Global analysis reveals the complexity of the human glomerular extracellular matrix
- PMID: 24436468
- PMCID: PMC4005295
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2013030233
Global analysis reveals the complexity of the human glomerular extracellular matrix
Abstract
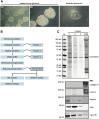
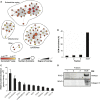
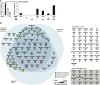
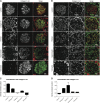
The glomerulus contains unique cellular and extracellular matrix (ECM) components, which are required for intact barrier function. Studies of the cellular components have helped to build understanding of glomerular disease; however, the full composition and regulation of glomerular ECM remains poorly understood. We used mass spectrometry-based proteomics of enriched ECM extracts for a global analysis of human glomerular ECM in vivo and identified a tissue-specific proteome of 144 structural and regulatory ECM proteins. This catalog includes all previously identified glomerular components plus many new and abundant components. Relative protein quantification showed a dominance of collagen IV, collagen I, and laminin isoforms in the glomerular ECM together with abundant collagen VI and TINAGL1. Protein network analysis enabled the creation of a glomerular ECM interactome, which revealed a core of highly connected structural components. More than one half of the glomerular ECM proteome was validated using colocalization studies and data from the Human Protein Atlas. This study yields the greatest number of ECM proteins relative to previous investigations of whole glomerular extracts, highlighting the importance of sample enrichment. It also shows that the composition of glomerular ECM is far more complex than previously appreciated and suggests that many more ECM components may contribute to glomerular development and disease processes. The mass spectrometry proteomics data have been deposited to the ProteomeXchange Consortium with the dataset identifier PXD000456.
Copyright © 2014 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Glomerular cell cross-talk influences composition and assembly of extracellular matrix.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014 May;25(5):953-66. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013070795. Epub 2014 Jan 16. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24436469 Free PMC article.
-
Altered glomerular extracellular matrix synthesis in experimental membranous nephropathy.Kidney Int. 1992 Sep;42(3):573-85. doi: 10.1038/ki.1992.321. Kidney Int. 1992. PMID: 1383596
-
Comprehensive profiling of cartilage extracellular matrix formation and maturation using sequential extraction and label-free quantitative proteomics.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010 Jun;9(6):1296-313. doi: 10.1074/mcp.M000014-MCP201. Epub 2010 Feb 26. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2010. PMID: 20190199 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical composition of the glomerular extracellular matrix in patients with diabetic kidney disease.World J Diabetes. 2022 Jul 15;13(7):498-520. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v13.i7.498. World J Diabetes. 2022. PMID: 36051430 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applying Proteomics to Investigate Extracellular Matrix in Health and Disease.Curr Top Membr. 2015;76:171-96. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2015.06.001. Epub 2015 Jul 7. Curr Top Membr. 2015. PMID: 26610914 Review.
Cited by
-
3D Mapping Reveals a Complex and Transient Interstitial Matrix During Murine Kidney Development.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Jul;32(7):1649-1665. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2020081204. Epub 2021 Apr 19. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33875569 Free PMC article.
-
Rethinking glomerular basement membrane thickening in diabetic nephropathy: adaptive or pathogenic?Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016 Nov 1;311(5):F831-F843. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00313.2016. Epub 2016 Aug 31. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27582102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enrichment of Extracellular Matrix Proteins from Tissues and Digestion into Peptides for Mass Spectrometry Analysis.J Vis Exp. 2015 Jul 23;(101):e53057. doi: 10.3791/53057. J Vis Exp. 2015. PMID: 26273955 Free PMC article.
-
Epithelial-mesenchymal status influences how cells deposit fibrillin microfibrils.J Cell Sci. 2014 Jan 1;127(Pt 1):158-71. doi: 10.1242/jcs.134270. Epub 2013 Nov 4. J Cell Sci. 2014. PMID: 24190885 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of podocyte adhesion for a healthy glomerulus.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014 Oct 14;5:160. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00160. eCollection 2014. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 25352829 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pozzi A, Jarad G, Moeckel GW, Coffa S, Zhang X, Gewin L, Eremina V, Hudson BG, Borza DB, Harris RC, Holzman LB, Phillips CL, Fassler R, Quaggin SE, Miner JH, Zent R: Beta1 integrin expression by podocytes is required to maintain glomerular structural integrity. Dev Biol 316: 288–301, 2008 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Has C, Spartà G, Kiritsi D, Weibel L, Moeller A, Vega-Warner V, Waters A, He Y, Anikster Y, Esser P, Straub BK, Hausser I, Bockenhauer D, Dekel B, Hildebrandt F, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Laube GF: Integrin α3 mutations with kidney, lung, and skin disease. N Engl J Med 366: 1508–1514, 2012 - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

