FoxO transcription factors promote AKT Ser473 phosphorylation and renal tumor growth in response to pharmacologic inhibition of the PI3K-AKT pathway
- PMID: 24448243
- PMCID: PMC4087030
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-1729
FoxO transcription factors promote AKT Ser473 phosphorylation and renal tumor growth in response to pharmacologic inhibition of the PI3K-AKT pathway
Abstract
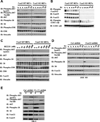
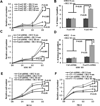
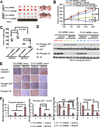
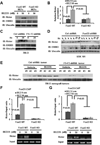
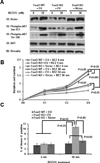
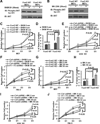
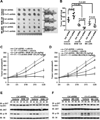
The PI3K-AKT pathway is hyperactivated in many human cancers, and several drugs to inhibit this pathway, including the PI3K/mTOR dual inhibitor NVP-BEZ235, are currently being tested in various preclinical and clinical trials. It has been shown that pharmacologic inhibition of the PI3K-AKT pathway results in feedback activation of other oncogenic signaling pathways, which likely will limit the clinical utilization of these inhibitors in cancer treatment. However, the underlying mechanisms of such feedback regulation remain incompletely understood. The PI3K-AKT pathway is a validated therapeutic target in renal cell carcinoma (RCC). Here, we show that FoxO transcription factors serve to promote AKT phosphorylation at Ser473 in response to NVP-BEZ235 treatment in renal cancer cells. Inactivation of FoxO attenuated NVP-BEZ235-induced AKT Ser473 phosphorylation and rendered renal cancer cells more susceptible to NVP-BEZ235-mediated cell growth suppression in vitro and tumor shrinkage in vivo. Mechanistically, we showed that FoxOs upregulated the expression of Rictor, an essential component of MTOR complex 2, in response to NVP-BEZ235 treatment and revealed that Rictor is a key downstream target of FoxOs in NVP-BEZ235-mediated feedback regulation. Finally, we show that FoxOs similarly modulate the feedback response on AKT Ser473 phosphorylation and renal tumor growth by other phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) or AKT inhibitor treatment. Together, our study reveals a novel mechanism of PI3K-AKT inhibition-mediated feedback regulation and may identify FoxO as a novel biomarker to stratify patients with RCC for PI3K or AKT inhibitor treatment, or a novel therapeutic target to synergize with PI3K-AKT inhibition in RCC treatment.
©2014 AACR.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure of Potential Conflicts of Interest: The authors disclose no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of autophagy enhances apoptosis induced by the PI3K/AKT/mTor inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 in renal cell carcinoma cells.Cell Biochem Funct. 2013 Jul;31(5):427-33. doi: 10.1002/cbf.2917. Epub 2012 Oct 22. Cell Biochem Funct. 2013. PMID: 23086777
-
The efficacy of the novel dual PI3-kinase/mTOR inhibitor NVP-BEZ235 compared with rapamycin in renal cell carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2010 Jul 15;16(14):3628-38. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-09-3022. Epub 2010 Jul 6. Clin Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20606035 Free PMC article.
-
Genotype-dependent efficacy of a dual PI3K/mTOR inhibitor, NVP-BEZ235, and an mTOR inhibitor, RAD001, in endometrial carcinomas.PLoS One. 2012;7(5):e37431. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0037431. Epub 2012 May 25. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 22662154 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiating mTOR inhibitors in renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Treat Rev. 2013 Nov;39(7):709-19. doi: 10.1016/j.ctrv.2012.12.015. Epub 2013 Feb 21. Cancer Treat Rev. 2013. PMID: 23433636 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The PI3K/AKT Pathway and Renal Cell Carcinoma.J Genet Genomics. 2015 Jul 20;42(7):343-53. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2015.03.003. Epub 2015 Mar 19. J Genet Genomics. 2015. PMID: 26233890 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Thyrotroph embryonic factor is downregulated in bladder cancer and suppresses proliferation and tumorigenesis via the AKT/FOXOs signalling pathway.Cell Prolif. 2019 Mar;52(2):e12560. doi: 10.1111/cpr.12560. Epub 2018 Dec 4. Cell Prolif. 2019. PMID: 30515906 Free PMC article.
-
mTOR Complexes as a Nutrient Sensor for Driving Cancer Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Oct 21;19(10):3267. doi: 10.3390/ijms19103267. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30347859 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of FOXOs and autophagy in cancer and metastasis-Implications in therapeutic development.Med Res Rev. 2020 Nov;40(6):2089-2113. doi: 10.1002/med.21695. Epub 2020 May 31. Med Res Rev. 2020. PMID: 32474970 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preclinical Efficacy of Ron Kinase Inhibitors Alone and in Combination with PI3K Inhibitors for Treatment of sfRon-Expressing Breast Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Dec 15;21(24):5588-600. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-3283. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26289070 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic Analysis as the First Step toward Personalized Treatment in Renal Cell Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2014 Jul 25;4:194. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2014.00194. eCollection 2014. Front Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25120953 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

