Human cytomegalovirus suppresses Fas expression and function
- PMID: 24394698
- PMCID: PMC3973480
- DOI: 10.1099/vir.0.058313-0
Human cytomegalovirus suppresses Fas expression and function
Abstract
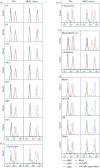
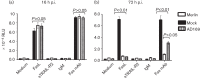
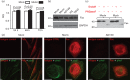
Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) is known to evade extrinsic pro-apoptotic pathways not only by downregulating cell surface expression of the death receptors TNFR1, TRAIL receptor 1 (TNFRSF10A) and TRAIL receptor 2 (TNFRSF10B), but also by impeding downstream signalling events. Fas (CD95/APO-1/TNFRSF6) also plays a prominent role in apoptotic clearance of virus-infected cells, so its fate in HCMV-infected cells needs to be addressed. Here, we show that cell surface expression of Fas was suppressed in HCMV-infected fibroblasts from 24 h onwards through the late phase of productive infection, and was dependent on de novo virus-encoded gene expression but not virus DNA replication. Significant levels of the fully glycosylated (endoglycosidase-H-resistant) Fas were retained within HCMV-infected cells throughout the infection within intracellular membranous structures. HCMV infection provided cells with a high level of protection against Fas-mediated apoptosis. Downregulation of Fas was observed with HCMV strains AD169, FIX, Merlin and TB40.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Apoptosis induced by human cytomegalovirus infection can be enhanced by cytokines to limit the spread of virus.Exp Hematol. 1999 Jul;27(7):1194-203. doi: 10.1016/s0301-472x(99)00044-2. Exp Hematol. 1999. PMID: 10390195
-
Effects of human cytomegalovirus infection on apoptosis and expression of apoptosis-regulating factors.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2005;25(5):480-3. doi: 10.1007/BF02895993. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2005. PMID: 16463650
-
Decreased neutrophil adhesion to human cytomegalovirus-infected retinal pigment epithelial cells is mediated by virus-induced up-regulation of Fas ligand independent of neutrophil apoptosis.J Immunol. 2000 Oct 15;165(8):4405-13. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.165.8.4405. J Immunol. 2000. PMID: 11035078
-
[Interrelationship between human cytomegalovirus infection and chemokine].Nihon Rinsho. 1998 Jan;56(1):69-74. Nihon Rinsho. 1998. PMID: 9465667 Review. Japanese.
-
Subversion of Immune Response by Human Cytomegalovirus.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 10;10:1155. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01155. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31244824 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HCMV-secreted glycoprotein gpUL4 inhibits TRAIL-mediated apoptosis and NK cell activation.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Dec 5;120(49):e2309077120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2309077120. Epub 2023 Nov 27. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023. PMID: 38011551 Free PMC article.
-
Apoptosis and Phagocytosis as Antiviral Mechanisms.Subcell Biochem. 2023;106:77-112. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-40086-5_3. Subcell Biochem. 2023. PMID: 38159224
-
The evolution of regulated cell death pathways in animals and their evasion by pathogens.Physiol Rev. 2022 Jan 1;102(1):411-454. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00002.2021. Physiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 34898294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Suppression of RIP3-dependent necroptosis by human cytomegalovirus.J Biol Chem. 2015 May 1;290(18):11635-48. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.646042. Epub 2015 Mar 16. J Biol Chem. 2015. PMID: 25778401 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Death in Coronavirus Infections: Uncovering Its Role during COVID-19.Cells. 2021 Jun 23;10(7):1585. doi: 10.3390/cells10071585. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34201847 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Arnoult D., Bartle L. M., Skaletskaya A., Poncet D., Zamzami N., Park P. U., Sharpe J., Youle R. J., Goldmacher V. S. (2004). Cytomegalovirus cell death suppressor vMIA blocks Bax- but not Bak-mediated apoptosis by binding and sequestering Bax at mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101, 7988–7993 10.1073/pnas.0401897101 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BB/F009836/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- G1000236/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- WT090323MA/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- BBS/B/02525/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/L018373/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

