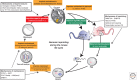
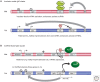
Genomic imprinting affects a subset of genes in mammals and results in a monoallelic, parental-specific expression pattern. Most of these genes are located in clusters that are regulated through the use of insulators or long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). To distinguish the parental alleles, imprinted genes are epigenetically marked in gametes at imprinting control elements through the use of DNA methylation at the very least. Imprinted gene expression is subsequently conferred through lncRNAs, histone modifications, insulators, and higher-order chromatin structure. Such imprints are maintained after fertilization through these mechanisms despite extensive reprogramming of the mammalian genome. Genomic imprinting is an excellent model for understanding mammalian epigenetic regulation.
Figures
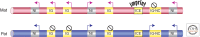

Similar articles
-
Genomic imprinting: employing and avoiding epigenetic processes.Genes Dev. 2009 Sep 15;23(18):2124-33. doi: 10.1101/gad.1841409. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19759261 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin mechanisms in genomic imprinting.Mamm Genome. 2009 Sep-Oct;20(9-10):544-56. doi: 10.1007/s00335-009-9223-4. Epub 2009 Sep 17. Mamm Genome. 2009. PMID: 19760321 Review.
-
Differential 3D chromatin organization and gene activity in genomic imprinting.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020 Apr;61:17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2020.03.004. Epub 2020 Apr 13. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2020. PMID: 32299027 Review.
-
Mammalian genomic imprinting.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011 Jul 1;3(7):a002592. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a002592. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2011. PMID: 21576252 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic imprinting mechanisms in mammals.Mutat Res. 2008 Dec 1;647(1-2):77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.08.008. Epub 2008 Aug 20. Mutat Res. 2008. PMID: 18778719 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Aberrations of Genomic Imprinting in Glioblastoma Formation.Front Oncol. 2021 Mar 12;11:630482. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.630482. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33777782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic Imprinting at the Porcine PLAGL1 Locus and the Orthologous Locus in the Human.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 8;12(4):541. doi: 10.3390/genes12040541. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33918057 Free PMC article.
-
ZFP57 maintains the parent-of-origin-specific expression of the imprinted genes and differentially affects non-imprinted targets in mouse embryonic stem cells.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 Sep 30;44(17):8165-78. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw505. Epub 2016 Jun 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 27257070 Free PMC article.
-
The role of M6A modification in the regulation of tumor-related lncRNAs.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021 Apr 9;24:768-779. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2021.04.002. eCollection 2021 Jun 4. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2021. PMID: 33996258 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation in adult neural stem cells.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jan 31;12:1331074. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1331074. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38357000 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Allis CD, Jenuwein T, Reinberg D 2014. Overview and concepts. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 10.1101/cshperspect.a018739 - DOI
-
- Barlow DP 2011. Genomic imprinting: A mammalian epigenetic discovery model. Annu Rev Genet 45: 379–403 - PubMed
-
- Barlow DP, Stoger R, Herrmann BG, Saito K, Schweifer N 1991. The mouse insulin-like growth factor type-2 receptor is imprinted and closely linked to the Tme locus. Nature 349: 84–87 - PubMed
WWW RESOURCES
-
- http://www.mousebook.org/catalog.php?catalog=imprinting. MouseBook, Medical Research Council.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
