Overexpression of VP, a vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase gene in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), improves tobacco plant growth under Pi and N deprivation, high salinity, and drought
- PMID: 24474810
- PMCID: PMC3904725
- DOI: 10.1093/jxb/ert442
Overexpression of VP, a vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase gene in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), improves tobacco plant growth under Pi and N deprivation, high salinity, and drought
Retraction in
-
RETRACTION of: Overexpression of VP, a vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase gene in wheat (Triticum aestivum L.), improves tobacco plant growth under Pi and N deprivation, high salinity, and drought.J Exp Bot. 2016 Apr;67(9):2913. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw149. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 27162277 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
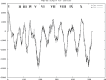
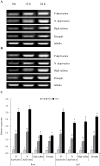
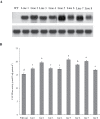
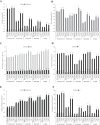
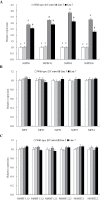
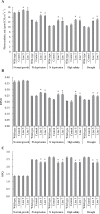
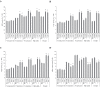
Establishing crop cultivars with strong tolerance to P and N deprivation, high salinity, and drought is an effective way to improve crop yield and promote sustainable agriculture worldwide. A vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase (V-H+-PPase) gene in wheat (TaVP) was functionally characterized in this study. TaVP cDNA is 2586-bp long and encodes a 775-amino-acid polypeptide that contains 10 conserved membrane-spanning domains. Transcription of TaVP was upregulated by inorganic phosphate (Pi) and N deprivation, high salinity, and drought. Transgene analysis revealed that TaVP overexpression improved plant growth under normal conditions and specifically under Pi and N deprivation stresses, high salinity, and drought. The improvement of growth of the transgenic plants was found to be closely related to elevated V-H+-PPase activities in their tonoplasts and enlarged root systems, which possibly resulted from elevated expression of auxin transport-associated genes. TaVP-overexpressing plants showed high dry mass, photosynthetic efficiencies, antioxidant enzyme activities, and P, N, and soluble carbohydrate concentrations under various growth conditions, particularly under the stress conditions. The transcription of phosphate and nitrate transporter genes was not altered in TaVP-overexpressing plants compared with the wild type, suggesting that high P and N concentrations regulated by TaVP were caused by increased root absorption area instead of alteration of Pi and NO3- acquisition kinetics. TaVP is important in the tolerance of multiple stresses and can serve as a useful genetic resource to improve plant P- and N-use efficiencies and to increase tolerance to high salinity and drought.
Keywords: Abiotic stresses; gene expression; physiological and biochemical property; plant growth; transgene analysis; vacuolar H+-pyrophosphatase..
Figures

Similar articles
-
Cloning of a vacuolar H(+)-pyrophosphatase gene from the halophyte Suaeda corniculata whose heterologous overexpression improves salt, saline-alkali and drought tolerance in Arabidopsis.J Integr Plant Biol. 2011 Sep;53(9):731-42. doi: 10.1111/j.1744-7909.2011.01066.x. J Integr Plant Biol. 2011. PMID: 21762382
-
Gene encoding vesicle-associated membrane protein-associated protein from Triticum aestivum (TaVAP) confers tolerance to drought stress.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018 May;23(3):411-428. doi: 10.1007/s12192-017-0854-1. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2018. PMID: 29116579 Free PMC article.
-
Expression of wheat Na(+)/H(+) antiporter TNHXS1 and H(+)- pyrophosphatase TVP1 genes in tobacco from a bicistronic transcriptional unit improves salt tolerance.Plant Mol Biol. 2012 May;79(1-2):137-55. doi: 10.1007/s11103-012-9901-6. Epub 2012 Mar 14. Plant Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22415161
-
Auxin response factors in plant adaptation to drought and salinity stress.Physiol Plant. 2022 May;174(3):e13714. doi: 10.1111/ppl.13714. Physiol Plant. 2022. PMID: 35560231 Review.
-
Improvement of morphophysiological and anatomical attributes of plants under abiotic stress conditions using plant growth-promoting bacteria and safety treatments.PeerJ. 2024 Apr 30;12:e17286. doi: 10.7717/peerj.17286. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 38708356 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Job Sharing in the Endomembrane System: Vacuolar Acidification Requires the Combined Activity of V-ATPase and V-PPase.Plant Cell. 2015 Dec;27(12):3383-96. doi: 10.1105/tpc.15.00733. Epub 2015 Nov 20. Plant Cell. 2015. PMID: 26589552 Free PMC article.
-
Constitutive and Companion Cell-Specific Overexpression of AVP1, Encoding a Proton-Pumping Pyrophosphatase, Enhances Biomass Accumulation, Phloem Loading, and Long-Distance Transport.Plant Physiol. 2016 Jan;170(1):401-14. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01409. Epub 2015 Nov 3. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26530315 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization and expression analyses of the H⁺-pyrophosphatase gene in rye.J Genet. 2016 Sep;95(3):565-72. doi: 10.1007/s12041-016-0664-8. J Genet. 2016. PMID: 27659326
-
MicroRNA: a new target for improving plant tolerance to abiotic stress.J Exp Bot. 2015 Apr;66(7):1749-61. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erv013. Epub 2015 Feb 19. J Exp Bot. 2015. PMID: 25697792 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nitrogen application and differences in leaf number retained after topping affect the tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) transcriptome and metabolome.BMC Plant Biol. 2022 Jan 19;22(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s12870-022-03426-x. BMC Plant Biol. 2022. PMID: 35045826 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ai PH, Sun SB, Zhao JN, et al. 2009. Two rice phosphate transporters, OsPht1;2 and OsPht1;6, have different functions and kinetic properties in uptake and translocation. The Plant Journal 57, 798–809 - PubMed
-
- Amiour N, Imbaud S, Clément G, et al. 2012. The use of metabolomics integrated with transcriptomic and proteomic studies for identifying key steps involved in the control of nitrogen metabolism in crops such as maize. Journal of Experimental Botany 63, 5017–5033 - PubMed
-
- Bartels D, Sunkar R. 2005. Drought and salt tolerance in plants. Critical Reviews in Plant Science 24, 23–58
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

