Tumor evolution and intratumor heterogeneity of an oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma revealed by whole-genome sequencing
- PMID: 24403859
- PMCID: PMC3884528
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.131400
Tumor evolution and intratumor heterogeneity of an oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma revealed by whole-genome sequencing
Abstract
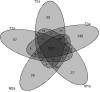
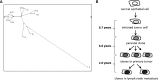
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is characterized by significant genomic instability that could lead to clonal diversity. Intratumor clonal heterogeneity has been proposed as a major attribute underlying tumor evolution, progression, and resistance to chemotherapy and radiation. Understanding genetic heterogeneity could lead to treatments specific to resistant and metastatic tumor cells. To characterize the degree of intratumor genetic heterogeneity within a single tumor, we performed whole-genome sequencing on three separate regions of an human papillomavirus (HPV)-positive oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma and two separate regions from one corresponding cervical lymph node metastasis. This approach achieved coverage of approximately 97.9% of the genome across all samples. In total, 5701 somatic point mutations (SPMs) and 4347 small somatic insertions and deletions (indels)were detected in at least one sample. Ninety-two percent of SPMs and 77% of indels were validated in a second set of samples adjacent to the discovery set. All five tumor samples shared 41% of SPMs, 57% of the 1805 genes with SPMs, and 34 of 55 cancer genes. The distribution of SPMs allowed phylogenetic reconstruction of this tumor's evolutionary pathway and showed that the metastatic samples arose as a late event. The degree of intratumor heterogeneity showed that a single biopsy may not represent the entire mutational landscape of HNSCC tumors. This approach may be used to further characterize intratumor heterogeneity in more patients, and their sample-to-sample variations could reveal the evolutionary process of cancer cells, facilitate our understanding of tumorigenesis, and enable the development of novel targeted therapies.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Investigation of somatic mutation profiles and tumor evolution of primary oropharyngeal cancer and sequential lymph node metastases using multiregional whole-exome sequencing.Mol Oncol. 2023 Jun;17(6):981-992. doi: 10.1002/1878-0261.13407. Epub 2023 Mar 8. Mol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36852664 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic characterization of clonal evolution during oropharyngeal carcinogenesis driven by human papillomavirus 16.BMB Rep. 2018 Nov;51(11):584-589. doi: 10.5483/BMBRep.2018.51.11.091. BMB Rep. 2018. PMID: 29936930 Free PMC article.
-
The degree of intratumor mutational heterogeneity varies by primary tumor sub-site.Oncotarget. 2016 May 10;7(19):27185-98. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8448. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27034009 Free PMC article.
-
Oral cavity and oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma genomics.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2013 Aug;46(4):545-66. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2013.04.001. Epub 2013 Jun 17. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2013. PMID: 23910469 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Basics of tumor development and importance of human papilloma virus (HPV) for head and neck cancer].Laryngorhinootologie. 2012 Mar;91 Suppl 1:S1-26. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1297241. Epub 2012 Mar 28. Laryngorhinootologie. 2012. PMID: 22456913 Review. German.
Cited by
-
Cancer Stem Cells in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Identification, Characterization and Clinical Implications.Cancers (Basel). 2019 May 2;11(5):616. doi: 10.3390/cancers11050616. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31052565 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Amplification of 3q26.2, 5q14.3, 8q24.3, 8q22.3, and 14q32.33 Are Possible Common Genetic Alterations in Oral Cancer Patients.Front Oncol. 2020 Apr 30;10:683. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00683. eCollection 2020. Front Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32426287 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple region whole-exome sequencing reveals dramatically evolving intratumor genomic heterogeneity in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.Oncogenesis. 2015 Nov 30;4(11):e175. doi: 10.1038/oncsis.2015.34. Oncogenesis. 2015. PMID: 26619400 Free PMC article.
-
Construction of Radiation Surviving/Resistant Lung Cancer Cell Lines with Equidifferent Gradient Dose Irradiation.Dose Response. 2020 Dec 22;18(4):1559325820982421. doi: 10.1177/1559325820982421. eCollection 2020 Oct-Dec. Dose Response. 2020. PMID: 33424518 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Inter-Individual Variability in Monoclonal Antibody Disposition.Antibodies (Basel). 2019 Dec 4;8(4):56. doi: 10.3390/antib8040056. Antibodies (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31817205 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Supplemental References
-
- Ewing B, Green P. Base-calling of automated sequencer traces using phred. II. Error probabilities. Genome Res. 1998;8:186–194. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
