Innate response activator B cells aggravate atherosclerosis by stimulating T helper-1 adaptive immunity
- PMID: 24488984
- PMCID: PMC3997655
- DOI: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.006381
Innate response activator B cells aggravate atherosclerosis by stimulating T helper-1 adaptive immunity
Abstract
Background: Atherosclerotic lesions grow via the accumulation of leukocytes and oxidized lipoproteins in the vessel wall. Leukocytes can attenuate or augment atherosclerosis through the release of cytokines, chemokines, and other mediators. Deciphering how leukocytes develop, oppose, and complement each other's function and shape the course of disease can illuminate our understanding of atherosclerosis. Innate response activator (IRA) B cells are a recently described population of granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor-secreting cells of hitherto unknown function in atherosclerosis.
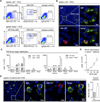
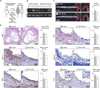
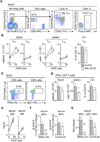
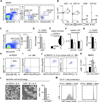
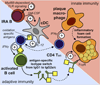
Methods and results: Here, we show that IRA B cells arise during atherosclerosis in mice and humans. In response to a high-cholesterol diet, IRA B cell numbers increase preferentially in secondary lymphoid organs via Myd88-dependent signaling. Mixed chimeric mice lacking B cell-derived granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor develop smaller lesions with fewer macrophages and effector T cells. Mechanistically, IRA B cells promote the expansion of classic dendritic cells, which then generate interferon γ-producing T helper-1 cells. This IRA B cell-dependent T helper-1 skewing manifests in an IgG1-to-IgG2c isotype switch in the immunoglobulin response against oxidized lipoproteins.
Conclusions: Granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor-producing IRA B cells alter adaptive immune processes and shift the leukocyte response toward a T helper-1-associated milieu that aggravates atherosclerosis.
Keywords: B-lymphocytes; T-lymphocytes; atherosclerosis; dendritic cells; granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; immunology.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-3/granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor promotes stem cell expansion, monocytosis, and atheroma macrophage burden in mice with hematopoietic ApoE deficiency.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014 May;34(5):976-84. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.113.303097. Epub 2014 Mar 20. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2014. PMID: 24651678 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically programmed biases in Th1 and Th2 immune responses modulate atherogenesis.Am J Pathol. 2008 Jun;172(6):1500-8. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070776. Epub 2008 May 8. Am J Pathol. 2008. PMID: 18467709 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidized low-density lipoproteins impair the pro-atherosclerotic effect of granulocyte-macrophage-colony-stimulating factor-producing T helper cells on macrophages.Scand J Immunol. 2024 May;99(5):e13362. doi: 10.1111/sji.13362. Epub 2024 Feb 14. Scand J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38605563
-
Innate response activator B cells: origins and functions.Int Immunol. 2015 Oct;27(10):537-41. doi: 10.1093/intimm/dxv028. Epub 2015 May 8. Int Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25957266 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune-inflammatory responses in atherosclerosis: Role of an adaptive immunity mainly driven by T and B cells.Immunobiology. 2016 Sep;221(9):1014-33. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2016.05.010. Epub 2016 May 24. Immunobiology. 2016. PMID: 27262513 Review.
Cited by
-
Lifestyle effects on hematopoiesis and atherosclerosis.Circ Res. 2015 Feb 27;116(5):884-94. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.303550. Circ Res. 2015. PMID: 25722442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Spectrum of B Cell Functions in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Apr 15;9:864602. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.864602. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35497984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disordered haematopoiesis and athero-thrombosis.Eur Heart J. 2016 Apr 7;37(14):1113-21. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehv718. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Eur Heart J. 2016. PMID: 26869607 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of immune cells in different stages of atherosclerosis.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Apr 22;21(6):1129-1143. doi: 10.7150/ijms.94570. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38774746 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-inflammatory and Immunomodulatory Therapies in Atherosclerosis.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022;270:359-404. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_505. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34251531 Review.
References
-
- Ait-Oufella H, Salomon BL, Potteaux S, Robertson AK, Gourdy P, Zoll J, Merval R, Esposito B, Cohen JL, Fisson S, Flavell RA, Hansson GK, Klatzmann D, Tedgui A, Mallat Z. Natural regulatory T cells control the development of atherosclerosis in mice. Nat Med. 2006;12:178–180. - PubMed
-
- Herbin O, Ait-Oufella H, Yu W, Fredrikson GN, Aubier B, Perez N, Barateau V, Nilsson J, Tedgui A, Mallat Z. Regulatory T-cell response to apolipoprotein B100-derived peptides reduces the development and progression of atherosclerosis in mice. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32:605–612. - PubMed
-
- Klingenberg R, Gerdes N, Badeau RM, Gistera A, Strodthoff D, Ketelhuth DF, Lundberg AM, Rudling M, Nilsson SK, Olivecrona G, Zoller S, Lohmann C, Luscher TF, Jauhiainen M, Sparwasser T, Hansson GK. Depletion of FOXP3+ regulatory T cells promotes hypercholesterolemia and atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 2013;123:1323–1334. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Kyaw T, Tay C, Krishnamurthi S, Kanellakis P, Agrotis A, Tipping P, Bobik A, Toh BH. B1a B lymphocytes are atheroprotective by secreting natural IgM that increases IgM deposits and reduces necrotic cores in atherosclerotic lesions. Circ Res. 2011;109:830–840. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

