Btk regulates macrophage polarization in response to lipopolysaccharide
- PMID: 24465735
- PMCID: PMC3897530
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085834
Btk regulates macrophage polarization in response to lipopolysaccharide
Abstract
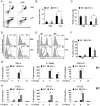
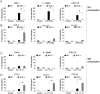
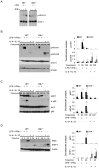
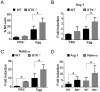
Bacterial Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) is a strong inducer of inflammation and does so by inducing polarization of macrophages to the classic inflammatory M1 population. Given the role of Btk as a critical signal transducer downstream of TLR4, we investigated its role in M1/M2 induction. In Btk deficient (Btk (-\-)) mice we observed markedly reduced recruitment of M1 macrophages following intraperitoneal administration of LPS. Ex vivo analysis demonstrated an impaired ability of Btk(-/-) macrophages to polarize into M1 macrophages, instead showing enhanced induction of immunosuppressive M2-associated markers in response to M1 polarizing stimuli, a finding accompanied by reduced phosphorylation of STAT1 and enhanced STAT6 phosphorylation. In addition to STAT activation, M1 and M2 polarizing signals modulate the expression of inflammatory genes via differential activation of transcription factors and regulatory proteins, including NF-κB and SHIP1. In keeping with a critical role for Btk in macrophage polarization, we observed reduced levels of NF-κB p65 and Akt phosphorylation, as well as reduced induction of the M1 associated marker iNOS in Btk(-/-) macrophages in response to M1 polarizing stimuli. Additionally enhanced expression of SHIP1, a key negative regulator of macrophage polarisation, was observed in Btk(-/-) macrophages in response to M2 polarizing stimuli. Employing classic models of allergic M2 inflammation, treatment of Btk (-/-) mice with either Schistosoma mansoni eggs or chitin resulted in increased recruitment of M2 macrophages and induction of M2-associated genes. This demonstrates an enhanced M2 skew in the absence of Btk, thus promoting the development of allergic inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pinosylvin Shifts Macrophage Polarization to Support Resolution of Inflammation.Molecules. 2021 May 8;26(9):2772. doi: 10.3390/molecules26092772. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34066748 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular HSP90α Induces MyD88-IRAK Complex-Associated IKKα/β-NF-κB/IRF3 and JAK2/TYK2-STAT-3 Signaling in Macrophages for Tumor-Promoting M2-Polarization.Cells. 2022 Jan 11;11(2):229. doi: 10.3390/cells11020229. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35053345 Free PMC article.
-
Pyropia yezoensis glycoprotein promotes the M1 to M2 macrophage phenotypic switch via the STAT3 and STAT6 transcription factors.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Aug;38(2):666-74. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2656. Epub 2016 Jun 24. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 27353313
-
Macrophage Polarization Induced by Probiotic Bacteria: a Concise Review.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2020 Sep;12(3):798-808. doi: 10.1007/s12602-019-09612-y. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2020. PMID: 31741313 Review.
-
Polarized Macrophages in Periodontitis: Characteristics, Function, and Molecular Signaling.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 7;12:763334. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.763334. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34950140 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gαi1 and Gαi3 regulate macrophage polarization by forming a complex containing CD14 and Gab1.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015 Apr 14;112(15):4731-6. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1503779112. Epub 2015 Mar 30. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015. PMID: 25825741 Free PMC article.
-
Small molecules in the treatment of COVID-19.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Dec 5;7(1):387. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01249-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 36464706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents for COVID-19: A review.Metabol Open. 2021 Sep;11:100116. doi: 10.1016/j.metop.2021.100116. Epub 2021 Jul 29. Metabol Open. 2021. PMID: 34345815 Free PMC article.
-
Protectin DX increases survival in a mouse model of sepsis by ameliorating inflammation and modulating macrophage phenotype.Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 7;7(1):99. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-00103-0. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28273909 Free PMC article.
-
CXCR4-BTK axis mediate pyroptosis and lipid peroxidation in early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage via NLRP3 inflammasome and NF-κB pathway.Redox Biol. 2023 Dec;68:102960. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2023.102960. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Redox Biol. 2023. PMID: 37979447 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

