Advancing the functional utility of PAR-CLIP by quantifying background binding to mRNAs and lncRNAs
- PMID: 24393468
- PMCID: PMC4053780
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2014-15-1-r2
Advancing the functional utility of PAR-CLIP by quantifying background binding to mRNAs and lncRNAs
Abstract
Background: Sequence specific RNA binding proteins are important regulators of gene expression. Several related crosslinking-based, high-throughput sequencing methods, including PAR-CLIP, have recently been developed to determine direct binding sites of global protein-RNA interactions. However, no studies have quantitatively addressed the contribution of background binding to datasets produced by these methods.
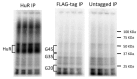
Results: We measured non-specific RNA background in PAR-CLIP data, demonstrating that covalently crosslinked background binding is common, reproducible and apparently universal among laboratories. We show that quantitative determination of background is essential for identifying targets of most RNA-binding proteins and can substantially improve motif analysis. We also demonstrate that by applying background correction to an RNA binding protein of unknown binding specificity, Caprin1, we can identify a previously unrecognized RNA recognition element not otherwise apparent in a PAR-CLIP study.
Conclusions: Empirical background measurements of global RNA-protein crosslinking are a necessary addendum to other experimental controls, such as performing replicates, because covalently crosslinked background signals are reproducible and otherwise unavoidable. Recognizing and quantifying the contribution of background extends the utility of PAR-CLIP and can improve mechanistic understanding of protein-RNA specificity, protein-RNA affinity and protein-RNA association dynamics.
Figures

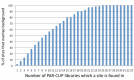

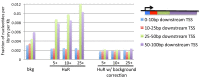
Similar articles
-
PAR-CLIP and streamlined small RNA cDNA library preparation protocol for the identification of RNA binding protein target sites.Methods. 2017 Apr 15;118-119:41-49. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.11.009. Epub 2016 Nov 18. Methods. 2017. PMID: 27871973 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome-wide Identification of RNA-binding Protein Binding Sites Using Photoactivatable-Ribonucleoside-Enhanced Crosslinking Immunoprecipitation (PAR-CLIP).Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2017 Apr 3;118:27.6.1-27.6.19. doi: 10.1002/cpmb.35. Curr Protoc Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 28369676
-
Optimization of PAR-CLIP for transcriptome-wide identification of binding sites of RNA-binding proteins.Methods. 2017 Apr 15;118-119:24-40. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2016.10.007. Epub 2016 Oct 17. Methods. 2017. PMID: 27765618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sensitive and highly resolved identification of RNA-protein interaction sites in PAR-CLIP data.BMC Bioinformatics. 2015 Feb 1;16:32. doi: 10.1186/s12859-015-0470-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2015. PMID: 25638391 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in CLIP Technologies for Studies of Protein-RNA Interactions.Mol Cell. 2018 Feb 1;69(3):354-369. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2018.01.005. Mol Cell. 2018. PMID: 29395060 Review.
Cited by
-
An Overview of Long Noncoding RNAs Involved in Bone Regeneration from Mesenchymal Stem Cells.Stem Cells Int. 2018 Jan 28;2018:8273648. doi: 10.1155/2018/8273648. eCollection 2018. Stem Cells Int. 2018. PMID: 29535782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
POSTAR3: an updated platform for exploring post-transcriptional regulation coordinated by RNA-binding proteins.Nucleic Acids Res. 2022 Jan 7;50(D1):D287-D294. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab702. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022. PMID: 34403477 Free PMC article.
-
RNA Binding to CBP Stimulates Histone Acetylation and Transcription.Cell. 2017 Jan 12;168(1-2):135-149.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.020. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Cell. 2017. PMID: 28086087 Free PMC article.
-
Robust transcriptome-wide discovery of RNA-binding protein binding sites with enhanced CLIP (eCLIP).Nat Methods. 2016 Jun;13(6):508-14. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.3810. Epub 2016 Mar 28. Nat Methods. 2016. PMID: 27018577 Free PMC article.
-
Distinct and Modular Organization of Protein Interacting Sites in Long Non-coding RNAs.Front Mol Biosci. 2018 Apr 4;5:27. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2018.00027. eCollection 2018. Front Mol Biosci. 2018. PMID: 29670884 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

