A biochemical landscape of A-to-I RNA editing in the human brain transcriptome
- PMID: 24407955
- PMCID: PMC3941116
- DOI: 10.1101/gr.162537.113
A biochemical landscape of A-to-I RNA editing in the human brain transcriptome
Abstract
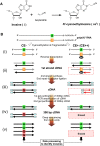
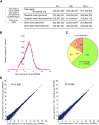
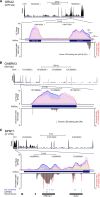
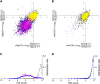
Inosine is an abundant RNA modification in the human transcriptome and is essential for many biological processes in modulating gene expression at the post-transcriptional level. Adenosine deaminases acting on RNA (ADARs) catalyze the hydrolytic deamination of adenosines to inosines (A-to-I editing) in double-stranded regions. We previously established a biochemical method called "inosine chemical erasing" (ICE) to directly identify inosines on RNA strands with high reliability. Here, we have applied the ICE method combined with deep sequencing (ICE-seq) to conduct an unbiased genome-wide screening of A-to-I editing sites in the transcriptome of human adult brain. Taken together with the sites identified by the conventional ICE method, we mapped 19,791 novel sites and newly found 1258 edited mRNAs, including 66 novel sites in coding regions, 41 of which cause altered amino acid assignment. ICE-seq detected novel editing sites in various repeat elements as well as in short hairpins. Gene ontology analysis revealed that these edited mRNAs are associated with transcription, energy metabolism, and neurological disorders, providing new insights into various aspects of human brain functions.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Biochemical and Transcriptome-Wide Identification of A-to-I RNA Editing Sites by ICE-Seq.Methods Enzymol. 2015;560:331-53. doi: 10.1016/bs.mie.2015.03.014. Epub 2015 Jul 9. Methods Enzymol. 2015. PMID: 26253977
-
Discovering A-to-I RNA Editing Through Chemical Methodology "ICE-seq".Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2181:113-148. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0787-9_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 32729078
-
Transcriptome-wide identification of adenosine-to-inosine editing using the ICE-seq method.Nat Protoc. 2015 May;10(5):715-32. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2015.037. Epub 2015 Apr 9. Nat Protoc. 2015. PMID: 25855956
-
Significance of A-to-I RNA editing of transcripts modulating pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics.Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Jan;181:13-21. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.07.003. Epub 2017 Jul 15. Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 28716651 Review.
-
Proteome diversification by adenosine to inosine RNA editing.RNA Biol. 2010 Mar-Apr;7(2):205-12. doi: 10.4161/rna.7.2.11286. Epub 2010 Mar 25. RNA Biol. 2010. PMID: 20200492 Review.
Cited by
-
Dynamic regulation of RNA editing in human brain development and disease.Nat Neurosci. 2016 Aug;19(8):1093-9. doi: 10.1038/nn.4337. Epub 2016 Jun 27. Nat Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27348216
-
Massive A-to-I RNA editing is common across the Metazoa and correlates with dsRNA abundance.Genome Biol. 2017 Oct 2;18(1):185. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1315-y. Genome Biol. 2017. PMID: 28969707 Free PMC article.
-
Restricting retrotransposons: ADAR1 is another guardian of the human genome.RNA Biol. 2017 Nov 2;14(11):1485-1491. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1341033. Epub 2017 Jul 21. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28640667 Free PMC article.
-
Protein-based molecular recognition tools for detecting and profiling RNA modifications.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021 Aug;69:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2020.12.006. Epub 2021 Jan 11. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2021. PMID: 33445115 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reduced RNA adenosine-to-inosine editing in hippocampus vasculature associated with Alzheimer's disease.Brain Commun. 2022 Sep 22;4(5):fcac238. doi: 10.1093/braincomms/fcac238. eCollection 2022. Brain Commun. 2022. PMID: 36196083 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
