Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states
- PMID: 24384568
- PMCID: PMC3941218
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a009191
Insulin receptor signaling in normal and insulin-resistant states
Abstract
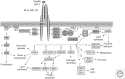
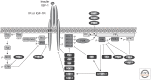
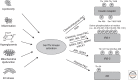
In the wake of the worldwide increase in type-2 diabetes, a major focus of research is understanding the signaling pathways impacting this disease. Insulin signaling regulates glucose, lipid, and energy homeostasis, predominantly via action on liver, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue. Precise modulation of this pathway is vital for adaption as the individual moves from the fed to the fasted state. The positive and negative modulators acting on different steps of the signaling pathway, as well as the diversity of protein isoform interaction, ensure a proper and coordinated biological response to insulin in different tissues. Whereas genetic mutations are causes of rare and severe insulin resistance, obesity can lead to insulin resistance through a variety of mechanisms. Understanding these pathways is essential for development of new drugs to treat diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and their complications.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Metabolism and insulin signaling in common metabolic disorders and inherited insulin resistance.Dan Med J. 2014 Jul;61(7):B4890. Dan Med J. 2014. PMID: 25123125 Review.
-
Role of reduced insulin-stimulated bone blood flow in the pathogenesis of metabolic insulin resistance and diabetic bone fragility.Med Hypotheses. 2016 Aug;93:81-6. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2016.05.008. Epub 2016 May 12. Med Hypotheses. 2016. PMID: 27372862
-
Intracellular pH Regulation of Skeletal Muscle in the Milieu of Insulin Signaling.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 23;12(10):2910. doi: 10.3390/nu12102910. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32977552 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Insulin action at a molecular level - 100 years of progress.Mol Metab. 2021 Oct;52:101304. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2021.101304. Epub 2021 Jul 15. Mol Metab. 2021. PMID: 34274528 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Adipose tissue compensates for defect of phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase induced in liver and muscle by dietary fish oil in fed rats.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006 Jan;290(1):E78-E86. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00200.2005. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2006. PMID: 16339925
Cited by
-
Dual-specificity phosphatase 3 deletion promotes obesity, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 12;11(1):5817. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85089-6. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33712680 Free PMC article.
-
Endometrial Cancer as a Metabolic Disease with Dysregulated PI3K Signaling: Shedding Light on Novel Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 23;21(17):6073. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176073. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32842547 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute Kaempferol Stimulation Induces AKT Phosphorylation in HepG2 Cells.Life (Basel). 2024 Jun 15;14(6):764. doi: 10.3390/life14060764. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929747 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-Like Proteins in Plant Sources: A Systematic Review.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020 Sep 30;13:3421-3431. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S256883. eCollection 2020. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2020. PMID: 33061503 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repurposing New Use for Old Drug Chloroquine against Metabolic Syndrome: A Review on Animal and Human Evidence.Int J Med Sci. 2021 May 13;18(12):2673-2688. doi: 10.7150/ijms.58147. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 34104100 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aguirre V, Uchida T, Yenush L, Davis R, White MF 2000. The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307). J Biol Chem 275: 9047–9054 - PubMed
-
- Aguirre V, Werner ED, Giraud J, Lee YH, Shoelson SE, White MF 2002. Phosphorylation of Ser307 in insulin receptor substrate-1 blocks interactions with the insulin receptor and inhibits insulin action. J Biol Chem 277: 1531–1537 - PubMed
-
- Akira S, Takeda K 2004. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 4: 499–511 - PubMed
-
- Alessi DR, James SR, Downes CP, Holmes AB, Gaffney PR, Reese CB, Cohen P 1997. Characterization of a 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase, which phosphorylates and activates protein kinase Bα. Curr Biol 7: 261–269 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
