Subclinical Breast Cancer: Minimally Invasive Approaches. Our Experience with Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation vs. Cryotherapy
- PMID: 24415989
- PMCID: PMC3861851
- DOI: 10.1159/000355707
Subclinical Breast Cancer: Minimally Invasive Approaches. Our Experience with Percutaneous Radiofrequency Ablation vs. Cryotherapy
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to compare the efficacy of radiofrequency ablation vs. cryoablation in the treatment of early breast cancer.
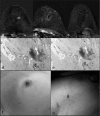
Patients and methods: 80 women (mean age 73 ± 5 years) with early breast cancer were retrospectively evaluated. 40 patients underwent cryoablation and 40 patients underwent radiofrequency ablation, both with sentinel lymph node excision. Tumor volume and histopatological data were compared by means of postprocedural 3.0-T magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). 30-45 days after the percutaneous ablation, all patients underwent surgical resection of the tumor. The mean follow-up was 18 months without any local recurrences.
Results: Both techniques allow good correlation with histopathological data. In 75 patients (93.8%) we observed complete necrosis; in 5 cases there was residual disease in the postprocedural MRI and postoperative histological examination. There was a good correlation between MRI volume and histologic samples. Cosmetic results were good in all patients but 2.
Conclusion: Both percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and cryotherapy are minimally invasive techniques with a good clinical and cosmetic outcome in selected cases. MRI examination is an ideal method to assess breast neoplasms in terms of quality and quantity as well as residual tumor extent after percutaneous ablation. Cryotherapy is the preferred method because of the analgesic effect of freezing with better patients compliance.
Hintergrund: Ziel dieser Studie war es, die Effizienz der Radiofrequenzablation im Vergleich zur Cryoablation zur Behandlung des frühen Mammakarzinoms zu vergleichen.
Patientinnen und methoden: 80 Frauen (mittleres Alter 73 ± 5 Jahre) mit einem primären Mammakarzinom wurden retrospektiv evaluiert. Bei 40 Patientinnen wurde eine Cryoablation und bei weiteren 40 eine Radiofrequenzablation durchgeführt (jeweils mit Sentinelknoten-entfernung). Tumorvolumen und histopatologische Daten wurden mittels 3.0-T-Magnetresonanztomogra-phie (MRT) im Anschluss an den Eingriff bestimmt. 30–45 Tage nach der perkutanen Ablation wurde bei allen Patientinnen eine chirurgische Tumorentfernung vorgenommen. Das mittlere Follow-up war 18 Monate; während dieser Zeit traten keine Lokalrezidive auf.
Ergebnisse: Für beide Methoden konnte eine gute Korrelation mit histopathologischen Daten gezeigt werden. Bei 75 (93,8%) Patientinnen wurde eine komplette Nekro-tisierung beobachtet; in 5 Fällen zeigten das Kontroll-MRT und die postoperative histologische Untersuchung Resttumorgewebe. Es bestand eine gute Korrelation zwischen MRT-Volumen und den histologischen Proben. Das kosmetische Outcome war bis auf 2 Fälle gut.
Schlussfolgerung: Die perkutane Radiofrequenzablation und die Cryotherapie sind minimalinvasive Methoden mit einem guten klinischen und kosmetischen Outcome in ausgewählten Fällen. MRT ist eine ideale Methode zur qualitativen und quantitativen Charakterisierung von Mammakarzinomen sowie dem Ausmaß von Resttumorgewebe nach perkutaner Ablation. Cryotherapie wird der RFA vorgezogen, da der analgetische Effekt des Vereisens mit besserer Patientcompliance einhergeht.
Keywords: Breast cancer; Cryoablation; MRI; Minimally invasive techniques; Percutaneous ablation; Radiofrequency ablation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Percutaneous local ablation of unifocal subclinical breast cancer: clinical experience and preliminary results of cryotherapy.Eur Radiol. 2011 Nov;21(11):2344-53. doi: 10.1007/s00330-011-2179-2. Epub 2011 Jun 17. Eur Radiol. 2011. PMID: 21681574
-
Small breast cancers: in vivo percutaneous US-guided radiofrequency ablation with dedicated cool-tip radiofrequency system.Radiology. 2009 May;251(2):339-46. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2512080905. Epub 2009 Mar 20. Radiology. 2009. PMID: 19304918 Clinical Trial.
-
Minimally invasive approaches for diagnosis and treatment of early-stage breast cancer.Oncologist. 2007 Jan;12(1):1-10. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.12-1-1. Oncologist. 2007. PMID: 17227896 Review.
-
Image-guided Microinvasive Percutaneous Treatment of Breast Lesions: Where Do We Stand?Radiographics. 2021 Jul-Aug;41(4):945-966. doi: 10.1148/rg.2021200156. Radiographics. 2021. PMID: 34197250
-
Technical success, technique efficacy and complications of minimally-invasive imaging-guided percutaneous ablation procedures of breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Eur Radiol. 2017 Aug;27(8):3199-3210. doi: 10.1007/s00330-016-4668-9. Epub 2017 Jan 3. Eur Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28050693 Review.
Cited by
-
Cryotherapy in the Treatment of Early-Stage Breast Cancer.World J Oncol. 2024 Oct;15(5):737-743. doi: 10.14740/wjon1909. Epub 2024 Sep 16. World J Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39328333 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical application of ultrasound-guided percutaneous microwave ablation for benign breast lesions: a prospective study.BMC Cancer. 2019 Apr 11;19(1):345. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-5523-6. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 30975107 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and Safety of Radiofrequency Ablation for Breast Cancer Smaller Than 2 cm: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Front Oncol. 2021 May 3;11:651646. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.651646. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34012918 Free PMC article.
-
Cryoablation In The Management Of Breast Cancer: Evidence To Date.Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2019 Oct 10;11:283-292. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S197406. eCollection 2019. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press). 2019. PMID: 31632134 Free PMC article.
-
Ablative Therapies for Breast Cancer: State of Art.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023 Jan-Dec;22:15330338231157193. doi: 10.1177/15330338231157193. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2023. PMID: 36916200 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Veronesi U, Cascinelli N, Mariani L. Twenty-years follow-up of a randomized study comparing breast-conserving surgery with radical mastectomy for early breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:1227–32. - PubMed
-
- Kimmick GG, Balducci L. Breast cancer and aging. Clinical interactions. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2000;14:213–34. - PubMed
-
- Parkin DM, Bray FI, Devesa SS. Cancer burden in the year 2000. The global picture. Eur J Cancer. 2000;37:S4–S66. - PubMed
-
- Fornage BD, Sneige N, et al. Small (< or = 2-cm) breast cancer treated with US-guided radiofrequency ablation: feasibility study. Radiology. 2004;231:215–24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

