Reproducible selection of high avidity CD8+ T-cell clones following secondary acute virus infection
- PMID: 24474775
- PMCID: PMC3910643
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1323736111
Reproducible selection of high avidity CD8+ T-cell clones following secondary acute virus infection
Abstract
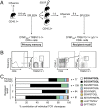
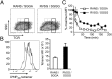
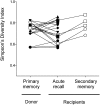
The recall of memory CD8(+) cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs), elicited by prior virus infection or vaccination, is critical for immune protection. The extent to which this arises as a consequence of stochastic clonal expansion vs. active selection of particular clones remains unclear. Using a parallel adoptive transfer protocol in combination with single cell analysis to define the complementarity determining region (CDR) 3α and CDR3β regions of individual T-cell receptor (TCR) heterodimers, we characterized the antigen-driven recall of the same memory CTL population in three individual recipients. This high-resolution analysis showed reproducible enrichment (or diminution) of particular TCR clonotypes across all challenged animals. These changes in clonal composition were TCRα- and β chain-dependent and were directly related to the avidity of the TCR for the virus-derived peptide (p) + major histocompatibility complex class I molecule. Despite this shift in clonotype representation indicative of differential selection, there was no evidence of overall repertoire narrowing, suggesting a strategy to optimize CTL responses while safeguarding TCR diversity.
Keywords: antiviral immunity; clonal selection; influenza virus; memory CD8+ T cells; recall CD8+ T-cell response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase is required for the establishment of private virus-specific CD8+ TCR repertoires and facilitates optimal CTL responses.J Immunol. 2008 Aug 15;181(4):2556-62. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.181.4.2556. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18684946 Free PMC article.
-
Paired TCRαβ analysis of virus-specific CD8(+) T cells exposes diversity in a previously defined 'narrow' repertoire.Immunol Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;93(9):804-14. doi: 10.1038/icb.2015.44. Epub 2015 Mar 25. Immunol Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 25804828 Free PMC article.
-
Homogenization of TCR repertoires within secondary CD62Lhigh and CD62Llow virus-specific CD8+ T cell populations.J Immunol. 2008 Jun 15;180(12):7938-47. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.180.12.7938. J Immunol. 2008. PMID: 18523257
-
Characterization of CD8+ T cell repertoire diversity and persistence in the influenza A virus model of localized, transient infection.Semin Immunol. 2004 Jun;16(3):179-84. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2004.02.005. Semin Immunol. 2004. PMID: 15130502 Review.
-
Establishment and recall of CD8+ T-cell memory in a model of localized transient infection.Immunol Rev. 2006 Jun;211:133-45. doi: 10.1111/j.0105-2896.2006.00386.x. Immunol Rev. 2006. PMID: 16824123 Review.
Cited by
-
Influenza-specific lung-resident memory T cells are proliferative and polyfunctional and maintain diverse TCR profiles.J Clin Invest. 2018 Feb 1;128(2):721-733. doi: 10.1172/JCI96957. Epub 2018 Jan 8. J Clin Invest. 2018. PMID: 29309047 Free PMC article.
-
Structural Basis for Clonal Diversity of the Public T Cell Response to a Dominant Human Cytomegalovirus Epitope.J Biol Chem. 2015 Nov 27;290(48):29106-19. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.691311. Epub 2015 Oct 1. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 26429912 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Sizing up the key determinants of the CD8(+) T cell response.Nat Rev Immunol. 2015 Nov;15(11):705-16. doi: 10.1038/nri3905. Epub 2015 Oct 9. Nat Rev Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26449178 Review.
-
Selective expansion of high functional avidity memory CD8 T cell clonotypes during hepatitis C virus reinfection and clearance.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Feb 1;13(2):e1006191. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006191. eCollection 2017 Feb. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28146579 Free PMC article.
-
Differential tumor immune microenvironment coupled with tumor progression or tumor eradication in HPV-antigen expressing squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) models.Front Immunol. 2024 Jul 11;15:1405318. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1405318. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39055715 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Williams MA, Bevan MJ. Effector and memory CTL differentiation. Annu Rev Immunol. 2007;25:171–192. - PubMed
-
- Messaoudi I, Guevara Patiño JA, Dyall R, LeMaoult J, Nikolich-Zugich J. Direct link between mhc polymorphism, T cell avidity, and diversity in immune defense. Science. 2002;298(5599):1797–1800. - PubMed
-
- Price DA, et al. T cell receptor recognition motifs govern immune escape patterns in acute SIV infection. Immunity. 2004;21(6):793–803. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

