Clinical significance of Keap1 and Nrf2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 24386210
- PMCID: PMC3873935
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0083479
Clinical significance of Keap1 and Nrf2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
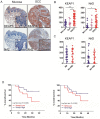
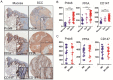
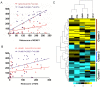
Oxidative stress has been reported to play an important role in progression and prognostication in various kinds of cancers. However, the role and clinical significance of oxidative stress markers Keap1 and Nrf2 in oral squamous cell carcinoma (OSCC) has not been elucidated. This study aimed to investigate the correlation of oxidative stress markers Keap1 and Nrf2 expression and pathological features in OSCC by using tissue microarray. Tissue microarrays containing 17 normal oral mucosa, 7 oral epithelial dysplasia and 43 OSCC specimens were studied by immunohistochemistry. The association among these proteins and pathological features were analyzed. Expression of oxidative stress markers Keap1, Nrf2, and antioxidants PPIA, Prdx6, as well as CD147 was found to increase consecutively from normal oral mucosa to OSCC, and the Keap1, Nrf2, PPIA, Prdx6, CD147 expression in OSCC were significantly higher when compared to normal oral mucosa. Expression of Keap1, Nrf2 in tumors was not found to be significantly associated with T category, lymph node metastases, and pathological grade. Furthermore, we checked the relationship among these oxidative stress markers and found that Keap1 was significantly correlated with Nrf2, Prdx6 and CD147. Significant relationship between Nrf2 and Prdx6 was also detected. Finally, we found patients with overexpression of Keap1 and Nrf2 had not significantly worse overall survival by Kaplan-Meier analysis. These findings suggest that ROS markers are associated with carcinogenesis and progression of OSCC, which may have prognostic value and could be regarded as potential therapeutic targets in OSCC.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Prognostic and predictive values of SPP1, PAI and caveolin-1 in patients with oral squamous cell carcinoma.Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014 Aug 15;7(9):6032-9. eCollection 2014. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014. PMID: 25337248 Free PMC article.
-
Antioral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Effects of Carvacrol via Inhibiting Inflammation, Proliferation, and Migration Related to Nrf2/Keap1 Pathway.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Jun 10;2021:6616547. doi: 10.1155/2021/6616547. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 34212035 Free PMC article.
-
Downregulation of SELENBP1 enhances oral squamous cell carcinoma chemoresistance through KEAP1-NRF2 signaling.Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2021 Aug;88(2):223-233. doi: 10.1007/s00280-021-04284-4. Epub 2021 Apr 27. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33907880
-
Role of the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway in cancer.Adv Cancer Res. 2014;122:281-320. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-420117-0.00008-6. Adv Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 24974185 Review.
-
The emerging role of the Nrf2-Keap1 signaling pathway in cancer.Genes Dev. 2013 Oct 15;27(20):2179-91. doi: 10.1101/gad.225680.113. Genes Dev. 2013. PMID: 24142871 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Overexpression of Malic Enzyme 2 Indicates Pathological and Clinical Significance in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Mar 5;17(6):799-806. doi: 10.7150/ijms.43832. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32218701 Free PMC article.
-
Dual roles of NRF2 in tumor prevention and progression: possible implications in cancer treatment.Free Radic Biol Med. 2015 Feb;79:292-9. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.11.009. Epub 2014 Nov 29. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015. PMID: 25458917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Expression and correlation of NRF2, KEAP1, NQO-1 and HO-1 in advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the larynx and their association with clinicopathologic features.Mol Med Rep. 2016 Dec;14(6):5171-5179. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2016.5913. Epub 2016 Nov 1. Mol Med Rep. 2016. PMID: 27840932 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Nrf2 overexpression on cholangiocarcinoma treatment and clinical prognosis.Korean J Clin Oncol. 2023 Jun;19(1):18-26. doi: 10.14216/kjco.23004. Epub 2023 Jun 30. Korean J Clin Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37449395 Free PMC article.
-
CD163+ tumor-associated macrophages correlated with poor prognosis and cancer stem cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma.Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:838632. doi: 10.1155/2014/838632. Epub 2014 May 6. Biomed Res Int. 2014. PMID: 24883329 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P (2005) Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin 55: 74–108. - PubMed
-
- Noguti J, De Moura CF, De Jesus GP, Da Silva VH, Hossaka TA, et al. (2012) Metastasis from oral cancer: an overview. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 9: 329–335. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Azad MB, Gibson SB (2009) Superoxide is the major reactive oxygen species regulating autophagy. Cell Death Differ 16: 1040–1052. - PubMed
-
- Wu WS (2006) The signaling mechanism of ROS in tumor progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 25: 695–705. - PubMed
-
- Wakabayashi N, Itoh K, Wakabayashi J, Motohashi H, Noda S, et al. (2003) Keap1-null mutation leads to postnatal lethality due to constitutive Nrf2 activation. Nat Genet 35: 238–245. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

